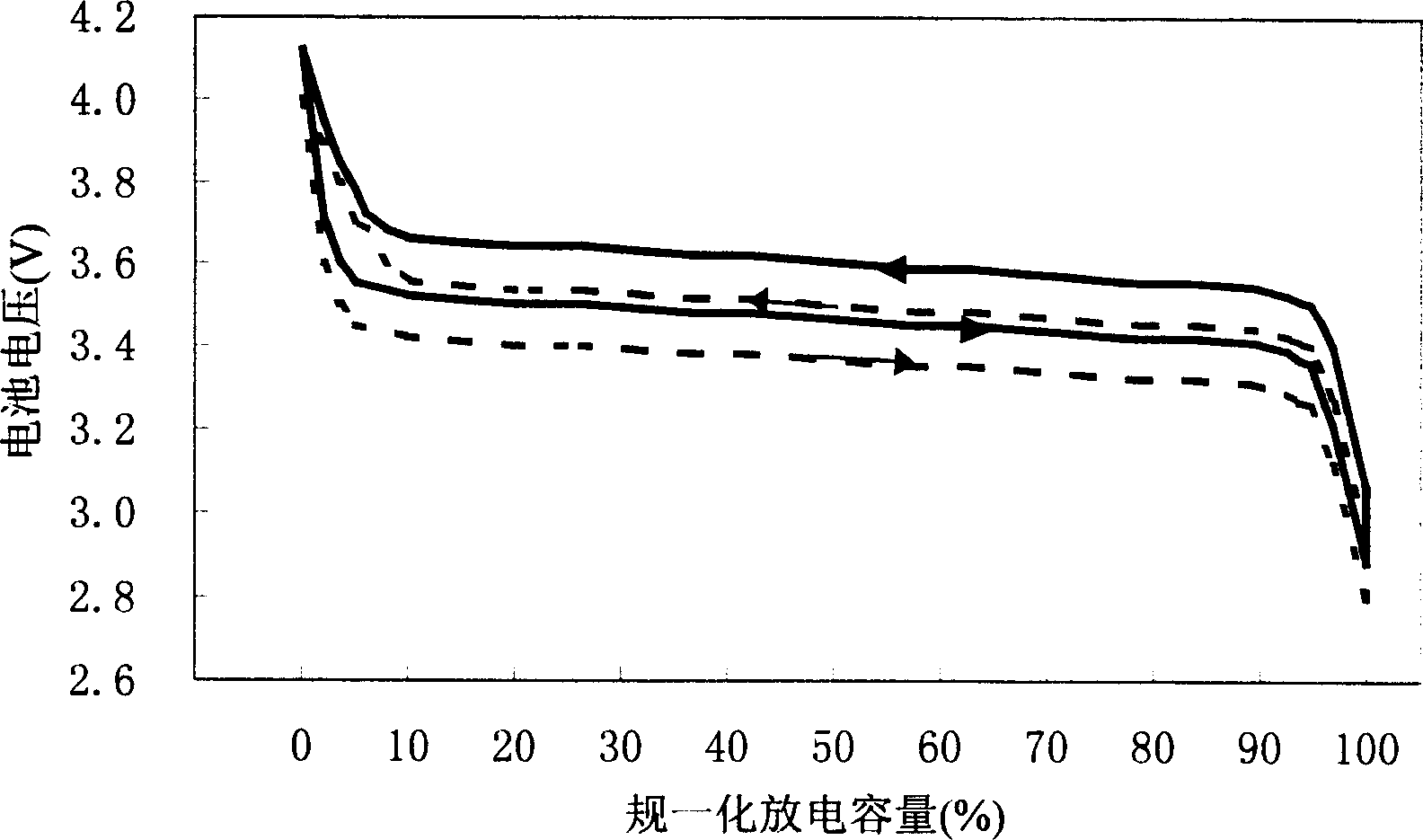
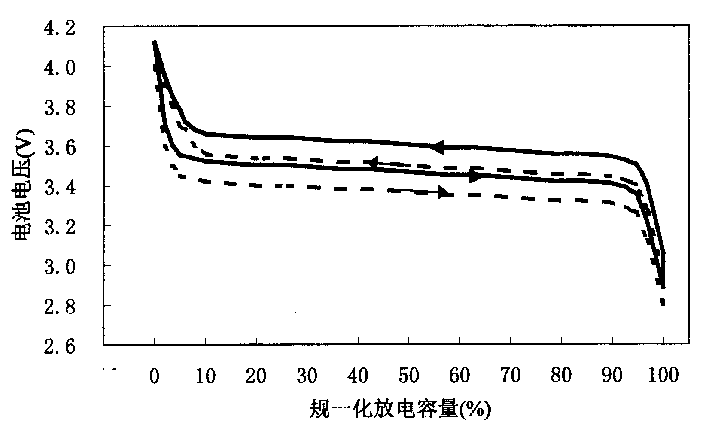
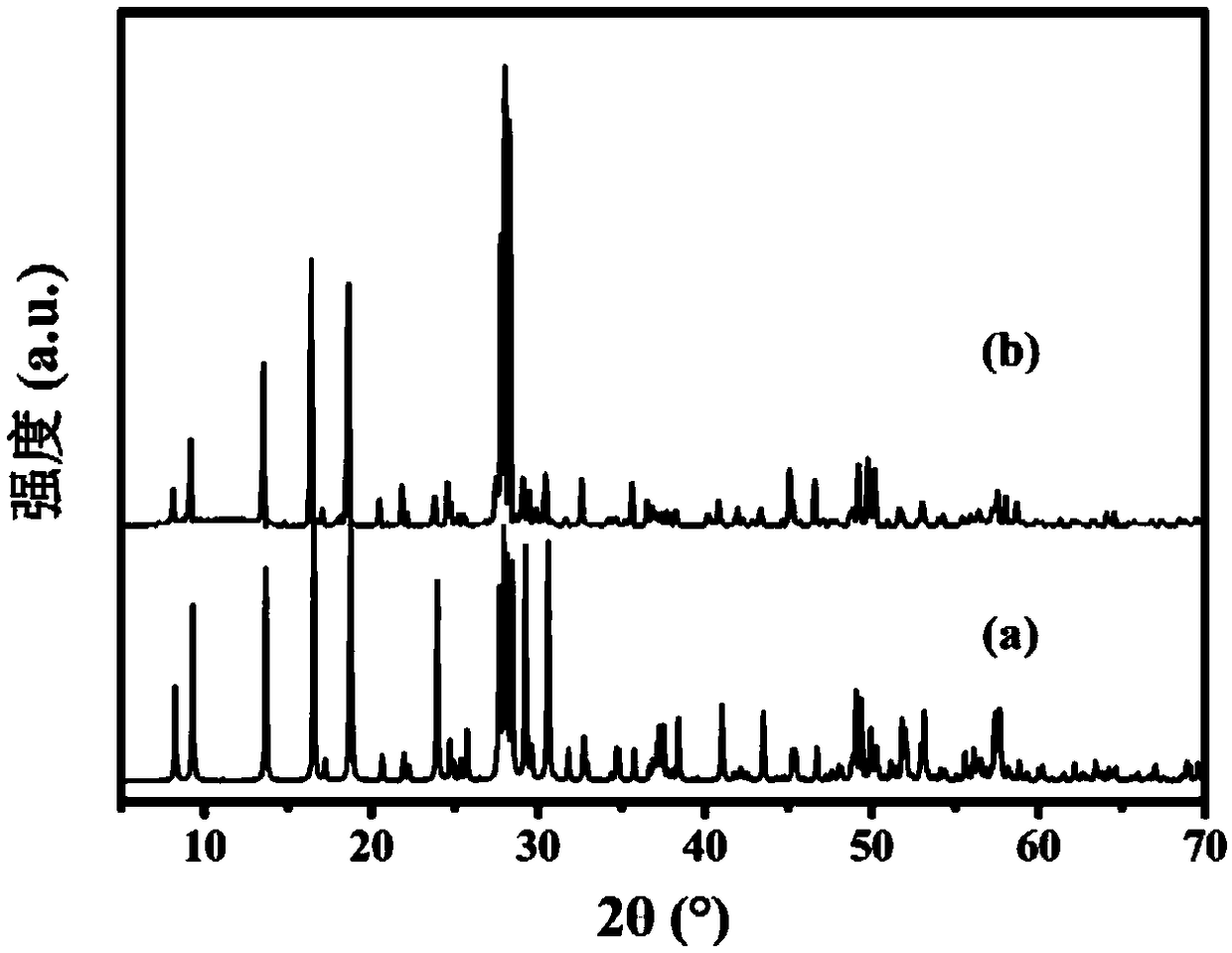
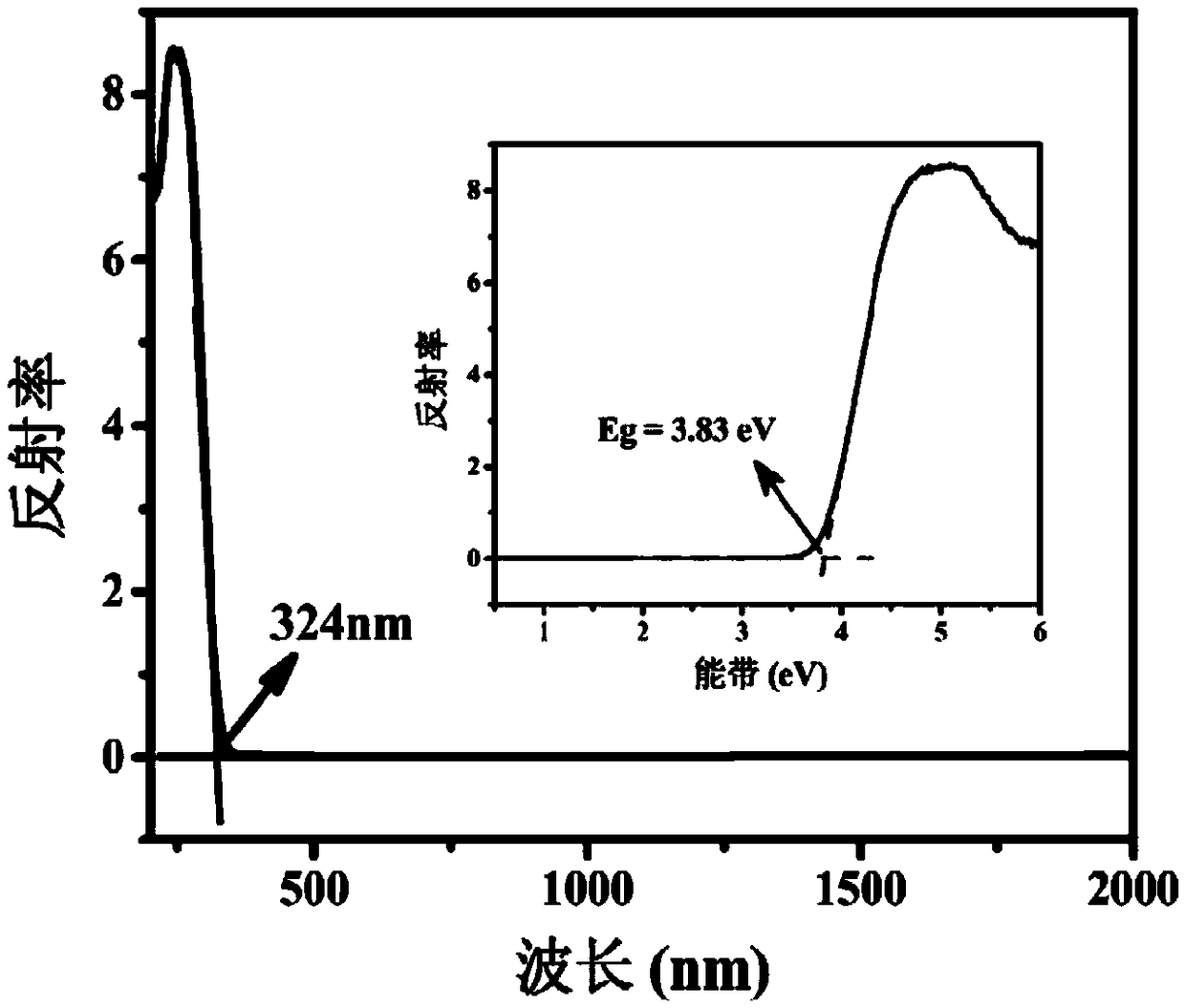
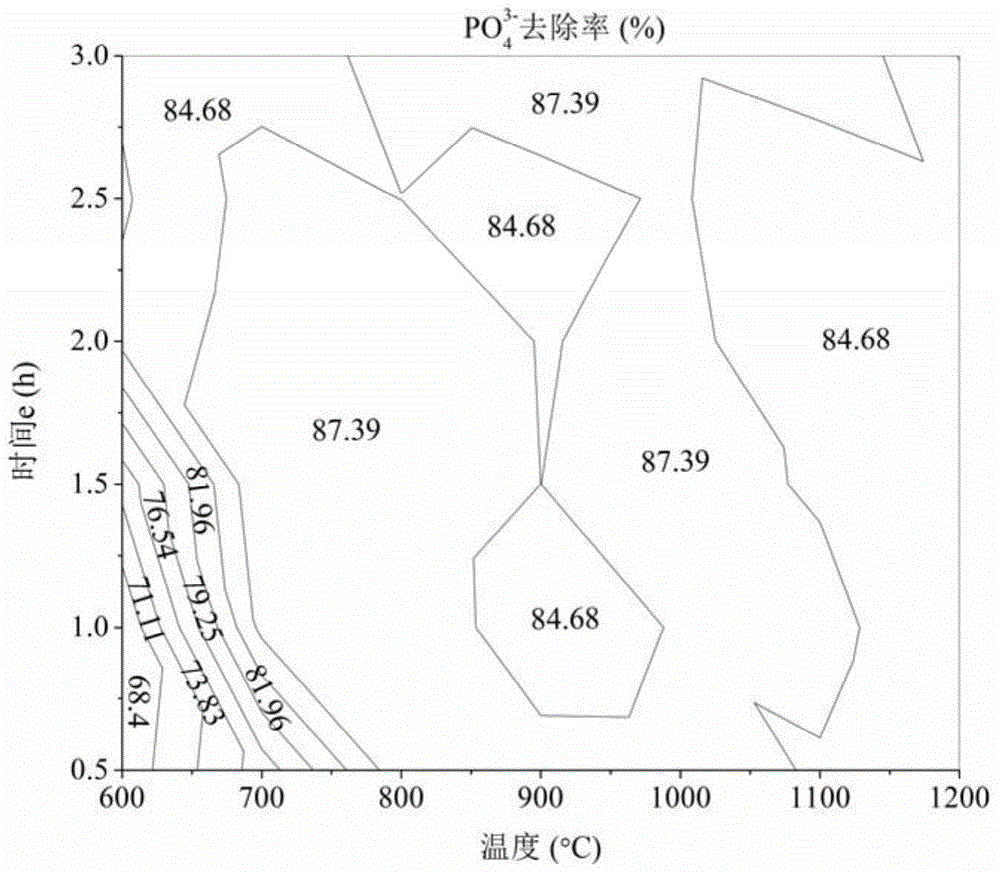
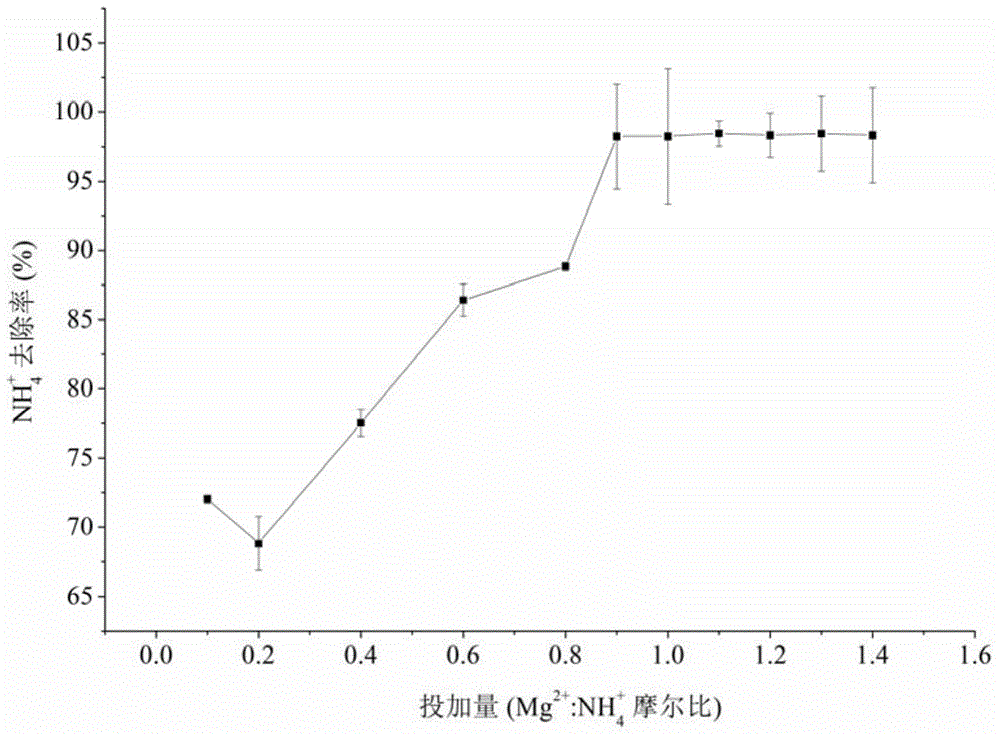
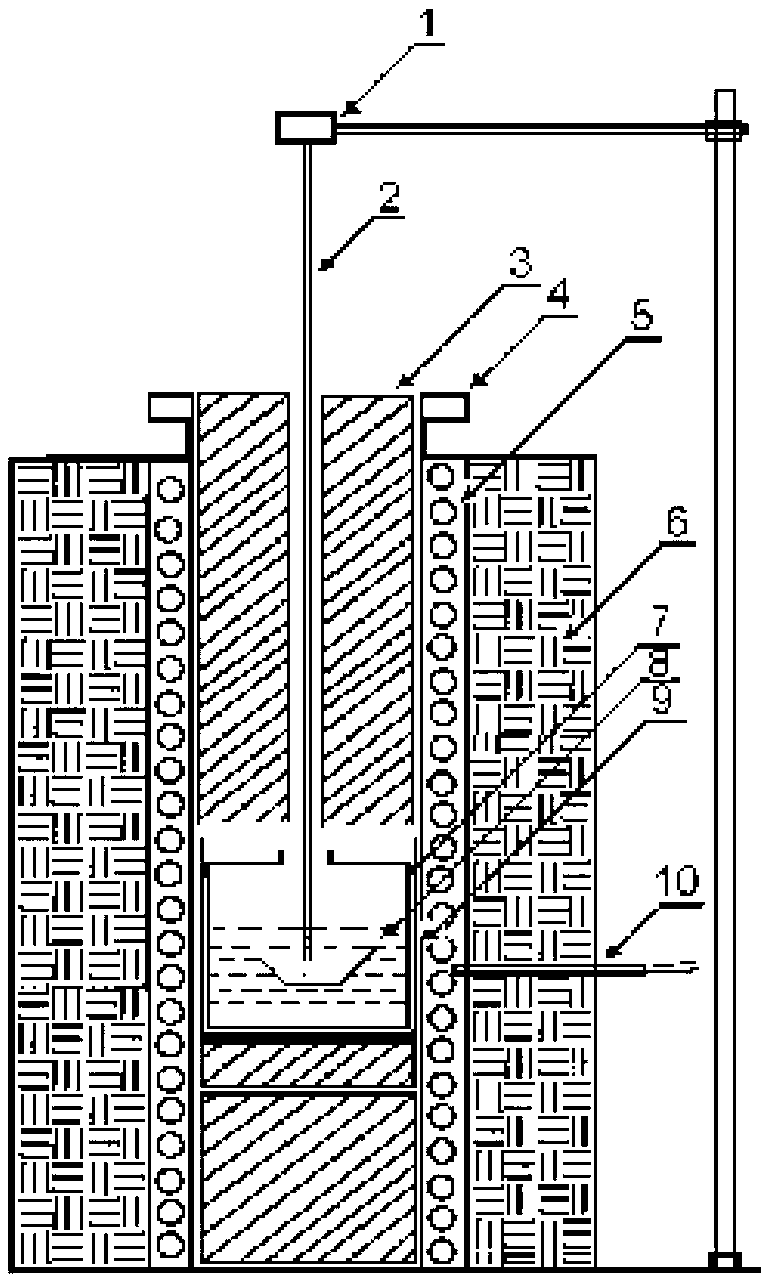
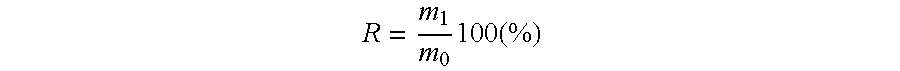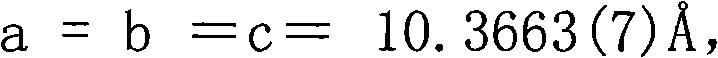Patents
Literature
182 results about "Phosphate crystals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lithium cell positive electrode materials and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1457111AImprove conductivityHigh conductivity at room temperatureElectrode thermal treatmentPositive electrodesNano structuringElectrical battery
The chemical general formula of the material is expressed as follows: LixM1-xFePO4, where M is selected from Mg2+, Ca2+...P5+ etc. With conduction adulterant added, reaction at 500-900 deg.C for 10 hr. by using metal oxide, phoshpate, fluoride etc. and non saturated crystal of Li-Fe phoshpate through nonstoichiometric method obtains the crystal of Li-Fe phosphate with high conductivity, which can be expressed as LiFePO4-y. The formula of material prepared by using method of pressurized type substitution ion is LixM1-xFezM'1-z. The formula of material of solid power prepared by using method of solid phase reaction is as LixM1-xFezMn1-zPO4. The formula of anode material in nano structure prepared by using method of vacuum sputter deposition is LixFePO4-y, whose conductivity and discharge capacity can reach 10 to the power -2 S / cm and 240 Ah / g.
Owner:徐瑞松
Method for adsorption of phosphate contaminants from water solutions and its recovery
InactiveUS20100243571A1Prevent precipitationReduce concentrationMaterial nanotechnologyIon-exchanger regenerationSorbentSludge
Aqueous fluid polluted with phosphate contaminants is mixed with or passed through an adsorbent material selected from: (i) particles of oxides or hydroxides of transition metals, aluminum oxides or hydroxides, TiO2, or mixtures thereof, or (ii) particles of activated carbon, activated alumina, aluminum oxide, activated TiO2, TiO2, mineral clay, zeolite, or an ion exchanger loaded with nanoparticles of oxides or hydroxides of transition metals, aluminum oxides or hydroxides or TiO2, or mixtures thereof, to yield aqueous fluid purified from phosphate. The adsorbent material is further regenerated by increasing the pH of the adsorbent sludge, concentrated phosphate solution or a phosphate crystal slurry is recovered as well.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
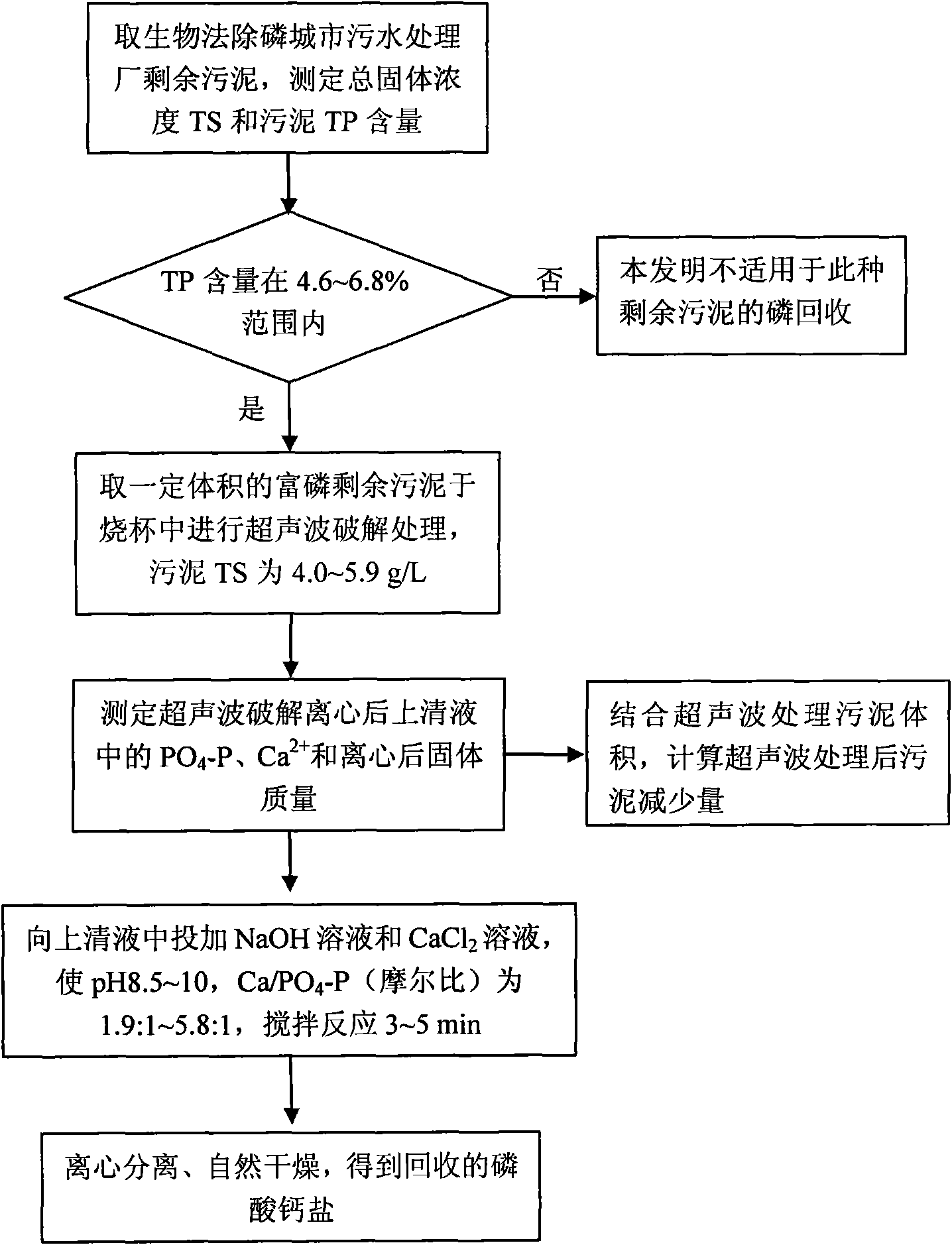
Method for recovering phosphonium compound from phosphorous excess sludge of urban sewage treatment plant
InactiveCN101654238AEasy to recycleImprove biodegradabilitySludge treatmentPhosphorus compoundsPhosphate crystalsSludge
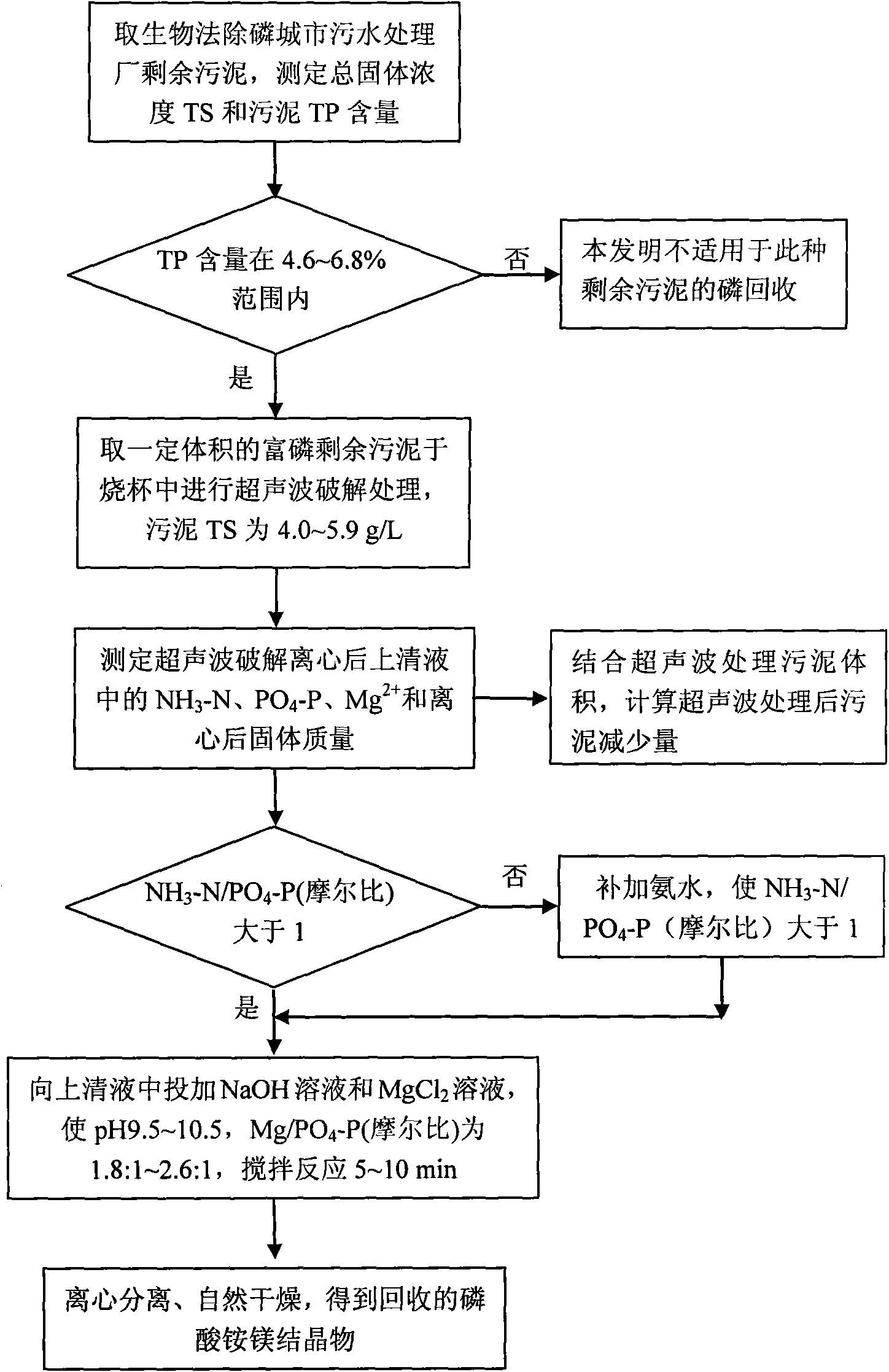
The invention relates to a method for recovering a phosphonium compound from phosphorous excess sludge of an urban sewage treatment plant, comprising the following steps: a. obtaining phosphorous excess sludge from a biological dephosphorization urban sewage treatment system; b. carrying out ultrasonic cracking treatment on the excess sludge obtained from the step a to release pnicogen in the sludge, centrifuging the sludge and carrying out solid-liquid separation on the sludge after cracking, collecting supernatant and carrying out the step c or d; c. obtaining a recovered ammoniomagnesium phosphate crystal by adopting a magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation process; and d. obtaining recovered phosphoric acid calcium salt by adopting a phosphoric acid calcium salt precipitation process. The invention can recovery the phosphonium compound from the excess sludge, reduce the sludge volume and lower the sludge treatment expense and is beneficial to the management operation of the urban sewage treatment plant.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
