Method for repairing waste lithium iron phosphate material
A technology of lithium iron phosphate and repair methods, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, waste collectors, etc., can solve the problems of lengthy steps, cumbersome follow-up processing, and high equipment requirements, and achieve uniform distribution, light particle agglomeration, The effect of complete grain development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
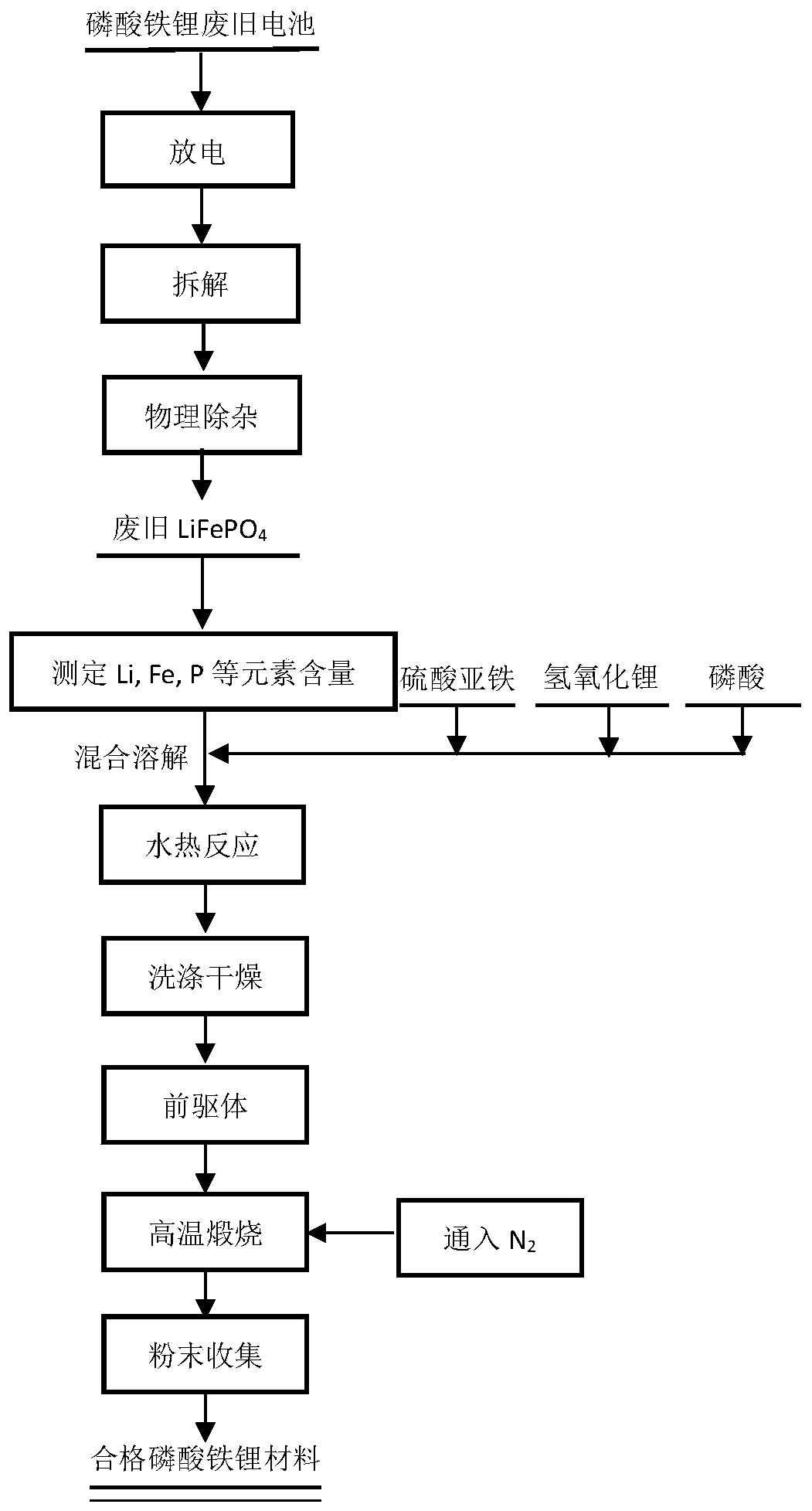
[0037] A method for repairing waste lithium iron phosphate materials, comprising the following steps:
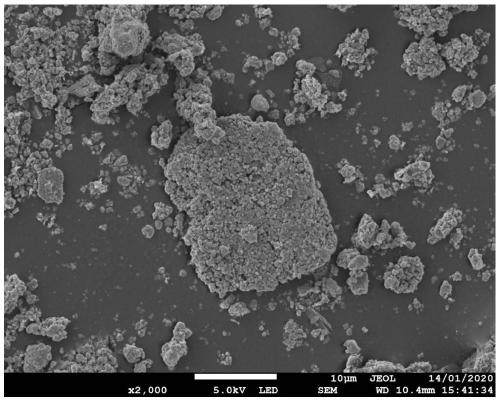
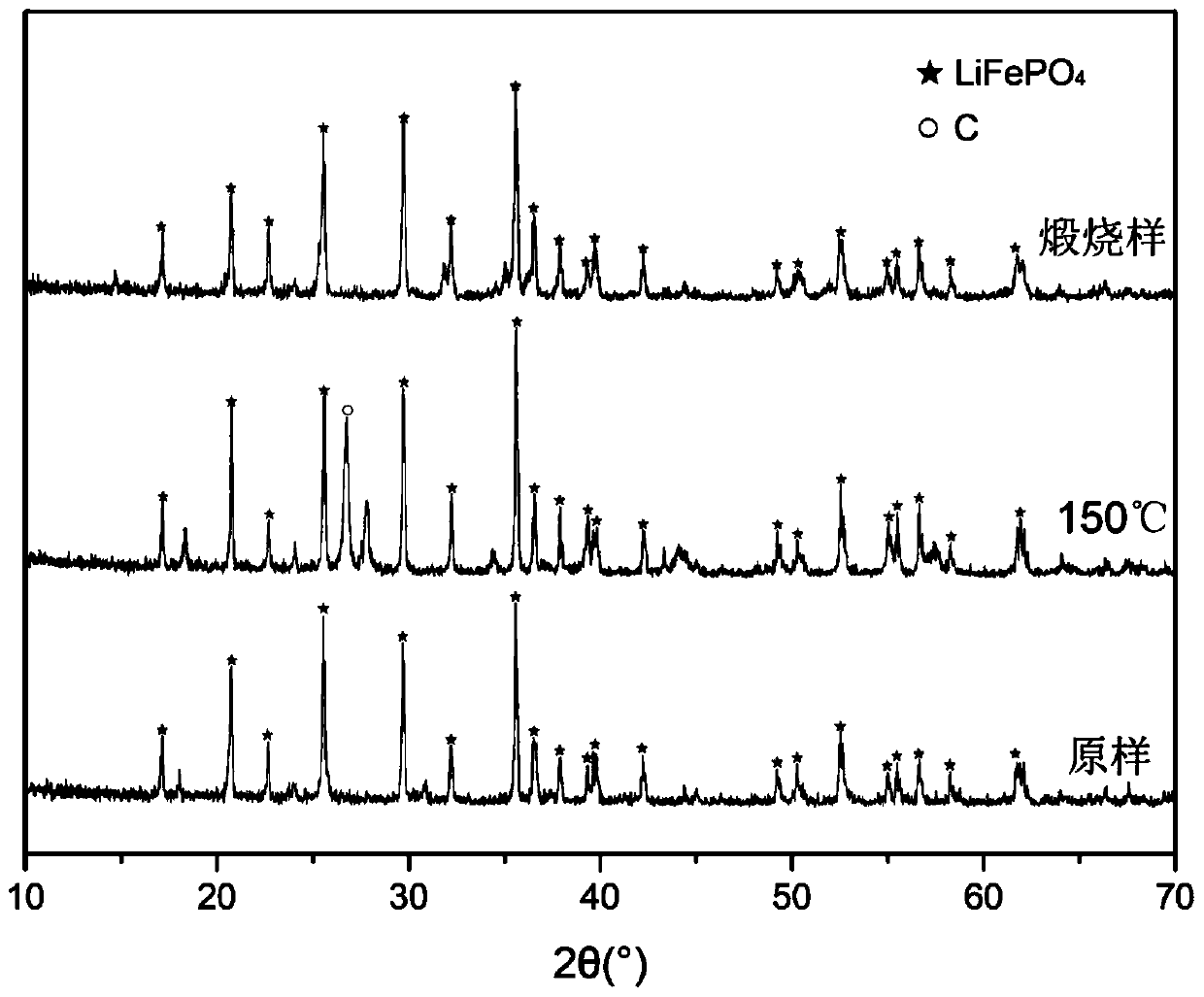
[0038] 1) After discharging the waste lithium iron phosphate battery, disassemble and remove the metal casing, and separate the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, diaphragm, and electrolyte. Then, the obtained positive electrode sheet was crushed and separated to obtain the positive electrode material and aluminum foil, which were further screened by gravity to obtain the waste lithium iron phosphate material. After physical removal of impurities, the total element content of impurities was ensured to be less than 0.5%, and the content of Li, Fe, P and other elements was measured.
[0039]2) Take 20g of waste lithium iron phosphate material, and configure a small amount of LiOH and FeSO with corresponding concentrations 4 , H 3 PO 4 Solution 20mL, after mixing evenly, add raw material samples, make the stoichiometric ratio Li:Fe:P=1:1:1, add 180mL deionize...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A method for repairing waste lithium iron phosphate materials, comprising the following steps:
