Method for recycling zinc ferrite solution
A technology of zinc-ferric acid and ferric acid, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problem of intensifying the reaction of iron-zinc alloys, reducing the adhesion between the coating and the substrate of the coating, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of wide source of raw materials and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036]The situation of zinc-ferric acid solution produced by a galvanizing plant is as follows: 10 cubic meters per day, pH is 0.1, total iron concentration is 56g / L, and zinc concentration is 9g / L.
[0037] The concrete steps of this zinc-ferric acid solution reuse are:
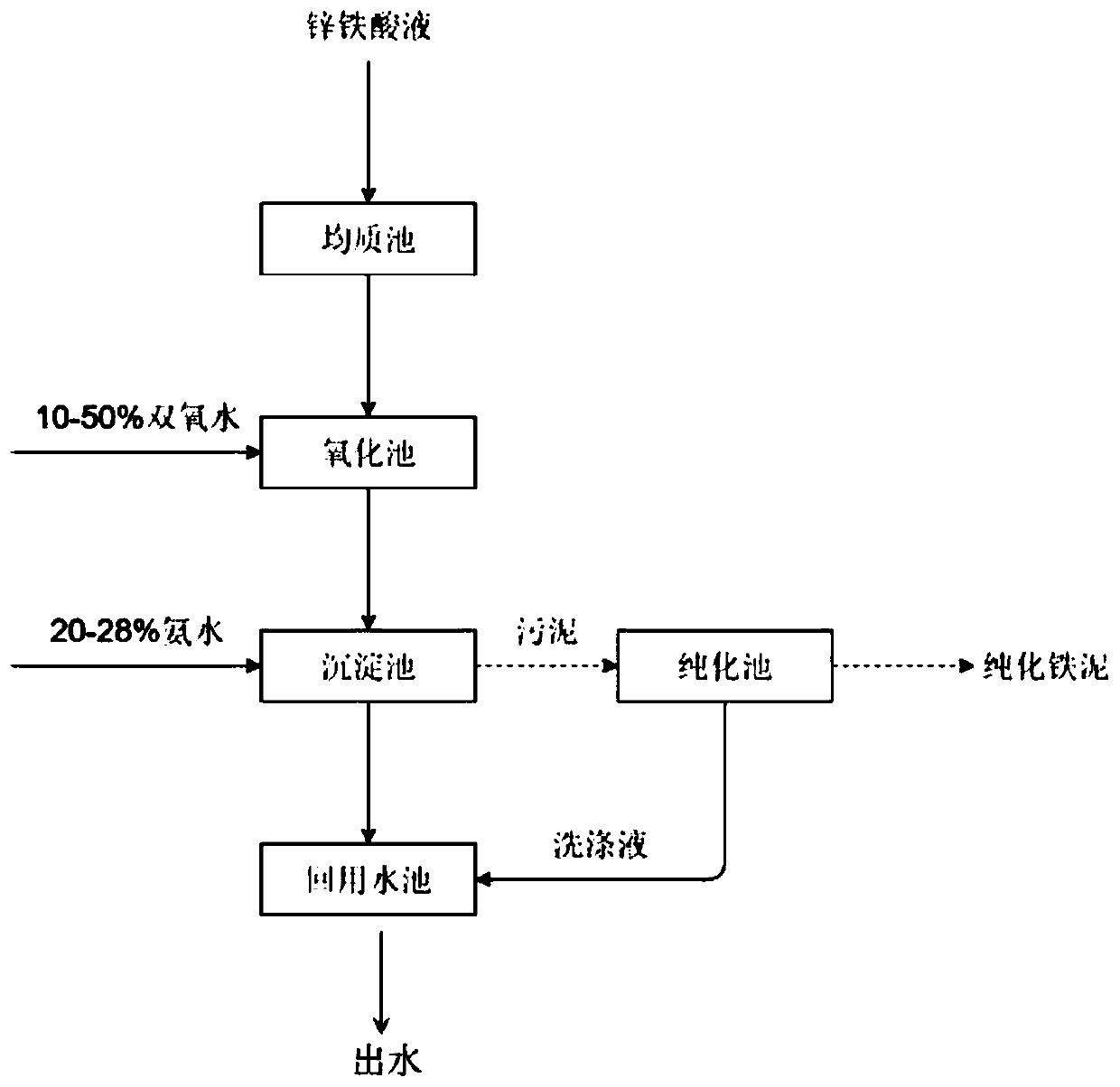
[0038] Step S0: Collect the zinc-ferric acid solution into the homogeneous tank for mixing, and mix thoroughly to keep the water quality stable.
[0039] Step 1: Send the zinc-ferric acid solution in the homogeneous tank into the oxidation tank, open the dosing tank, and automatically control the hydrogen peroxide with a mass concentration of 10% from the dosing tank to the oxidation tank for oxidation through the automatic control valve. The molar ratio of content is 4:1, and the flow rate is controlled at 0.2m 3 / h. The oxidation reaction time at the end of dosing was 130min.
[0040] Step 2: After the oxidation reaction is completed, send the oxidized zinc-ferric acid solution into the primary sediment...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The situation of zinc-ferric acid solution produced by a galvanizing plant is as follows: 40 cubic meters per day, pH is 1, total iron concentration is 34g / L, and zinc concentration is 5g / L.
[0045] The concrete steps of this zinc-ferric acid solution reuse are:
[0046] Step S0: Collect the zinc-ferric acid solution into the homogeneous tank for mixing, and mix thoroughly to keep the water quality stable.
[0047] Step 1: Send the zinc-ferric acid solution in the homogeneous tank into the oxidation tank, open the dosing tank, and automatically control the hydrogen peroxide with a mass concentration of 35% from the dosing tank to the oxidation tank for oxidation through the automatic control valve. The molar ratio of content is 3:1, and the flow rate is controlled at 0.2m 3 / h. The oxidation reaction time at the end of dosing was 90 minutes.
[0048] Step 2: After the oxidation reaction is completed, send the oxidized zinc-ferric acid solution into the primary sedim...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The situation of zinc-ferric acid solution produced by a galvanizing plant is as follows: 30 cubic meters per day, pH is 1, total iron concentration is 19g / L, and zinc concentration is 8g / L.
[0053] The concrete steps of this zinc-ferric acid solution reuse are:
[0054] Step S0: Collect the zinc-ferric acid solution into the homogeneous tank for mixing, and mix thoroughly to keep the water quality stable.
[0055] Step 1: Send the zinc-ferric acid solution in the homogeneous tank into the oxidation tank, open the dosing tank, and automatically control the hydrogen peroxide with a mass concentration of 50% from the dosing tank to the oxidation tank for oxidation through the automatic control valve. The molar ratio of the content is 2.5:1, and the flow rate is controlled at 0.3m 3 / h. The oxidation reaction time at the end of dosing was 80 minutes.
[0056] Step 2: After the oxidation reaction is completed, send the oxidized zinc-ferric acid solution into the primary...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com