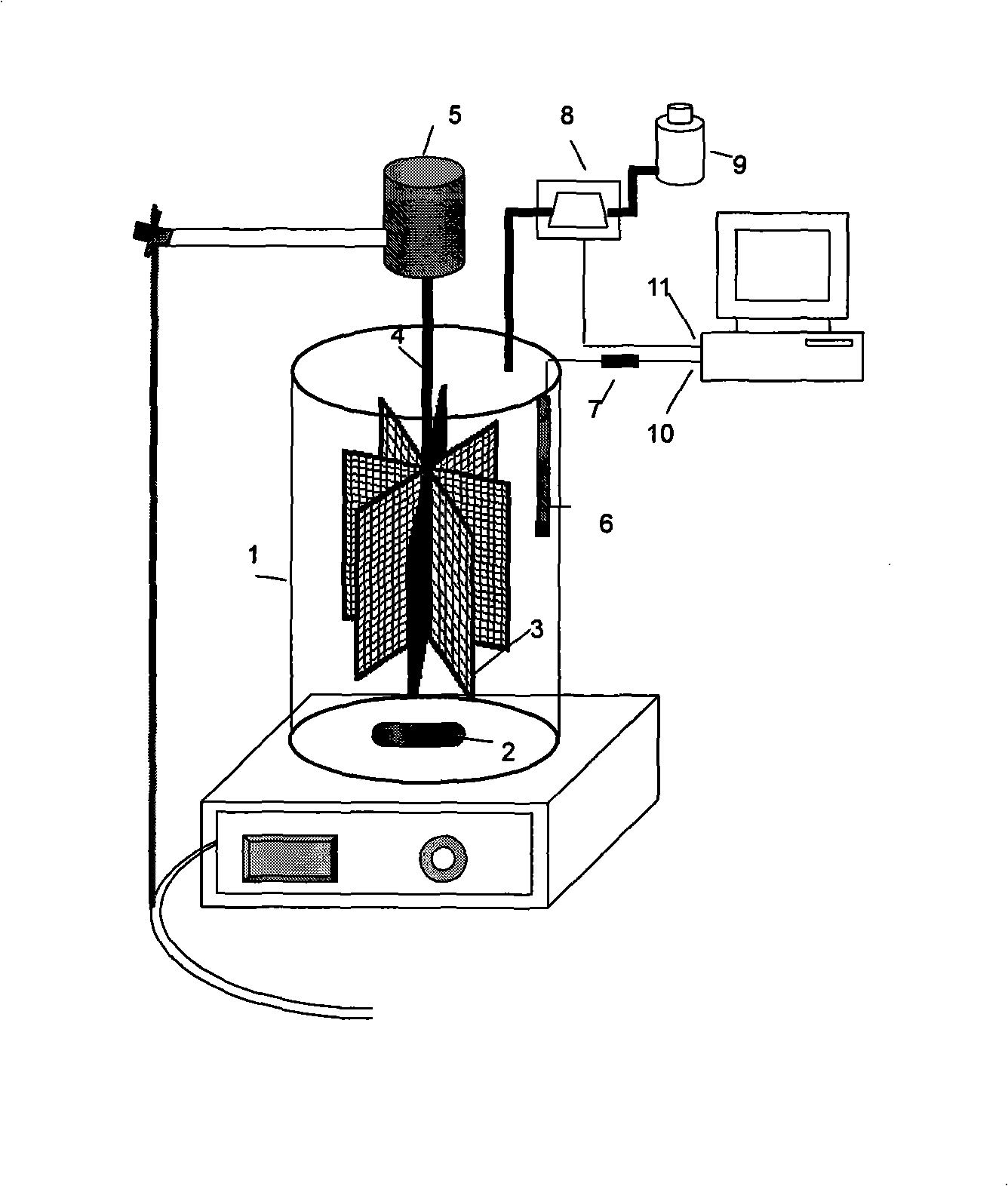
Apparatus for reclaiming sewerage nitrogen and phosphor by ammoniomagnesium phosphate crystal method and method thereof
InactiveCN101298324AHigh recovery rateStir wellWater/sewage treatmentPhosphorus compoundsPhosphate crystalsPhosphor
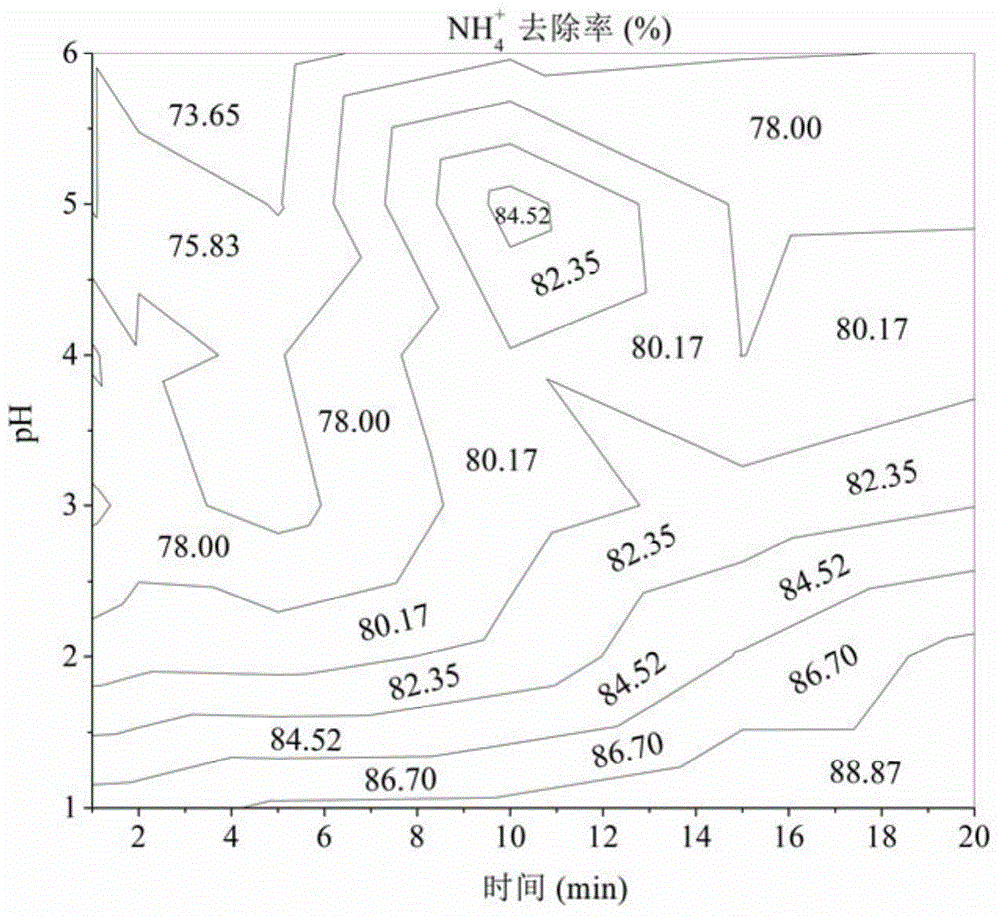
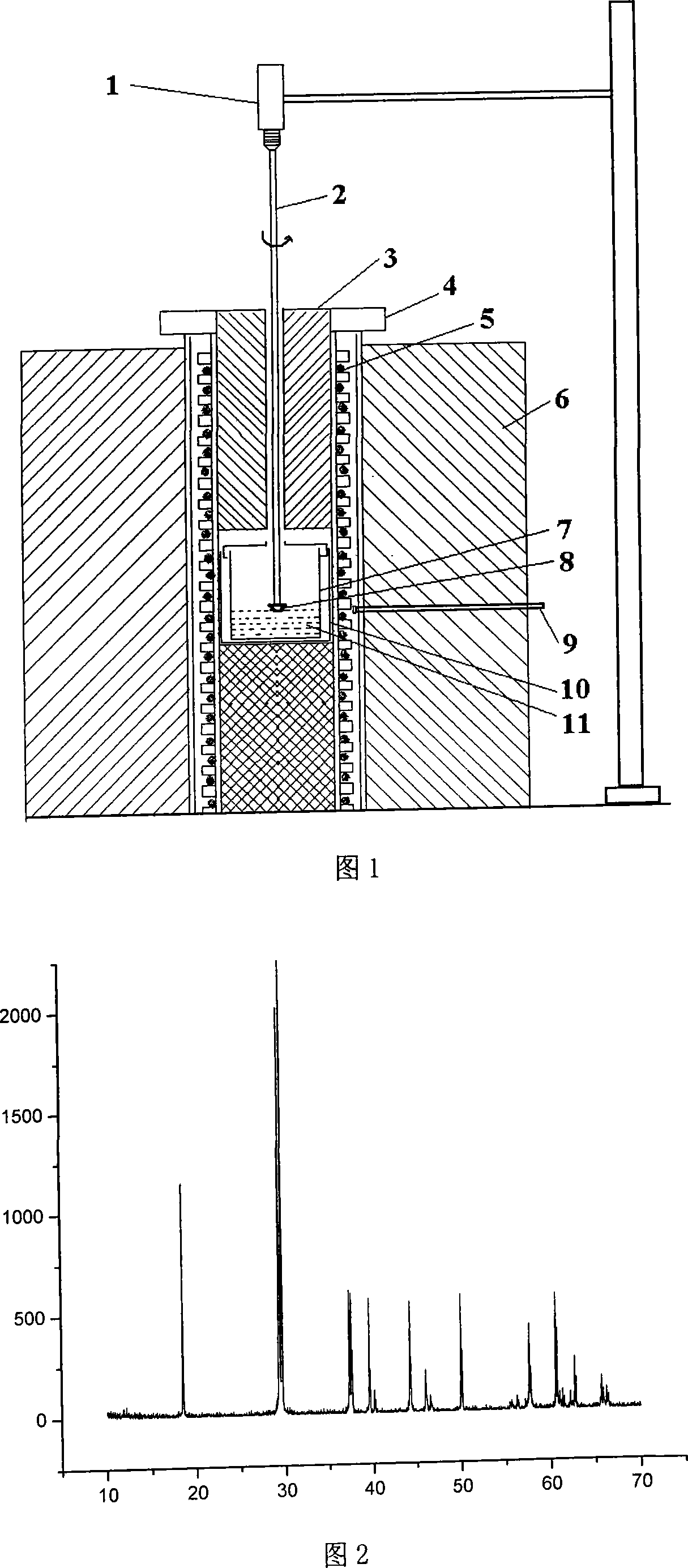
The invention discloses a device and method for recovering nitrogen and phosphor in the wastewater by the ammoniomagnesium phosphate crystal method. The invention adopts an MAP nitrogen and phosphor recovery device which has a two-stage agitation of a magnetic stirring apparatus and a deposit catcher, then the wastewater of 3 / 5 to 4 / 5 of the volume of the device is added as the reactant liquor, then add magnesium source and phosphorus source regulation reaction liquor with the ration of NH4<+>: PO4<3->: Mg<2+> equal to 1:1:1 to 1:1.2:1.2, then alkali liquor is dropped continuously to maintain the PH value of the reaction liquor at 9.0 plus / minus 0.1, the magnetic stirring apparatus rotates at the speed of 400-600 r / m and the deposit catcher is driven by a motor stirrer and agitates continuously at the speed of 40-60 r / m, and finally the MAP can be obtained. The invention overcomes the problem that the activity of the crystal-forming ions drops when the PH value decreases during the crystallization process, promotes the MAP crystallization process and improves the MAP recovery rate; the magnetic stirring apparatus and the deposit catcher adopted in the MAP recovery device reduces the stirring dead area in the reactor, the reaction liquor is stirred more sufficiently, which is favorable for the MAP crystal-forming ions to form crystal; the deposit catcher that is designed to catch MAP is favorable to improve the MAP purity in the recovered products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method for substituted molybdophosphate crystal catalyst
InactiveCN102218348ASolve the problems of high toxicity and serious pollutionEasy to recycleOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRecyclable catalystChemical industry
The invention relates to a preparation method for a substituted molybdophosphate crystal catalyst. The design and synthesis of a high-activity, selective, environmentally-friendly and recyclable catalyst have an important significance in the research and chemical industry fields. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises two steps: step one, mixing sodium molybdate Na2MoO4.2H2O, transition metal sulfate, phosphoric acid H3PO4 and 1,3-bis(4-pyridyl)-propane or ethylene diamine at a molar ratio of 6: 2.9: 30: 2.6 in water with the molar fraction of 2000 and stirring for 30 minutes to obtain a mixed liquid; and step two, enclosing the mixed liquid obtained in the step one in a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel reaction kettle at a filling degree of 60-70%, then placing the reaction kettle in a 165 DEG C oven to heat and crystallize for 7 days, and then naturally cooling to room temperature to obtain the dark red polyacid crystal catalyst. The preparation method can be used for preparing the substituted molybdenum phosphate crystal catalyst.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for recovering and removing nitrogen and phosphor in urine by ammoniomagnesium phosphate crystal method
InactiveCN101811687AThe reaction process is simpleEasy to operatePhosphorus compoundsPhosphate crystalsPhosphor
