Method for identifying clubroot resistance of radishes
A radish root and resistance technology is applied in the field of vegetable crop genetics and breeding, and achieves the effects of simple and convenient detection method, clear and simple band pattern of amplified products, and low requirements for equipment and technology.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Identification of Radish Germplasm Clubroot Resistance
[0033] Radish germplasm seeds are sown in plug trays equipped with vermiculite: peat = 1:1 sterilized matrix after being sterilized, washed and accelerated germination. Sow 6 seeds for each germplasm, 1 seed for each hole, repeat 3 times, and plant a protective line around the tested materials to prevent marginal effects.
[0034] After sowing, inject 2 mL of 'XY-2' Plasmodium brassica bacteria solution into each hole for inoculation (spore concentration 1×10 7 mL -1 ).
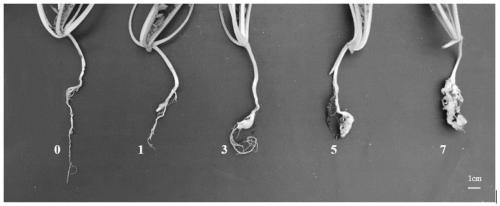
[0035] After 40 days of inoculation, investigate, identify and analyze the diseased conditions of the roots of the tested plants, identify and grade them one by one.
[0036] Refer to as figure 1 The grading standards for the identification of radish clubroot at the seedling stage are as follows: Grade 0, each root system grows normally, without galls; Grade 1, the main root does not expand, and there are small galls on the fibrous...
Embodiment 2
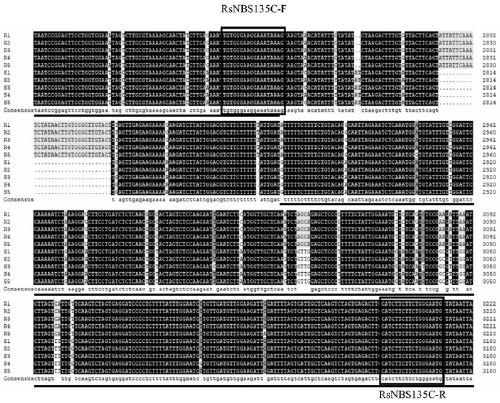
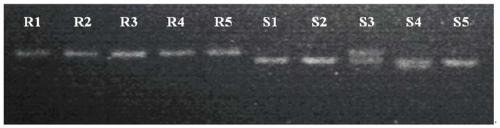
[0042] Example 2: Development and application of radish clubroot resistance marker based on RsNBS135 gene
[0043] The whole genome nucleotide sequence, annotated CDS sequence and amino acid sequence of radish were downloaded from Radish Genome Database (http: / / radish.kazusa.or.or.jp / ). According to the NBS protein domain (NB-ACR, PF00931) (http: / / pfam.xfam.org / family / PF00931) using the Markov model (HMM, Hidden MarkovModel) to search the radish genome protein sequence, E-value is set to 0.01. All sequences were submitted to Pfam, NCBI and SMART to verify the reliability of the sequences. After removing the non-NBS domain and incomplete sequences, the identified 188 NBS-containing disease resistance candidate genes were named RsNBS001-RsNBS188, respectively. The TIR-NBS-LRR gene RsNBS135 was closely related to the resistance to clubroot disease (race 4) through the sequence difference analysis of the clubroot disease-resistant germplasm. Using RT-qPCR to analyze the expression...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com