Cellulose degradation composite flora and application thereof in decomposing phellinusribis bran
A technology of cellulose degradation and complex flora, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of weak competitiveness of indigenous microorganisms, ideal practical application effect, poor fixed value, etc., to promote rapid decomposition and nutrient transformation, and accelerate mineralization and decay. Colonization process, the effect of improving maturity and quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The implementation of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings and examples.
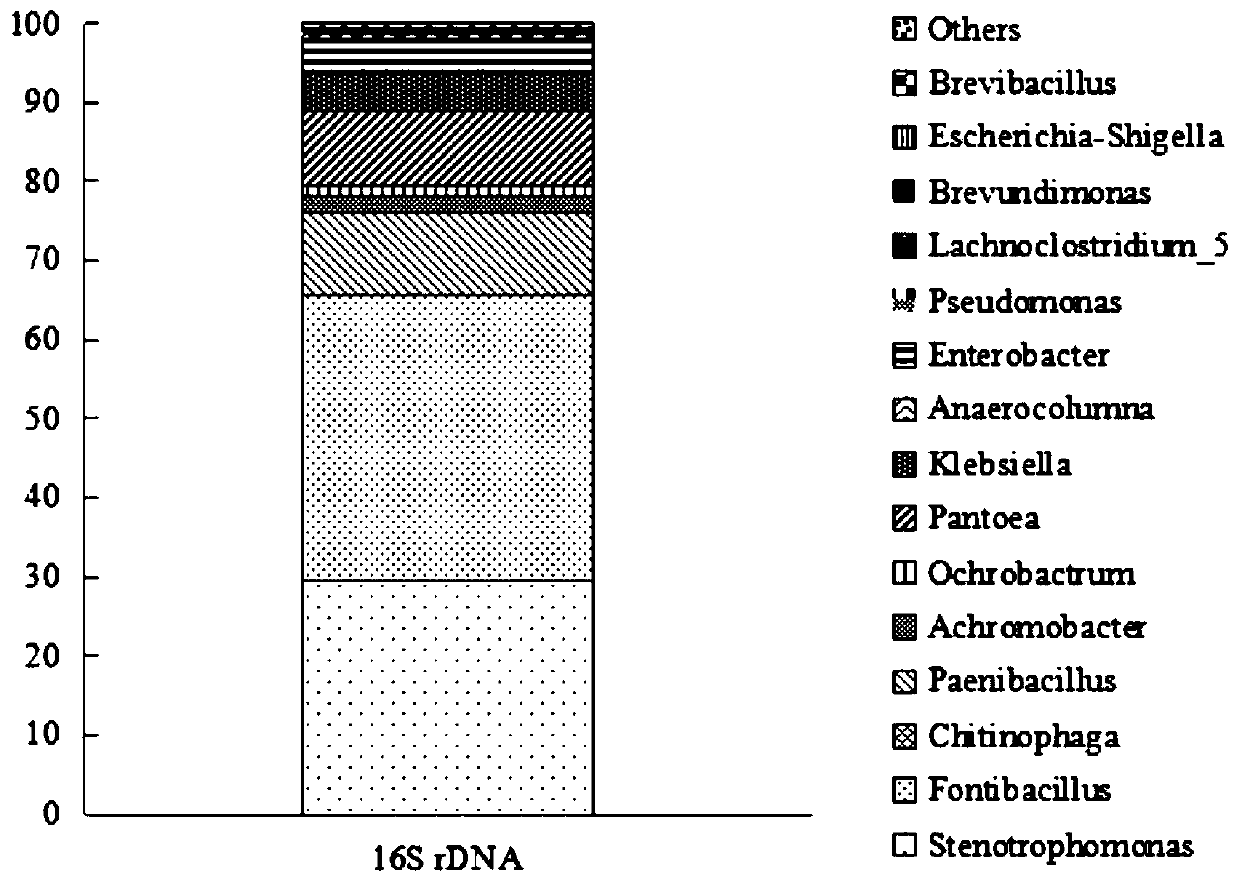
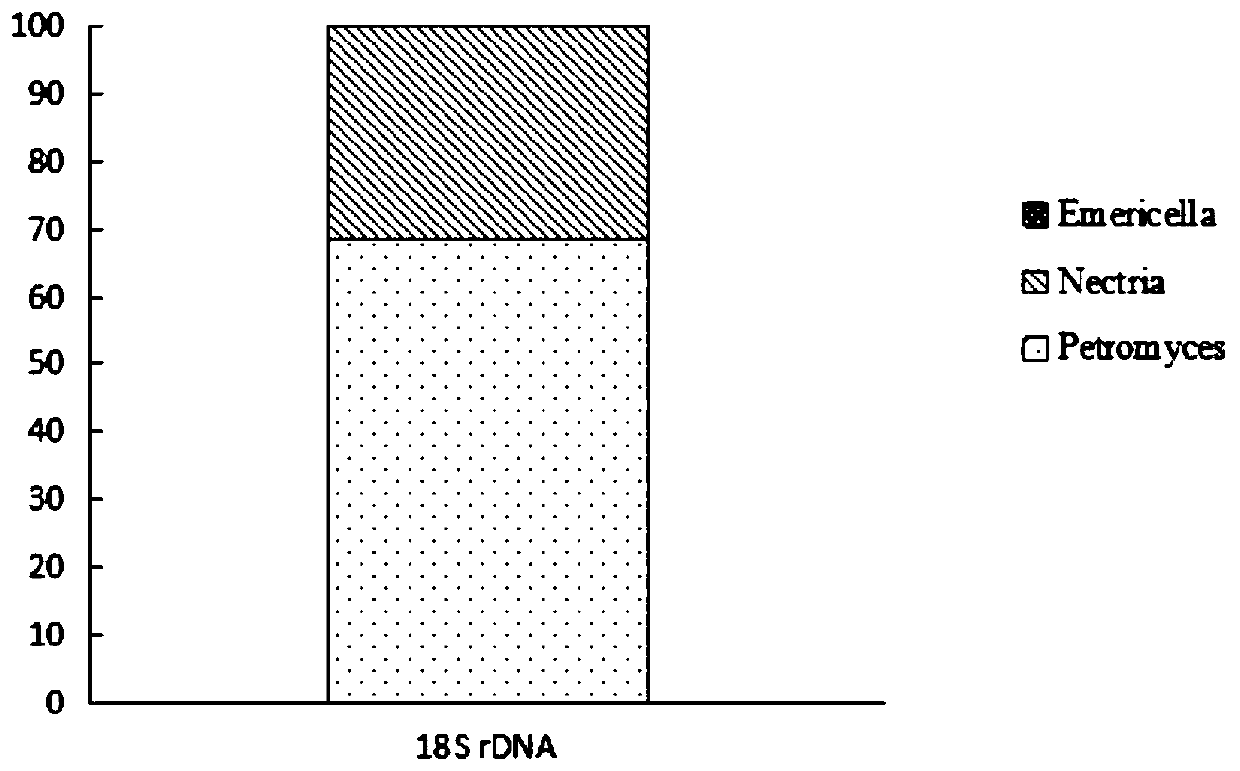
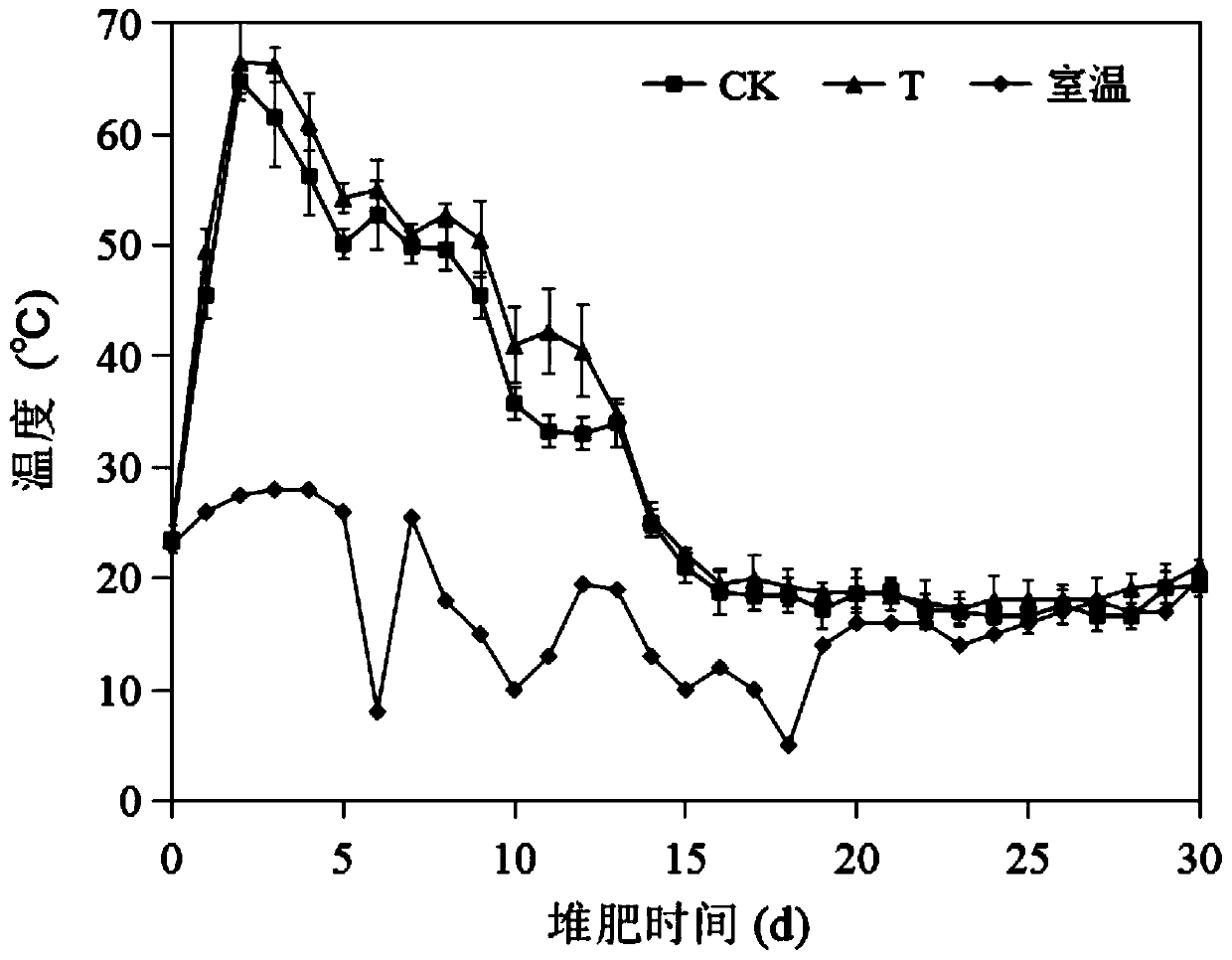
[0027]Microorganisms in nature are extremely abundant, and under the action of natural selection, they form relatively stable communities with specific functions through interactions such as competition, antagonism, and mutual benefit. In the process of decomposing complex compounds, the bacterial population of complex compounds can be used to synthesize a variety of hydrolytic enzymes through substrate induction, and decompose substrates into small molecular compounds for their own growth. In this process, due to the lack of substrates, they cannot The growing population is inhibited, or even completely eliminated, and finally forms a dominant synbiotic flora with a certain synergistic effect. The present invention utilizes this process, adopts the subgeneration continuous culture method, and uses wheat straw as the sole carbon source to separa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com