The invention discloses a method for recovering and removing nitrogen and phosphor in urine by an ammoniomagnesium phosphate crystal method, relating to a method for recovering and removing the nitrogen and phosphor in urine and recovering the reaction product of the urine through urine source separation. The method for recovering and removing the nitrogen and phosphor comprises the following steps: evenly stirring the urine, regulating the pH value of the urine by utilizing NaOH solution the mass fraction of which is 10%, adding reaction precipitant, stirring, precipitating, filtering and drying to obtain the ammoniomagnesium phosphate crystal. Therefore, nitrogen and phosphor load on domestic sewage is reduced, and the product can also be utilized as manure for agriculture, so the method of the invention is a sustainable sewage disposal technology.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
A method for wet phosphoric acid producing high pure calcium hydrogen orthophosphate
InactiveCN101549862AHigh in total calcium and phosphorusLess impuritiesPhosphatesAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserHydrogenPhosphate crystals
The invention relates to a method for wet phosphoric acid producing high pure calcium hydrogen orthophosphate and monoammonium phosphate of fertiliser stage, which is indicated as wet phosphoric acid aminated, filtrating the ground paste after aminated, drying and packing the filter residue and obtaining monoammonium phosphate of fertiliser stage, obtaining high pure monoammonium phosphate crystal after the filtrate evaporated, crystallized and refiltered, generating calcium hydrogen orthophosphate and ammine by taking monoammonium phosphate reacting with calcium hydrogen orthophosphate of technical grade or alimentary products stage, aminating phosphoric acid after ammine recovered, and drying the calcium hydrogen orthophosphate deposition, then the high pure calcium hydrogen orthophosphate products is produced. The method in this invention can use wet method phosphoric acid with high impurity content to produce high pure calcium hydrogen orthophosphate, which can be used as calcium phosphorus additive agent of feed stuff stage or alimentary products stage based on the raw charge.
Owner:中国-阿拉伯化肥有限公司
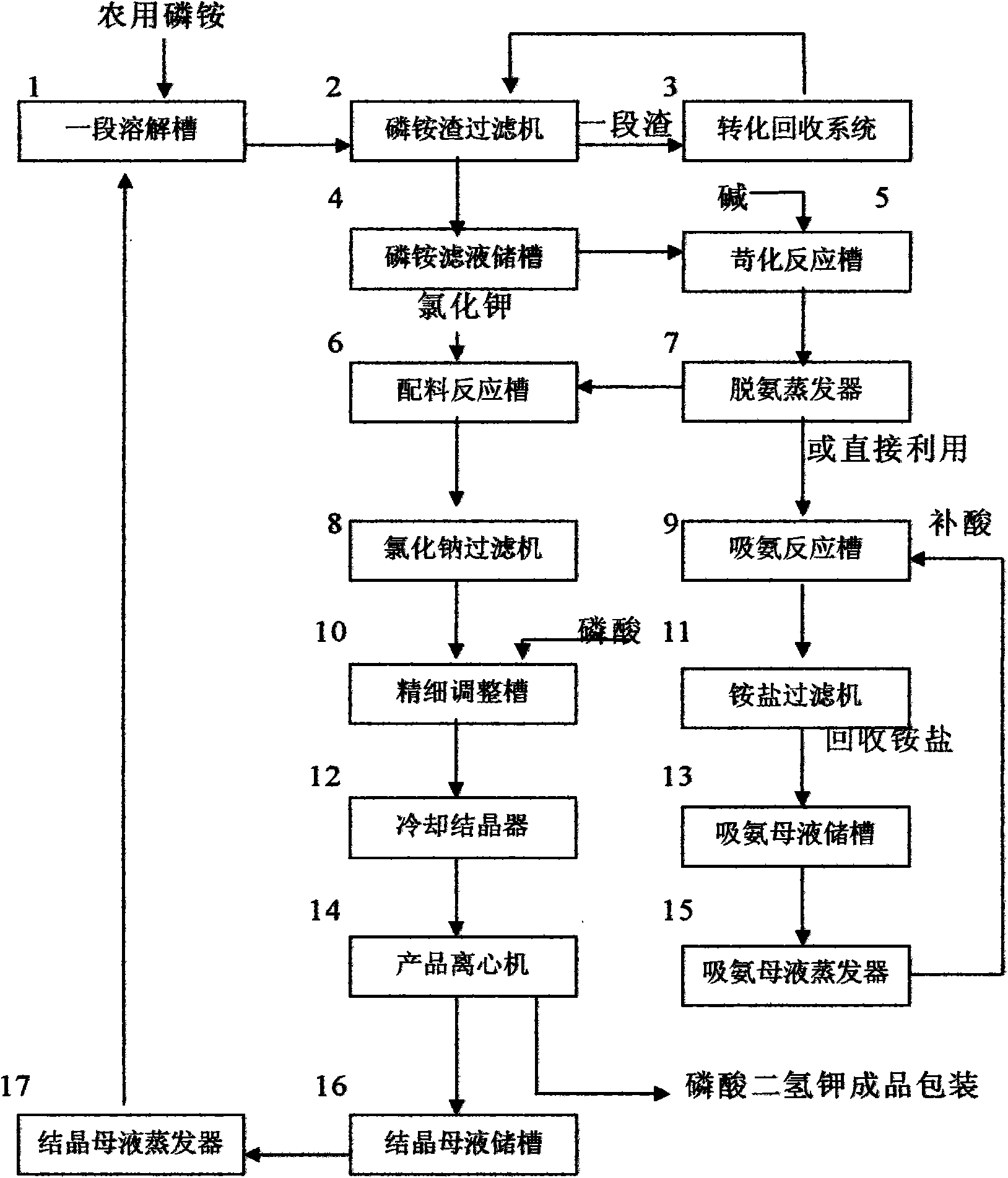
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate prepared by agricultural ammonium phosphate and water-insoluble phosphorus recovery method thereof
InactiveCN101602499AQuality improvementImprove product qualityPhosphorus preparationMonopotassium phosphateWater treatment
The invention relates to potassium dihydrogen phosphate prepared by agricultural ammonium phosphate and a water-insoluble phosphorus recovery method thereof; the method is characterized by comprising the following steps: dissolving the agricultural monoammonium phosphate or the diammonium phosphate by utilizing the circulatory potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystal mother liquor to prepare ammonium salt solution of phosphoric acid, filtering the solution, processing ammonium phosphate residues to recover all the phosphorus pentoxide and potassium oxide contained in the residues by utilizing hydrocarbonate, carbonate and / or hydroxide; adding alkaline substances into the ammonium phosphate solution, evaporating and recovering ammonia, meanwhile, obtaining sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution or potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution, after reacting with potassium chloride, filtering the solution to remove sodium chloride, adjusting the pH by phosphoric acid, cooling to obtain potassium dihydrogen phosphate. The steps also comprise: preparing ammonium sulfate by absorbing ammonia by using sulfuric acid, preparing sewage water or water treatment drug by utilizing the residues after recovering phosphorus and potassium. With the method of the invention adopted, any inferior quality ammonium phosphate and the potassium chloride with use value can be used, and phosphorus and potassium has high coefficient of recovery, good quality products, low raw material consumption, low energy consumption, low production cost, removal pollution, and has great technological economic and social benefits.
