Method for preparing contact electrode of infrared detector chip
An infrared detector and contact electrode technology, applied in the field of infrared detectors, can solve the problems of damaged chips and complex electrode preparation process, and achieve the effects of reducing process steps, reducing the number of lithography, and reducing the difficulty of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
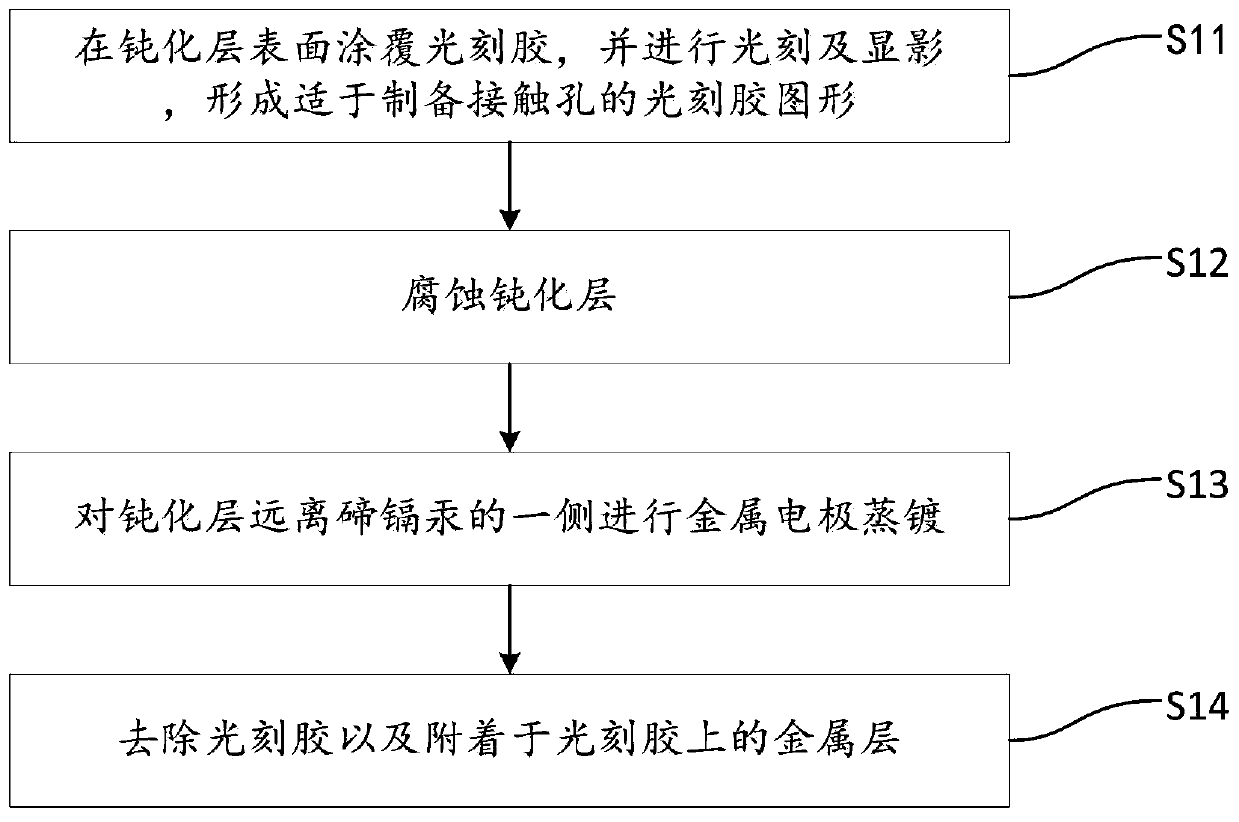
[0035] The embodiment of the present invention proposes a method for preparing a contact electrode of an infrared detector chip, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0036] S11, coating a photoresist on the surface of the passivation layer, and performing photolithography and development to form a photoresist pattern suitable for preparing contact holes.