[0047] 1) After discharging the waste lithium iron phosphate battery, disassemble and remove the metal casing, and separate the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, diaphragm, and electrolyte. Then, the obtained positive electrode sheet was crushed and separated to obtain the positive electrode material and aluminum foil, which were further screened by gravity to obtain the waste lithium iron phosphate material. After physical removal of impurities, the total element content of impurities was ensured to be less than 0.5%, and the content of Li, Fe, P and other elements was measured.
[0048] 2) Take 20g of waste lithium iron phosphate material, and configure a small amount of LiOH and FeSO with corresponding concentrations 4 , H 3 PO 4 Solution 20mL, after mixing evenly, add raw material samples, make the stoichiometric ratio Li:Fe:P=1:1:1, add 180mL deioniz...
Embodiment 3
[0054] A method for repairing waste lithium iron phosphate materials, comprising the following steps:
[0055] 1) After discharging the waste lithium iron phosphate battery, disassemble and remove the metal casing, and separate the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, diaphragm, and electrolyte. Then, the obtained positive electrode sheet was crushed and separated to obtain the positive electrode material and aluminum foil, which were further screened by gravity to obtain the waste lithium iron phosphate material. After physical removal of impurities, the total element content of impurities was ensured to be less than 0.5%, and the content of Li, Fe, P and other elements was measured.
[0056] 2) Take 20g of waste lithium iron phosphate material, and configure a small amount of LiOH and FeSO with corresponding concentrations 4 , H 3 PO 4 Solution 20mL, after mixing evenly, add raw material samples, make the stoichiometric ratio Li:Fe:P=1:1:1, add 180mL deioniz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com