Owner:绵阳市联创化工有限公司
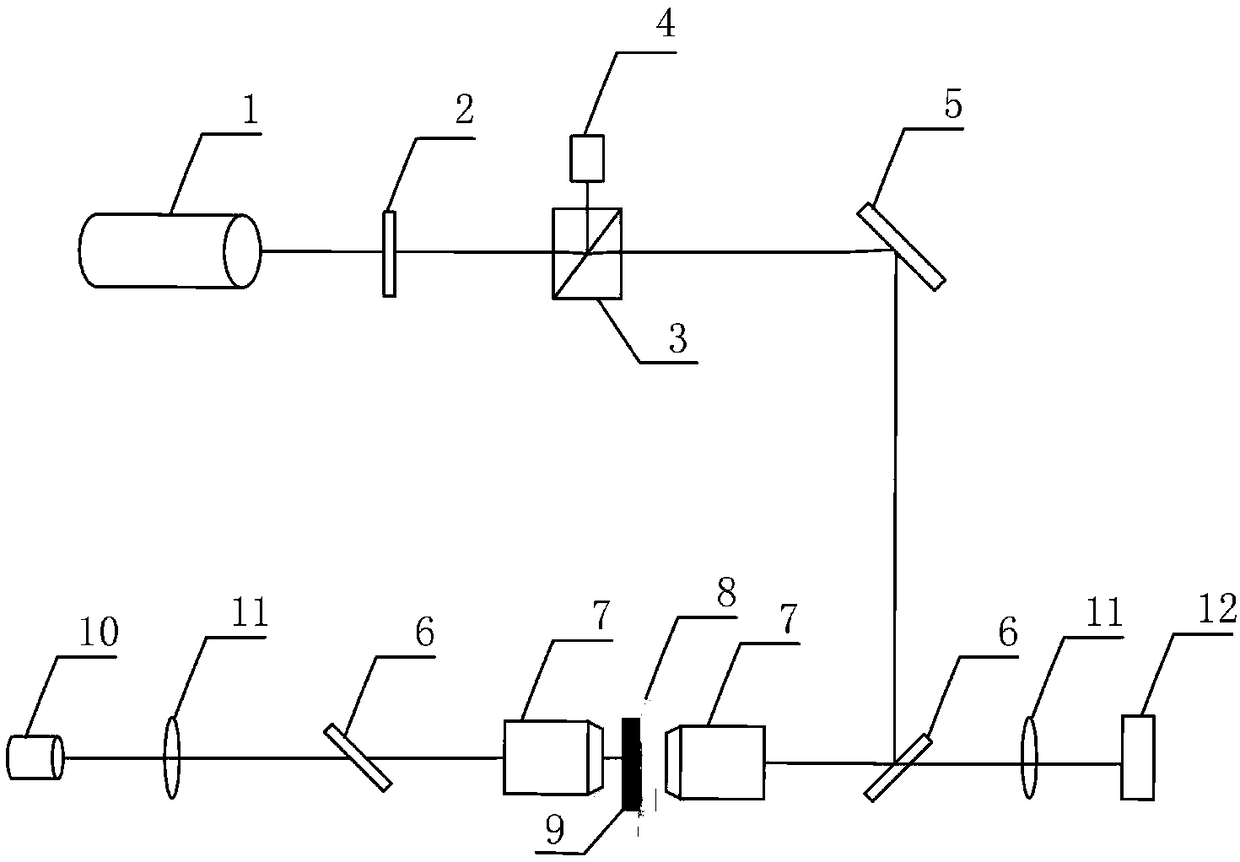
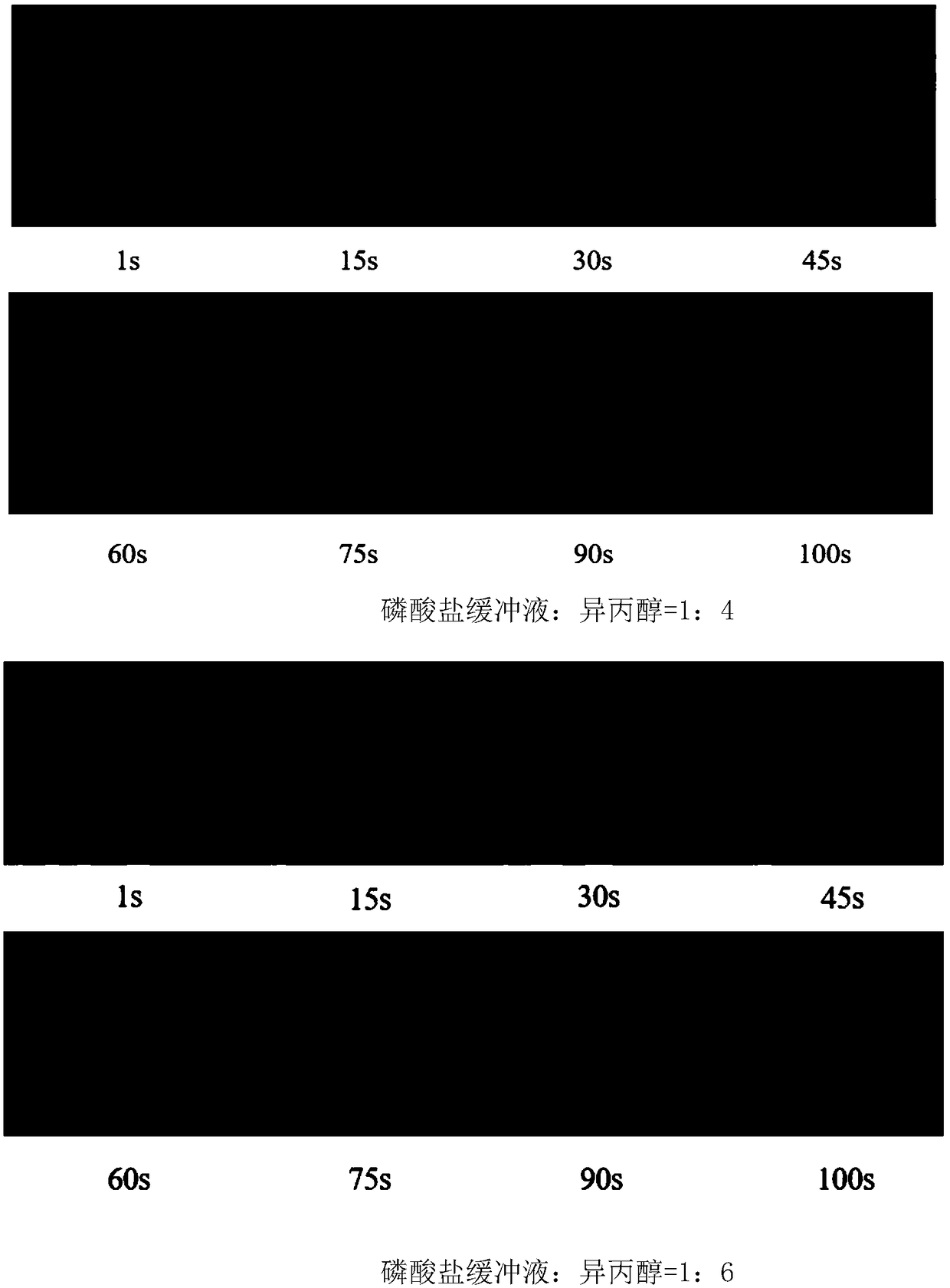
Microsphere controllable equipment based on optical tweezers and operation method
ActiveCN109225080AReduce solubilityEasy to operateEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMicroballoon preparationPhosphate crystalsMicrosphere
The invention relates to microsphere controllable equipment based on optical tweezers and an operation method. The microsphere controllable equipment based on the optical tweezers comprises an opticaltweezers system, a sample pond and an illumination imaging light path. The operation method comprises the following steps: initializing the optical tweezers system; preparing a mixed solution capableof separating out microspheres; uniformly mixing a phosphate buffer solution and isopropanol according to a volume ratio of 1:(3.5-6); injecting the mixture into the sample pond; placing the sample pond on a sample platform of the optical tweezers system; locally heating the phosphate buffer solution and isopropanol mixed solution by using a highly converged laser spot, so that phosphate crystalsnear the spot are separated out to form phosphate microspheres; observing the prepared phosphate microspheres by using the illumination imaging light path; and controlling and operating sizes, preparation speeds and positions of phosphate crystal particles by adjusting laser light intensity, a laser light beam direction and a laser light illumination time.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
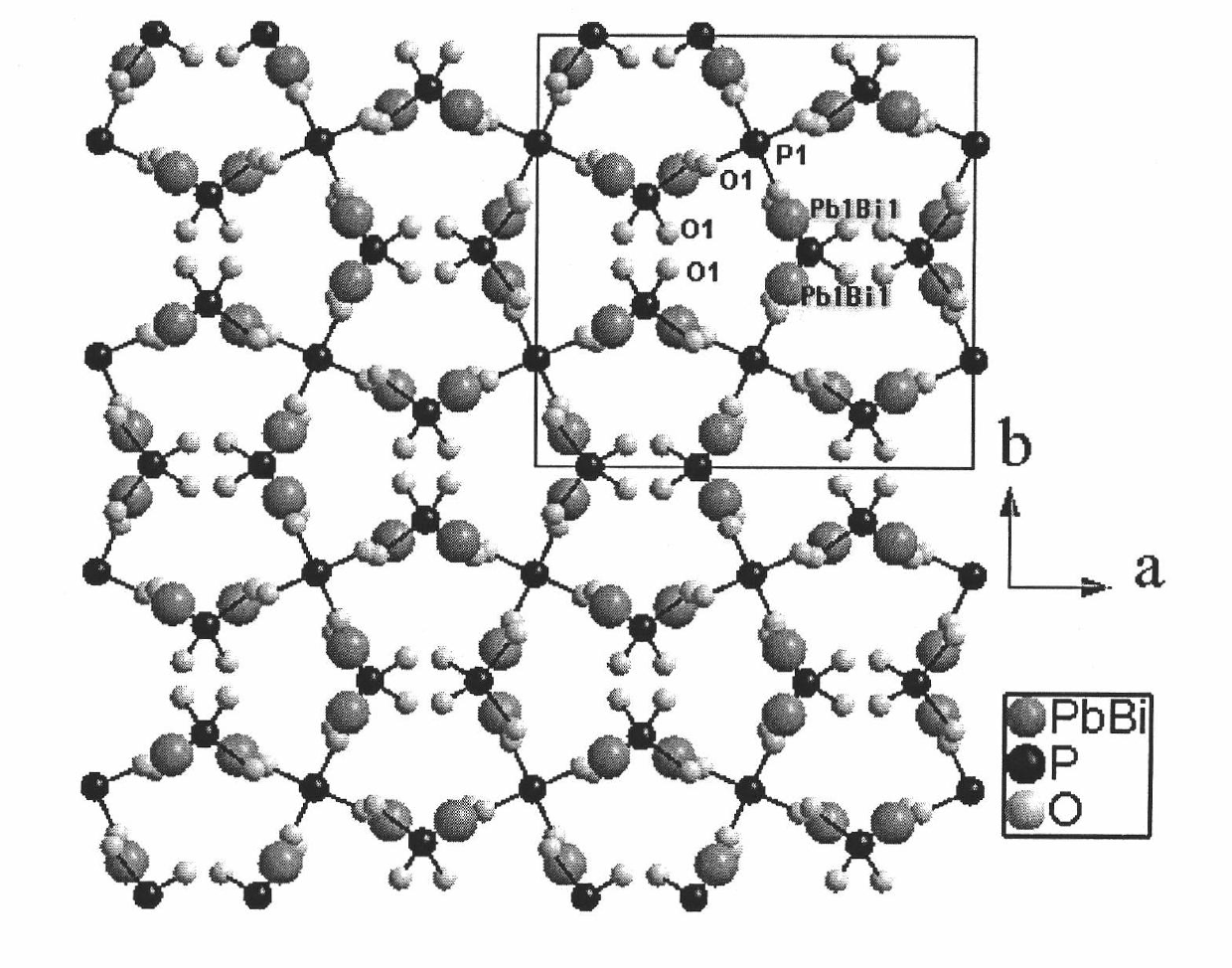
Non-linear optical material lead bismuth phosphate crystal
InactiveCN102086530ANonlinear Optical Performance ImprovementPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsSpace groupCell parameter
The invention discloses a non-linear optical material, namely a lead bismuth phosphate crystal, and relates to the field of non-linear optical materials. A chemical formula of lead bismuth phosphate is Pb3Bi (PO4)3; the molecular weight is 2230.98; the lead bismuth phosphate belongs to a cubic crystal system; the space group is I43d; and single-cell parameters, namely alpha, beta and gamma are 90.00 degrees, and Z is equal to 2. The lead bismuth phosphate crystal is prepared by adopting a high-temperature solid-state method. The lead bismuth phosphate has excellent non-linear optical performance; a powder secondary harmonic generation (SHG) coefficient of the lead bismuth phosphate is three times that of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP); and the lead bismuth phosphate crystal can be used for deep water communication of submarines, laser blinding weapons, marine fish detection, optical disk recording, color laser printing, laser projection televisions, and optical computing or optical fiber communication.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing gypsum whisker by using phosphate tailings and raffinate phosphoric acid
InactiveCN104328481ASolve environmental problemsRegular crystal formPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsChemical industryO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing gypsum whisker by using phosphate tailings and raffinate phosphoric acid. A technical scheme adopted in the invention is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: taking a certain amount tailing powder with a certain particle size, adding a certain amount of distilled water to prepare a tailing slurry with a certain solid content, gradually adding raffinate phosphoric acid, reacting under certain conditions, filtering after the reaction, gradually adding a certain concentration of