Method for continuously producing polycarbonate-polyether polyol in channelization mode through liquid phase method
A technology of polyether polyol and polycarbonate, which is applied in the field of continuous production of polycarbonate-polyether polyol by liquid phase method, can solve the problem of large variation of amplification effect, high proportion of cyclic carbonate, time-consuming Loss and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving mass transfer and heat transfer capacity and effect, increasing the content of carbonate units, and improving reaction equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
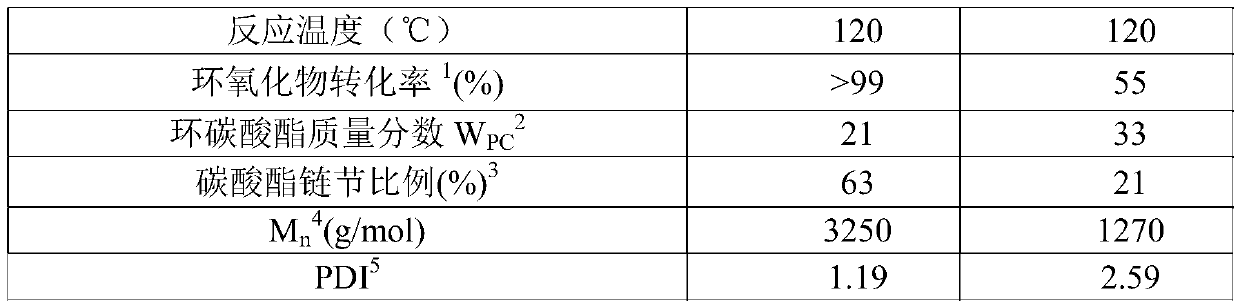
Embodiment 1
[0045] A method for the continuous production of polycarbonate-polyether polyols in pipelines by liquid phase method,
[0046] The method comprises the steps of:
[0047] (1) The raw material is pumped in from the inlet of the pipeline reactor, and the pipeline reactor includes a heating section group and a cooling section group, and the heating section group is placed at the inlet end of the pipeline reactor, and the cooling section group is placed at the inlet end of the pipeline reactor. The segment group is placed at the outlet end of the pipelined reactor, and the raw materials include initiator, epoxy compound, catalyst and carbon dioxide, so that in the presence of the catalyst, the initiator, epoxy compound and carbon dioxide are formed in the pipelined reactor. Contact in the reactor to form a copolymerization reaction system, thereby carrying out the polymerization reaction to obtain a polymerization reaction product stream comprising polycarbonate-polyether polyol a...
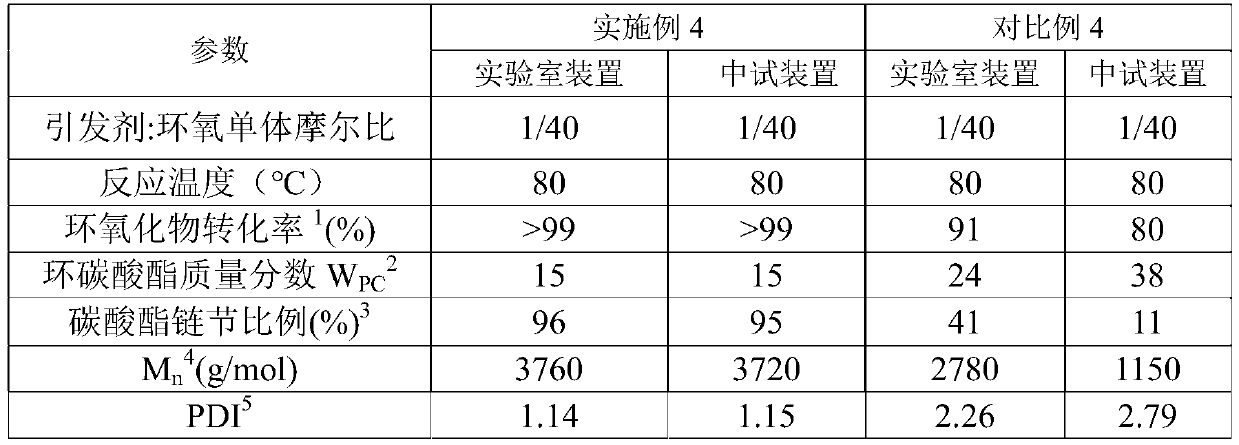
Embodiment 2
[0080] Embodiment 2 With reference to Example 1, the difference is that the raw materials are mixed into a reaction liquid in the pipeline reactor, and carbon dioxide is added through the heating section group of the pipeline reactor, so that the pressure of the pipeline reactor is 1-20MPa , the purpose is to make the pipeline reactor have enough carbon dioxide and mix it with other polymerization raw materials evenly, and also by adding carbon dioxide, on the one hand, the temperature of the polymerization reaction can be precisely controlled, and on the other hand, the pipeline reactor can avoid A dead zone occurs.
Embodiment 3
[0090] Embodiment 3 With reference to Example 1, the difference is that the raw materials are mixed into a reaction solution in the pipeline reactor, and an epoxy compound is added to the pipeline reactor from the heating section group of the pipeline reactor, so that the step In (1) and (2), in the pipelined reactor, the concentration of the epoxy compound is at 20-50wt%, and the purpose is to make the pipelined reactor have enough epoxy compounds and react with other polymerization reactions The raw materials are mixed evenly, and the temperature of the polymerization reaction can be precisely controlled by adding epoxy compounds, secondly, the pipeline reactor can avoid dead zones, and finally, the viscosity of the polycarbonate can be controlled by adjusting the viscosity of the polymerization reaction product stream to an appropriate range. - Molecular weight of polyether polyols and their distribution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com