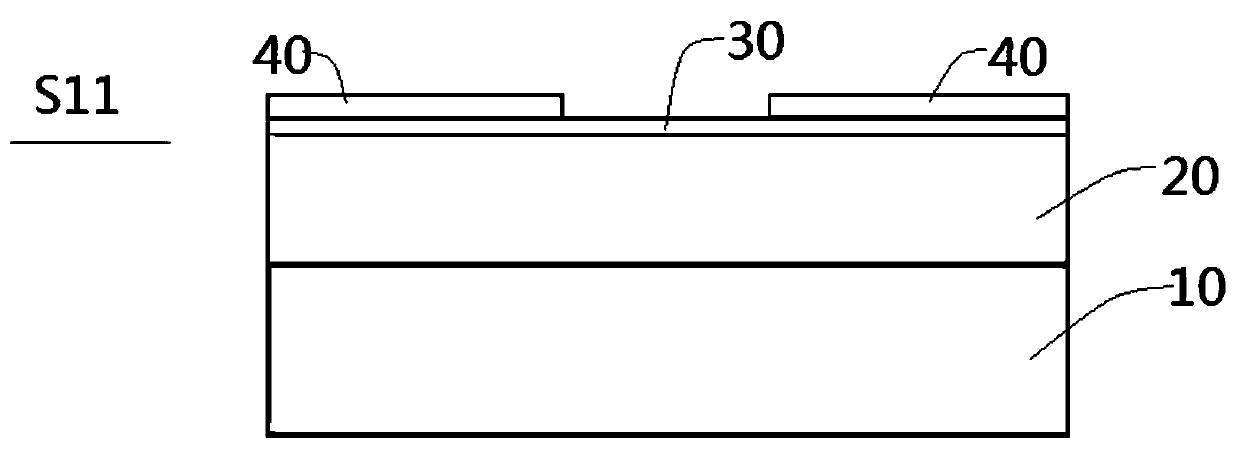
[0037] Such as figure 2 As shown, numeral 10 denotes a substrate (such as a cadmium zinc telluride substrate), numeral 20 denotes mercury cadmium telluride, numeral 30 denotes a passivation layer, and numeral 40 denotes a photoresist.
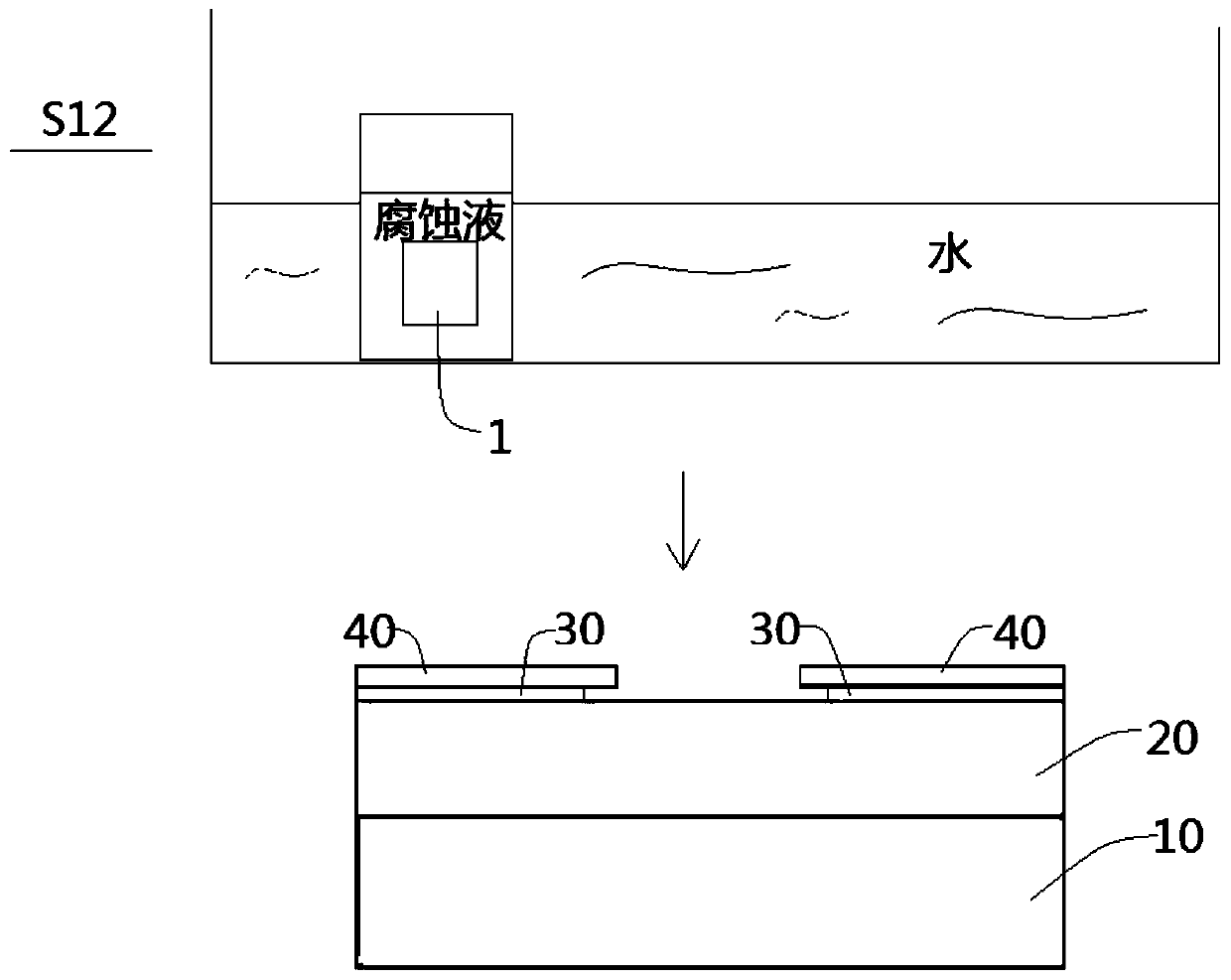
[0038] S12, corrosion passivation layer;
[0039] It will be appreciated that portions of the passivation layer not coated with photoresist may be etched away. Due to the omnidirectional nature of the corrosion, the part of the passivation layer covered by the photoresist will also be corroded by a small amount, forming a lateral corrosion area. Such as image 3 As shown, a...
Embodiment 1
[0063] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the contact electrode preparation method of the infrared detector chip of the embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0064] S21, using corrosion-resistant positive photoresist or negative photoresist with a thickness of 1-4 μm, and obtaining a photoresist pattern of a contact hole through a photolithography and development process.
[0065] S22, use concentrated hydrochloric acid, or a mixed solution of concentrated hydrochloric acid and water (volume ratio: 0.1-10), and use an ultrasonic frequency: 20KHz to 200KHz to ultrasonically corrode the ZnS passivation layer.
[0066] S23, using thermal evaporation technology to sequentially vapor-deposit metal layers Cr and Au, wherein the thickness of Cr is The thickness of Au in A contact metal layer is evaporated onto the chip surface.
[0067] S24, using acetone solution or other organic solvents to dissolve the photoresist, and peel off the metal electrodes.
Embodiment 2
[0069] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the contact electrode preparation method of the infrared detector chip of the embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0070] S31, using corrosion-resistant positive photoresist or negative photoresist with a thickness of 1-4 μm, and obtaining a photoresist pattern of a contact hole through a photolithography and development process.
[0071] S32, use a mixed solution of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid, volume ratio: 0.1-10, use ultrasonic frequency: 20KHz-200KHz, ultrasonically corrode the ZnS passivation layer.
[0072] S33, using thermal evaporation technology to sequentially vapor-deposit metal layers Cr and Au, wherein the thickness of Cr is The thickness of Au in A contact metal layer is evaporated onto the chip surface.
[0073] S34, using acetone solution or other organic solvents to dissolve the photoresist, and peel off the metal electrodes.
[0074] By adopting the embodiment of the presen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com