sulfuric acid into the obtained filtrate, reacting for a certain time, filtering, washing the obtained filter cake, and drying the washed filter cake in a drying box to obtain the gypsum whisker. The gypsum whisker is prepared through a two-step technology by using the raffinate phosphoric acid, the phosphate tailings and other phosphorus chemical industry enterprise waste resources as raw materials, and the growth form of the crystals of the gypsum whisker is controlled in the formation process of the phosphate crystals, so compared with traditional gypsum whisker preparation technologies, the method has the advantages of production cost reduction, solving of the environmental protection problem of the phosphorous chemical enterprises to a certain extent, and full use of magnesium resources in the raffinate phosphoric acid and the tailings.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
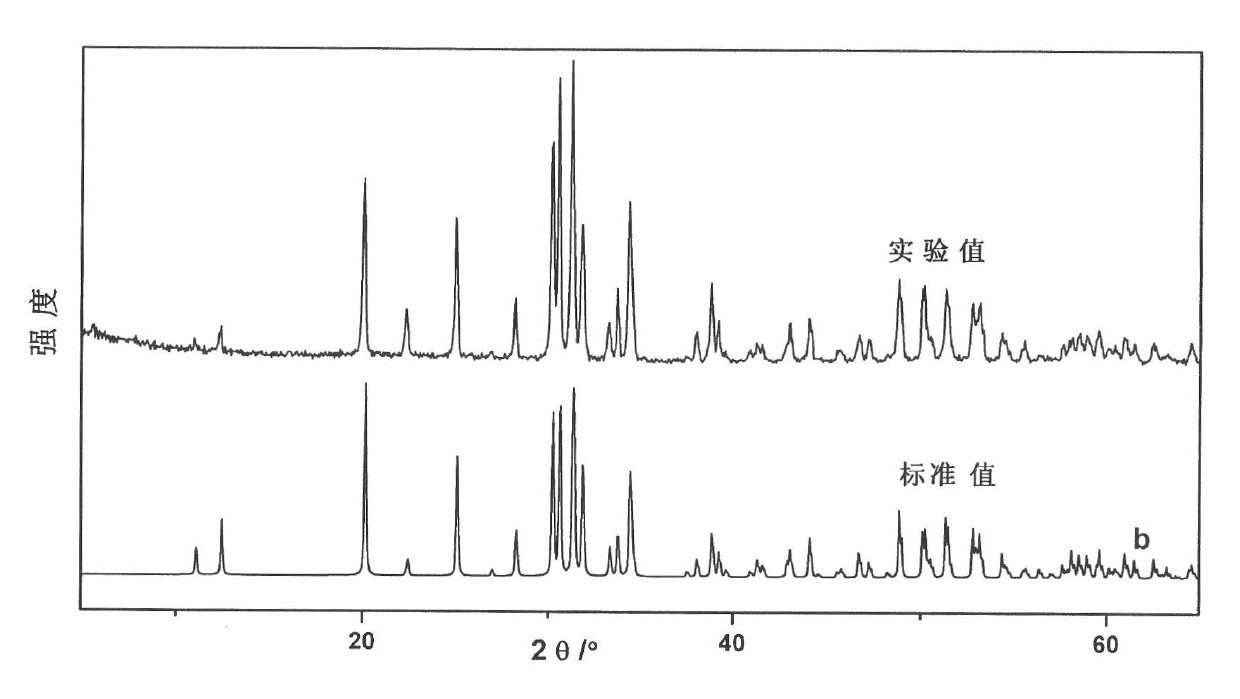
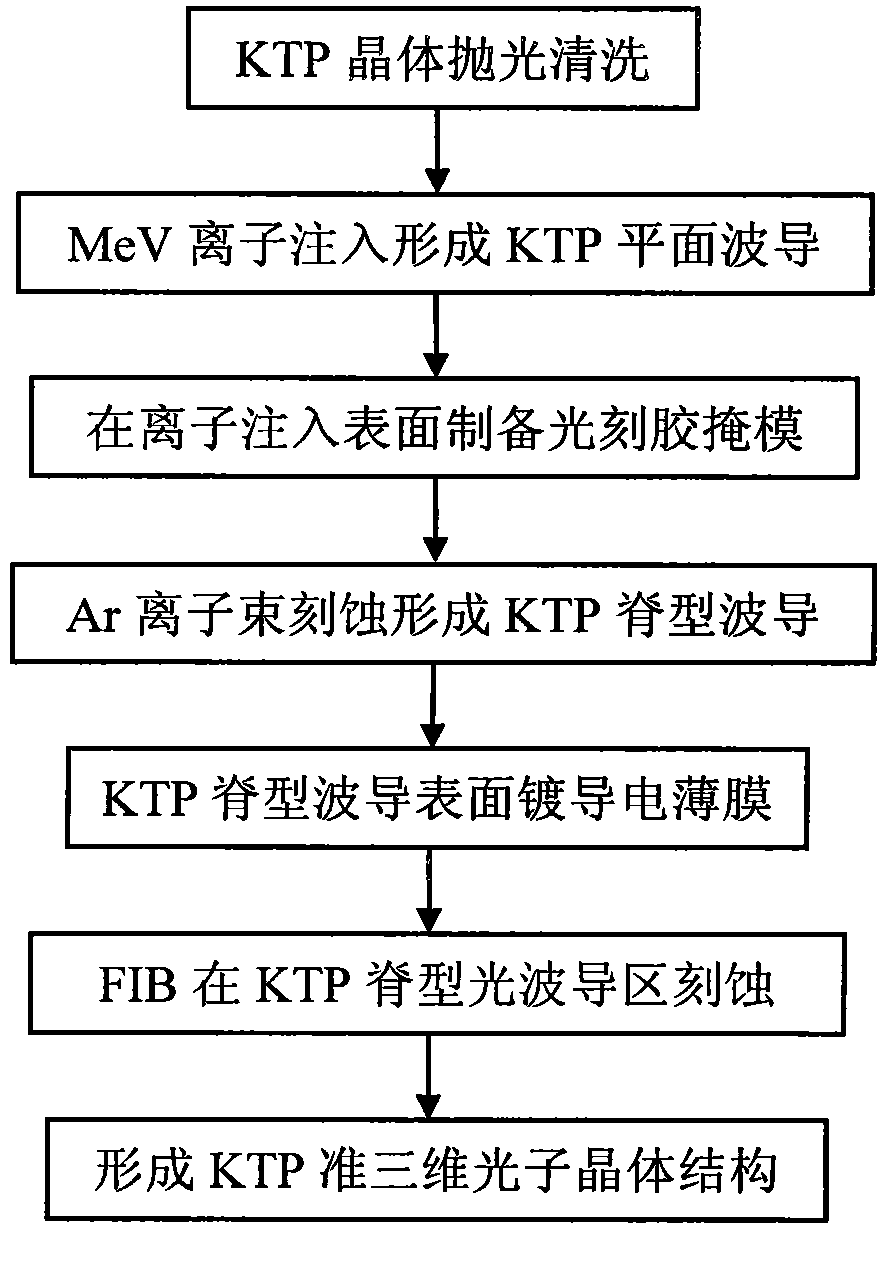
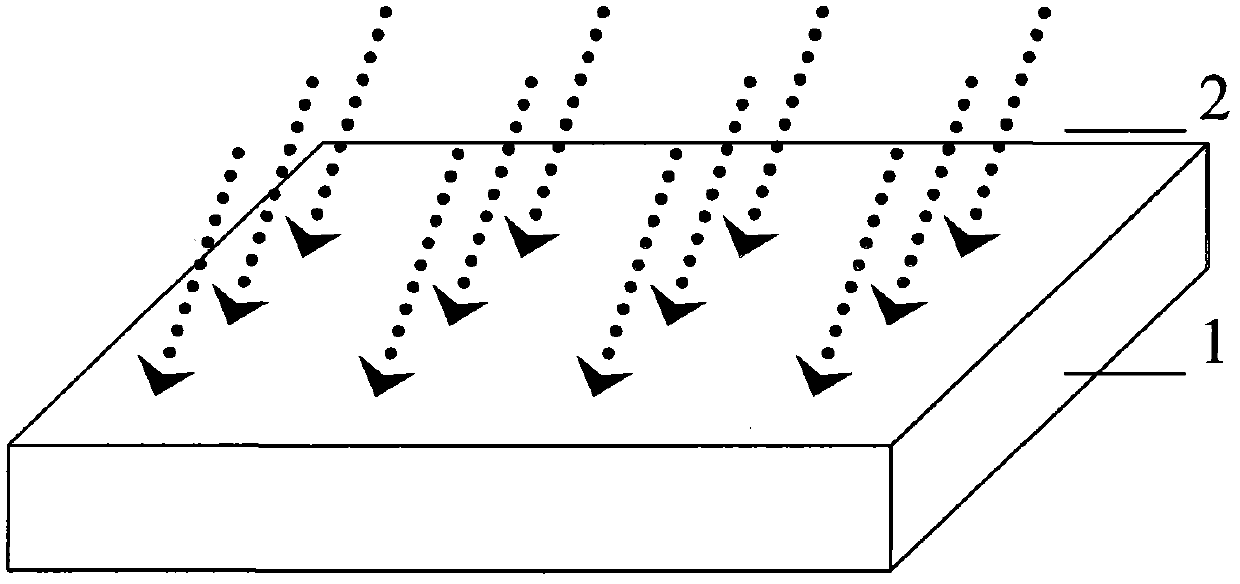
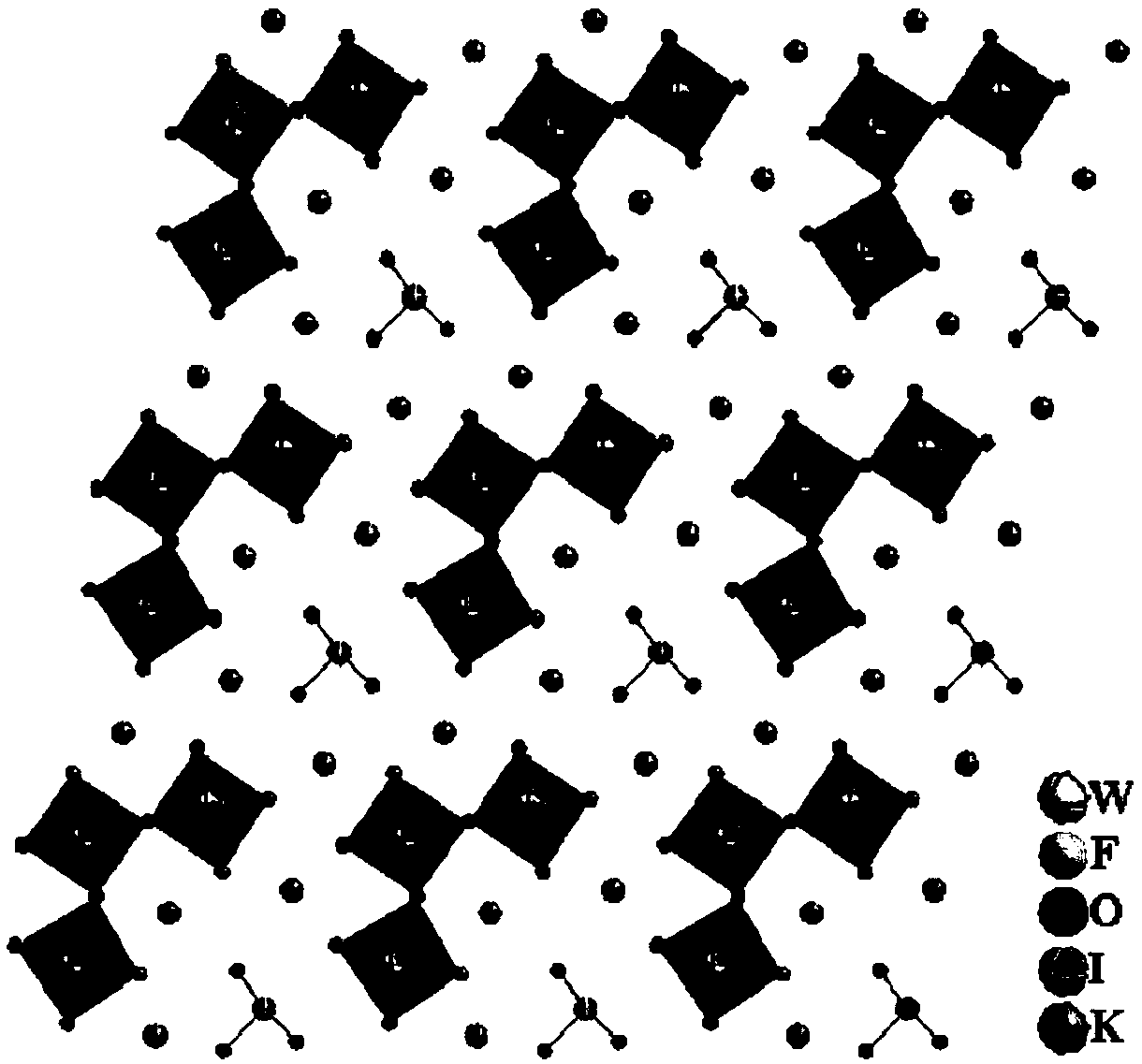
Method for preparing quasi three-dimensional photonic crystals on potassium titanyl oxygenic phosphate crystals
The invention discloses a method for preparing quasi three-dimensional photonic crystals on potassium titanyl oxygenic phosphate (KTP) crystals, which belongs to the technical field of optoelectronic device manufacturing. The preparation method comprises: firstly, cutting the KTP crystals to make a 10mm*10mm*2mm sample, and polishing the surfaces and two opposite end faces of the sample optically; placing the sample in an accelerator target room and performing ion implantation to form a planar optical waveguide; washing the sample with deionized water, ethanol and acetone, rotationally coating BP218 photoresist on the sample, exposing, developing and hardening film to form a photoresist strip mask; making a ridge waveguide by etching with an Ar ion beam; and plating a conductive film on the surface of the ridge waveguide, etching a submicron photonic crystal structure in a ridge waveguide area by using an FIB system, and obtaining the submicron quasi three-dimensional photonic crystals with high performance by regulating system parameter and working conditions. The method can realize the three-dimensional restraining of light beams and can be used for manufacturing photonic crystal filters, beam splitters, reflectors and other photoelectric devices.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Cascaded optical frequency converter based on monolithic phosphate crystal and application of cascaded optical frequency converter
The invention relates to a cascaded optical frequency converter based on a monolithic phosphate crystal and application of the cascaded optical frequency converter. The optical frequency converter comprises a first beam splitter, a phosphate crystal, a polarization conversion module, a second beam splitter and a third beam splitter which are arranged in the direction of an optical path. The cascaded optical frequency converter takes the phosphate crystal as a nonlinear optical medium, changes the polarization state of frequency doubled light through a quarter-wave plate, performs cascaded frequency converting between frequency doubling and frequency tripling through a turn-back light path, and realizes the direct output from near-infrared laser to ultraviolet laser in one crystal; the phosphate crystal has the advantages of low material cost, high easiness in growth, large size and good quality; as within a 1 micrometer wave band, the phase matching directions of class II frequency doubling and class II frequency tripling of the phosphate crystal are basically the same, the light conversion efficiency is high.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Multilayer, corrosion-resistant finish and method
ActiveUS20060008668A1Increase the effective surface areaDomestic articlesSpecial surfacesXylanPhosphate crystals
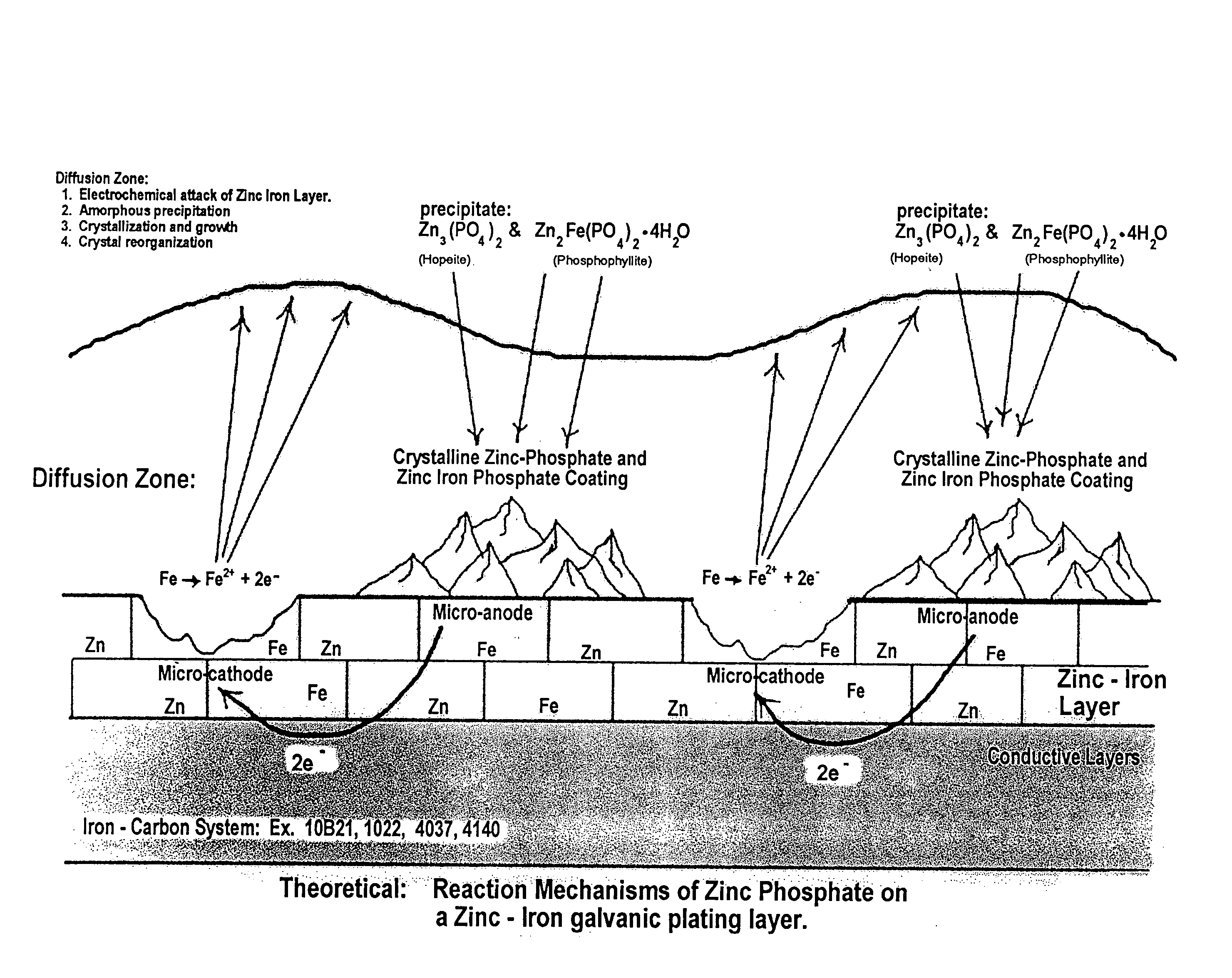
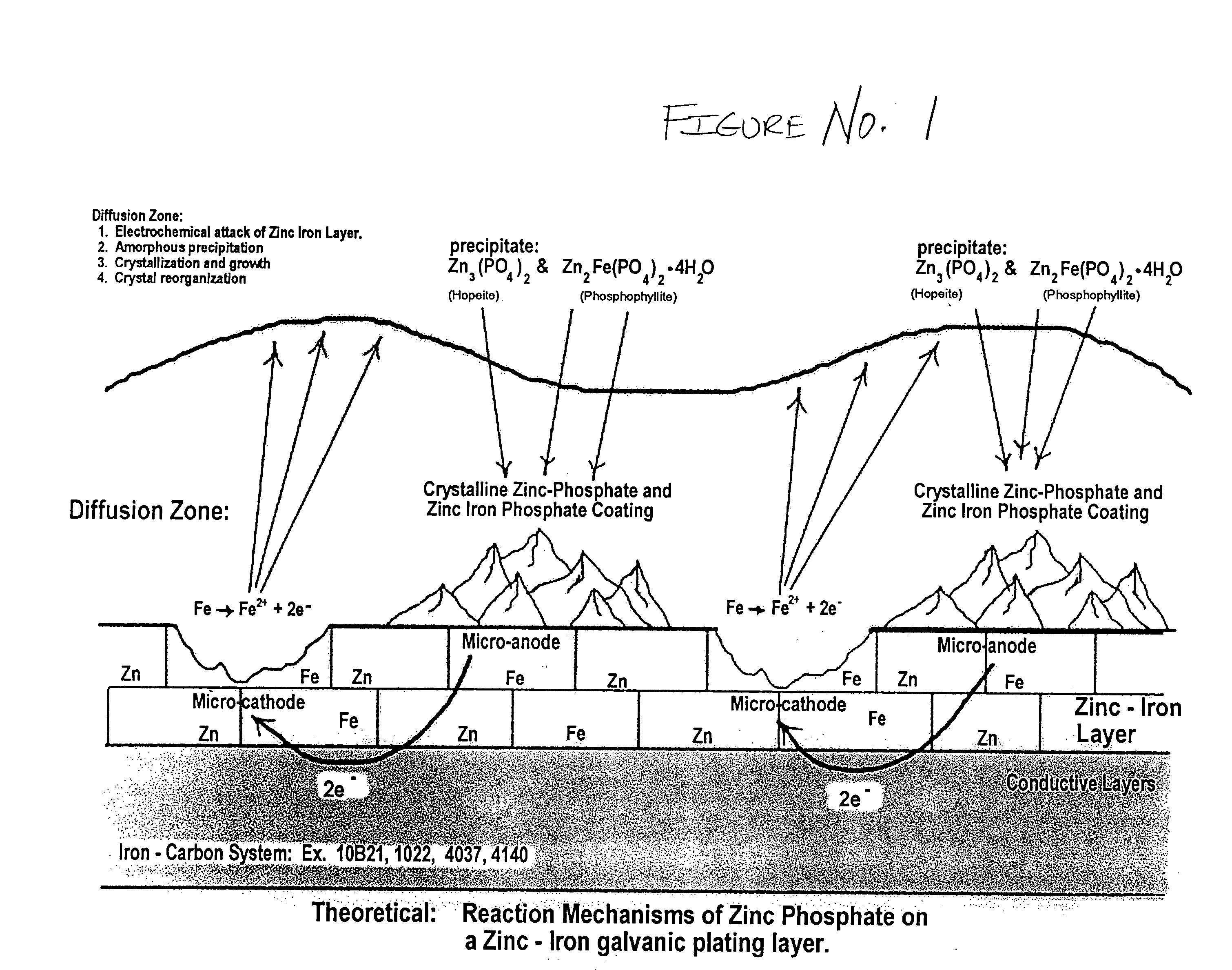
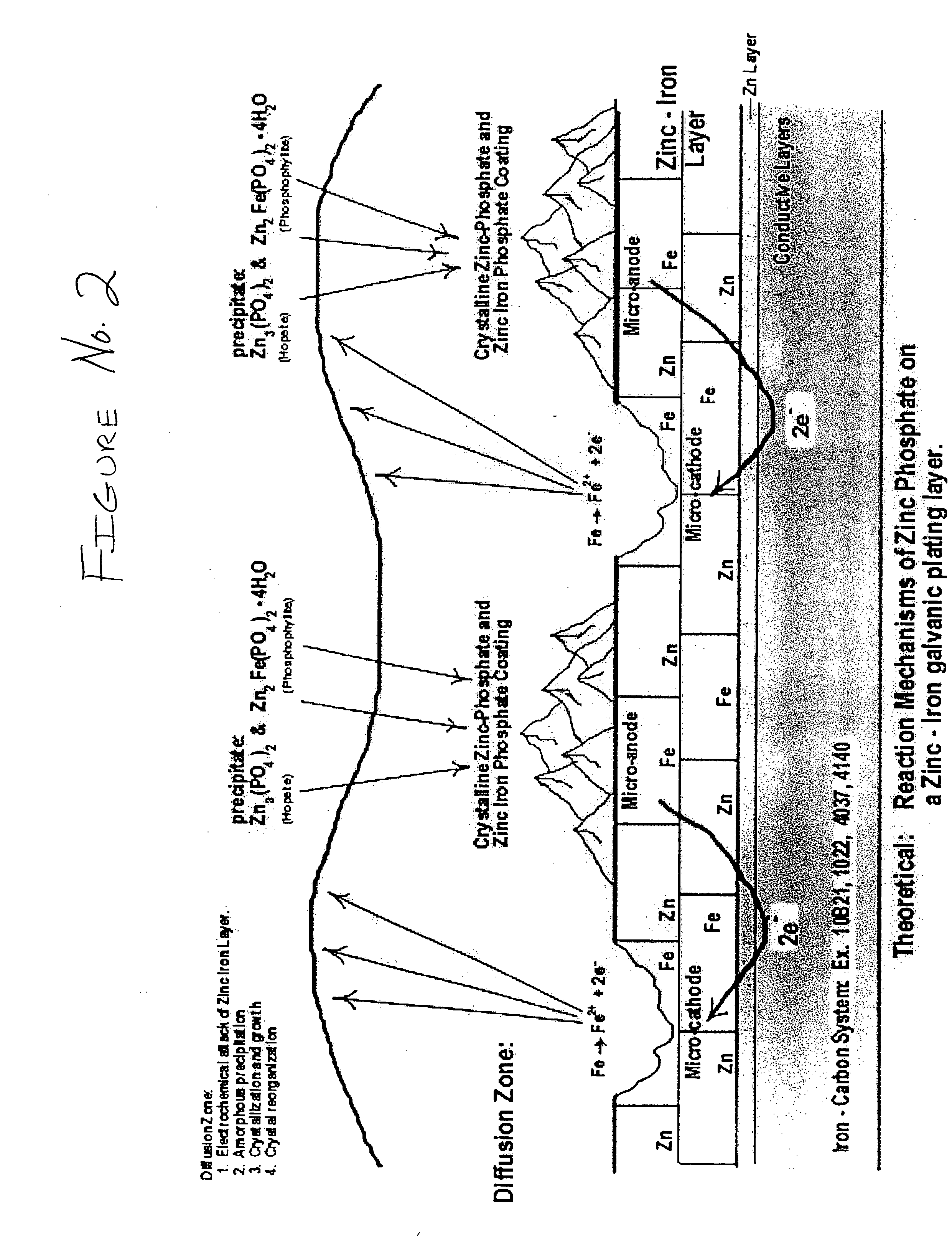
The present invention provides a black, chrome-free, multilayer corrosion protection finish designed to meet extended corrosion properties. This corrosion-resistant finish is engineered to meet a minimum of 500 salt spray testing hours to white corrosion, and 1500 salt spray testing hours to red corrosion when tested to ASTM B117 standards. It is also designed to comply with the European Union Directive on End of Life Vehicles. This multilayer system is designed for use on automotive body sheet steel, automotive underbody parts, automotive under-hood parts, and some automotive interior parts specifying a gloss requirement greater than 4. This chrome-free, multilayer finish is a combination of a zinc-iron electroplated substrate, a non-electrolytic phosphate crystal conversion layer using orthophosphoric acid, and a Xylan / Teflon fluorocarbon sealer coating to form a three layer total corrosion protection system.
Owner:THOMAE KURT J
Intermediate infrared optical doubling frequency crystal fluorinated tungsten potassium iodate material as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN109338471ALarge frequency doubling effectAchieve phase matchingPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsMonopotassium phosphateLaser damage
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removing method based on magnesite
ActiveCN104944561ASolve the costSolve the problem of impurity of precipitated productsWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationMagnesiteCalcination
The invention discloses a wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removing method based on magnesite, and belongs to the field of wastewater treatment. The wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removing method comprises the following steps: (1) crushing magnesite, sieving the magnesite powder, and carrying out high-temperature calcination, so as to obtain a calcined product; (2) adjusting the initial pH value of wastewater, adding the calcined product obtained in the step (1) into the adjusted wastewater, adjusting the molar ratio of the calcined product to ammonia nitrogen or phosphate in the wastewater added with the calcined product, and stirring for a preset time; (3) adding sodium dihydrogen phosphate or ammonia chloride into the mixed product, so as to obtain magnesium ammonium phosphate crystals. The wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removing method has the advantages that as the calcined product of magnesite is taken as a magnesium source, the adding method of ammoniomagnesium phosphate crystal medicament is replaced, the problem of relatively high medicament cost of the conventional ammoniomagnesium phosphate crystal method is solved, while the nitrogen and phosphorus removing efficiencies are improved; the recycled solid magnesium ammonium phosphate can be used for preparation of controlled-release fertilizers or cyclic utilization.
Owner:JINGDEZHEN CERAMIC INSTITUTE
Fluxing agent growth method for trigallium phosphate crystal
InactiveCN101104950AImprove optical qualityFast growthPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsFlux growthSeed crystal
The invention provides a flux growth of trigallium phosphate crystal. The method comprises weighing ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, gallium oxide, lithium carbonate and molybdenum oxide at the weight ratio of 1:2.44:(1.96-4.41):(11.45-25.77), mixing thoroughly, placing in a platinum crucible, heating for smelting in a growth furnace, cooling down to a temperature 10-20 DEG C above the saturation point of melt to obtain a mixed fusant composed of Ga3PO7 and flux, introducing a seed crystal into the growth furnace, feeding the seed crystal until the temperature drops to 1-2 DEG C above the saturation point and rotating at a speed of 30 r / min, cooling until the seed crystal begins to melt, taking out the crystals from the melt when the crystal growth stops, cooling down to 200 DEG C at a rate of 20-30 DEG C per hour, and naturally cooling down to room temperature to obtain centimeter-sized Ga3PO7 crystal. The invention has the advantages of simple equipment, rapid growth rate, easy operation, and yield of large-size Ga3PO7 with good optical quality.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Crystallization method of 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate
ActiveCN103265444AReduce usageHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationFiltrationIon exchange
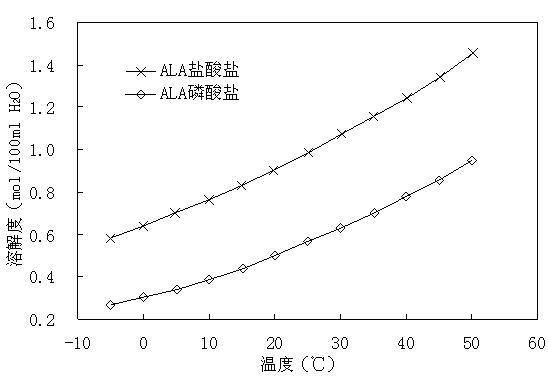
The invention relates to a crystallization method of 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate. The crystallization method comprises the following steps of carrying out ion-exchange of 5-aminolevulinate broth or other solutions containing 5-aminolevulinate to remove anions and a part of impurities, adding phosphoric acid into the treated solution according to a mole ratio of 1: 1 to 1.2: 1 to obtain a 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate solution, carrying out decoloring and filtration of the 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate solution, carrying out vacuum condensation of the 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate solution to obtain 400 to 600g / l of the concentrated solution, gradually cooling the concentrated solution at a cooling rate of 10 to 15 DEG C / h with stirring at a stirring rate of 50 to 200rpm until crystal nucleuses are produced in the concentrated solution, carrying out constant-temperature crystal growing for 1 to 2h, sequentially carrying out stirring cooling until a temperature is in a range of -5 to 0 DEG C, carrying out filtration separation of the crystals, and drying at a temperature of 50 to 70 DEG C to obtain the 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate crystals. The crystallization method does not adopt an organic solvent, avoids solvent residual and is conducive to use of 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate in the medicine field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of tylosin phosphate or tartrate crystal
InactiveCN103275155AAvoid pollutionReduce pollutionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationDispersityDissolution
The invention relates to a preparation method of tylosin phosphate or a tartrate crystal. The method comprises the steps that tylosin tartrate or phosphate powder is sufficiently dissolved in ethyl acetate; butyl acetate is slowly and dropwise added in a stirring state and at 0-5 DEG C, and is sufficiently mixed; the stirring state is kept for 1-2h after the adding is completed; centrifugal separation is performed; and the obtained crystal is subjected to drip washing by cold butyl acetate, and then subjected to vacuum drying until the drying loss is less than 1%. According to the preparation method, tylosin phosphate or tartrate is prepared into crystalline particles, and the crystalline particles replace powder; the specific gravity of the crystalline particles is greater, so that dust pollution is avoided in packaging and using processes; the particles are added to animal drinking water and can sink into the water bottom easily; the particles are better in dispersity, faster in dissolution rate and higher in content, can be directly added to animal feed or the animal drinking water; a solvent is very easy to recover; and the preparation method has a certain application prospect in a production process.
Owner:宁夏泰瑞制药股份有限公司
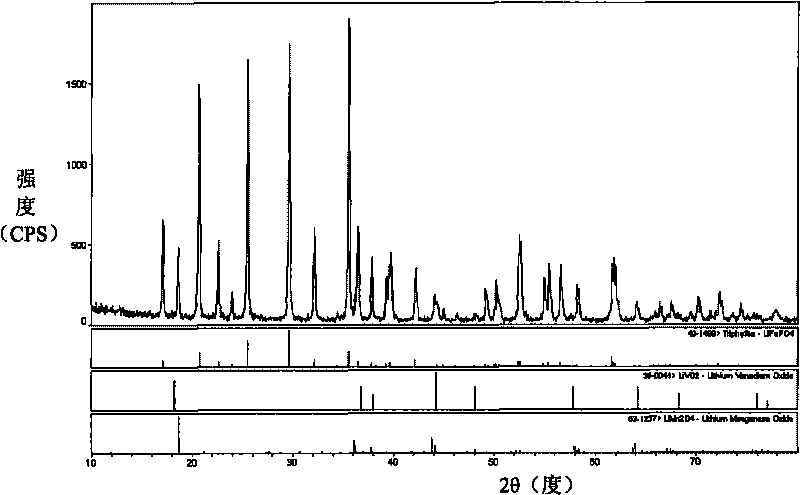
Method for preparing anode active substance, anode active substance, anode and battery
ActiveCN101734636AQuality improvementImprove cycle performanceFinal product manufactureCell electrodesLithiumPhosphate crystals
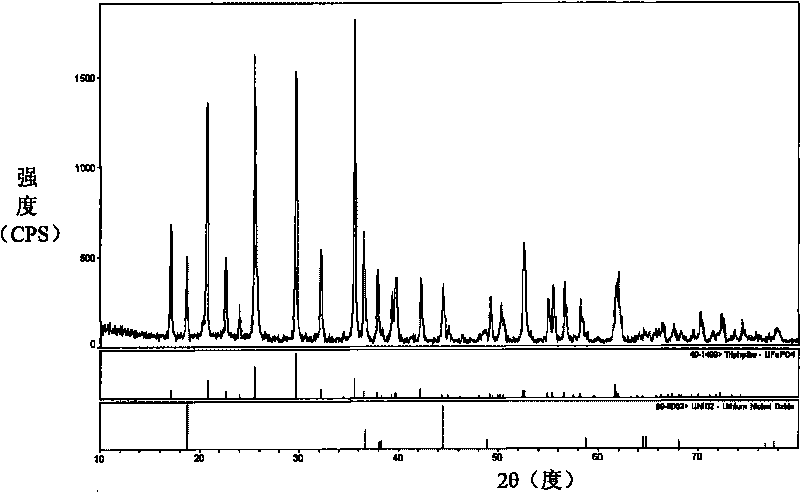
The invention provides a method for preparing an anode active substance, the anode active substance prepared by the method, an anode comprising the anode active substance and a battery comprising the anode. The method for preparing the anode active substance comprises the step of sintering a mixture which comprises a raw material 1 and a raw material 2; the raw material 1 comprises a lithium source, an iron source and a phosphorus source; and the raw material 2 is one or more of compounds represented by LiDcO2, LiiNi1-d-eCodMneO2, LiNi1-f-gCofAlgO2, LixNi1-yCoO2 and LimMn2-nEnOj, wherein D is one of B, Mg, Al, Ti, Cr, Fe, Cu, Zn, Ga, Y, La and V; c is more than 0 and less than or equal to 3, i is more than or equal to 0.9 and less than or equal to 1.2, d is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.5, e is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.3, f is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.5, g is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.3, x is more than or equal to 0.9 and less than or equal to 1.1, and y is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1; E is one of boron, magnesium, aluminum, gallium and transition metallic elements except Mn; m is more than or equal to 0.9 and less than or equal to 1.1, n is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1, and j is more than 1 and less than 6; and due to the sintering condition, the prepared anode active substance comprises a lithium ferrous phosphate crystal. The battery made of the anode active substance prepared by the method provided by the invention has good specific capacity of quality and good cycle performance.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method for preparing potassium titanium oxide phosphate crystal by liquid phase coprecipitation sythesis of growth material
InactiveCN101469449AWell mixedQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsIce waterPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing KTP crystals by synthesizing a growth material through liquid phase coprecipitation, which comprises the following steps: 1) a TiCl4 solution is added into a clear solution consisting of KH2PO4, K2CO3 and deionized water in an ice-water bath to form a milky coprecipitation compound, the mol ratio of TiCl4 to KH2PO4 to K2CO3 is 0.1-0.303: 0.86-1.36: 0.125-0.31, and the milky coprecipitation compound is dried, ground into powder, and placed into a platinum crucible to be sintered to obtain a sintered body; and 2) the sintered body obtained in step 1) is melted at the temperature of 1,000 DEG C, keeps the constant temperature, and is cooled to be between 10 and 20 DEG C above a saturation temperature to obtain a melt, and seed crystals enter the melt for remelting and then are subjected to crystal growth to obtain the KTP crystals. The method adopts a liquid phase to synthesize a growth raw material of the KTP crystals and then performs the sintering, and the obtained crystals have good optical homogeneity and no crystal defects such as scattering particles and so on.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
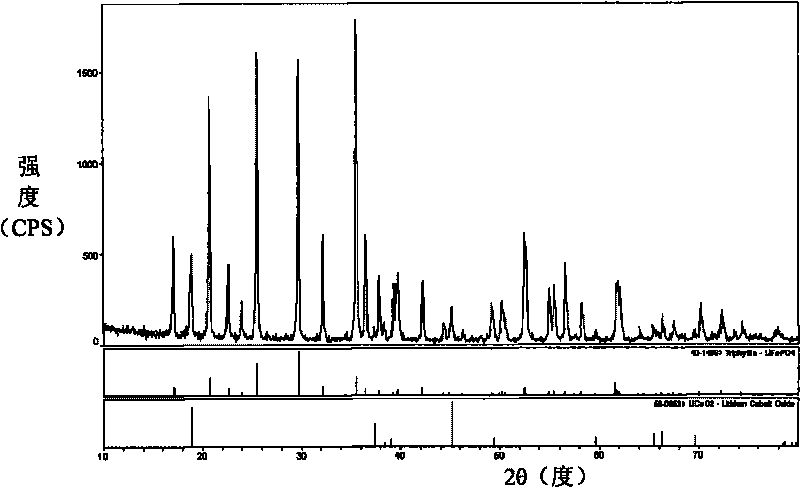
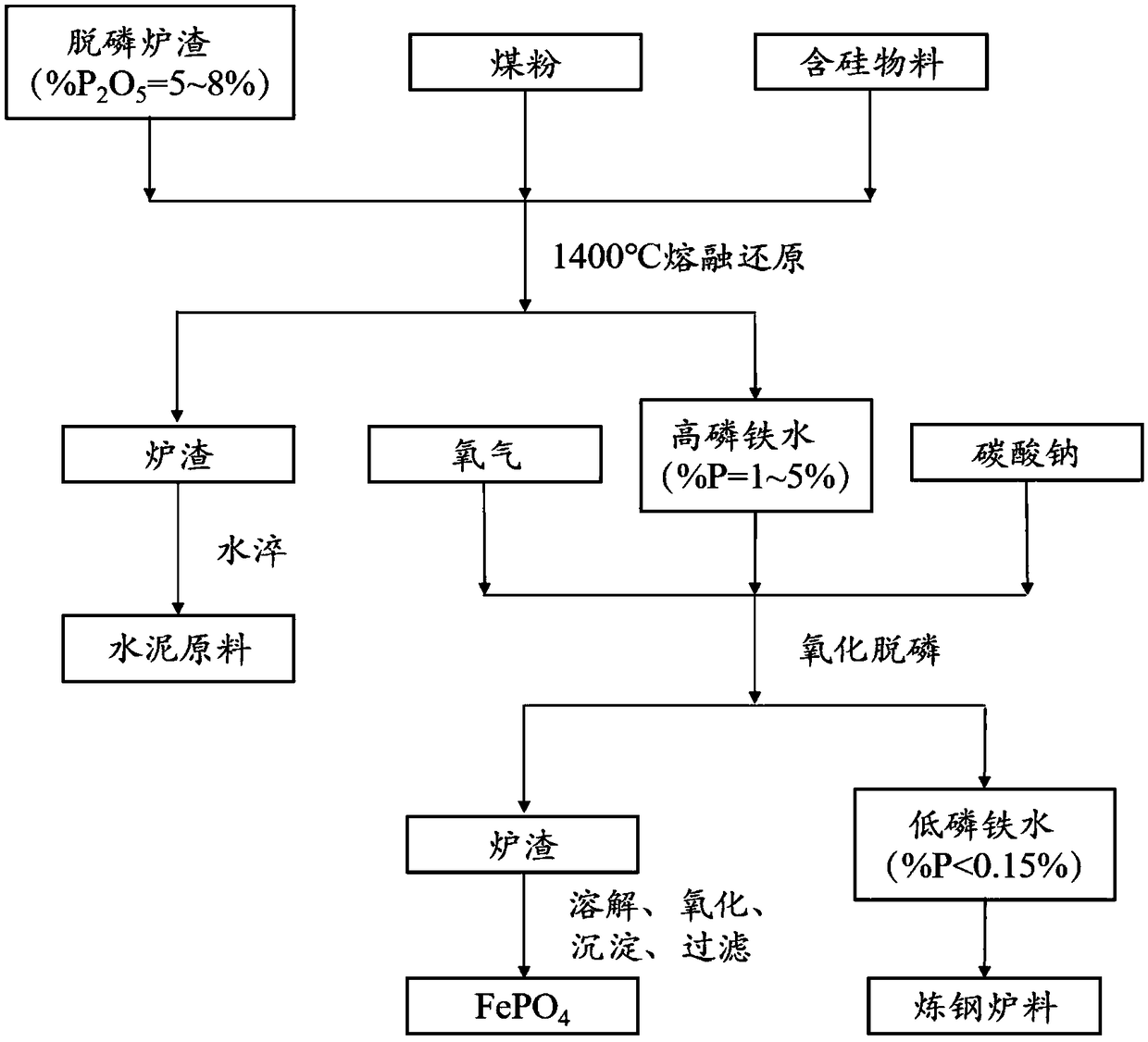
Method for producing ferric phosphate by dephosphorized converter slag
The invention discloses a method for producing ferric phosphate by dephosphorized converter slag and belongs to the field of metallic materials, particularly relates to a process of producing ferric phosphate by multiple steps of extracting iron and phosphorus by reduction reaction, dephosphorizing to produce slag, dissolving phosphorus-rich slag and purifying and finally precipitating, washing and drying. The method includes subjecting dephosphorized converter slag to basicity regulation and carbon-burdened reduction to obtain high-phosphorus molten iron (%P=1-5%), jetting Na2Co3 into the high-phosphorus molten iron to dephosphorize and produce slag to obtain qualified molten iron (%P<0.15%) and phosphorus-rich slag (%P2O5>20%), returning the qualified molten iron to an iron producing process, while dissolving the phosphorus-rich slag to obtain solution containing rich Na<+>, Fe<3+> and PO4<3->, purifying the solution and then regulating the pH value to obtain ferric phosphate, precipitating, washing and drying the ferric phosphate to obtain the ferric phosphate crystal product. The method has the advantages of low energy consumption, high utilization rate of resources, high additional value of products, low production cost, remarkable economic benefit and the like, and solves the problems about utilization of the dephosphorized converter slag and periodic enrichment of phosphorus for iron and steel enterprises.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Phosphate preparation device with high drying strength
InactiveCN106839665AVibrateIncrease swingDrying gas arrangementsDrying machines with local agitationPhosphate crystalsAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a phosphate preparation device with high drying strength, which comprises a drying box, a hot air blower is installed at the inner bottom of the drying box, a fixed column is horizontally installed above the hot air blower, and a plurality of ovens are connected below the fixed column. Dry bag, the drying bag is located between the hot air blower and the fixed column, the wind direction of the hot air blower faces the drying bag, one end of the fixed column is connected to the first telescopic rod, the other end of the fixed post is connected to the second telescopic rod, and the first telescopic rod , The lower ends of the second telescopic rods are all fixed on the bottom of the drying box, and an exhaust fan is installed on the drying box above the fixed column, and the air outlet of the exhaust fan is located directly above the fixed column. In the present invention, the potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals are dispersed by causing the potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals to collide with each other, and then the drying strength of the potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals is increased by means of air flow heat transfer, so that the potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals are dried More uniform, and finally obtain potassium dihydrogen phosphate whose quality meets the production requirements.
Owner:SICHUAN BESTLUCK CHEM
Recycling method of phosphorus in phosphorus containing waste
The invention belongs to the technical field of lithium battery recycling, and relates to a recycling method of phosphorus in phosphorus containing waste. The invention solves the technical problems of low treatment efficiency and the like of the phosphorus containing waste in the prior art. The invention discloses the recycling method of the phosphorus containing waste which comprises the following steps of step 1, enabling the phosphorus containing waste to react with alkaline substance (or an alkaline solution) to produce an indissolvable solid and soluble phosphate; step 2, performing solid-liquid separation (or directly performing solid-liquid separation) on the reaction products obtained in step 1 after performing water-leaching on the reaction products to obtain a phosphorus-rich solution and solid slag; step 3, performing crystallization or precipitation on the phosphorus-rich solution obtained in step 2 to obtain phosphate crystal or phosphate precipitation. The process of theinvention is simple, the recycling rate is high, the cost is low, the diversification and high purity of the products are realized, and thereby considerable economic value of the recycling of the phosphorus containing waste is achieved.
Owner:柯芬
Preparation method of self-activation laser crystal phosphoric acid trisneodymium
InactiveCN102912435AHigh active ion concentrationRealize laser operationPolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsSpace groupPhosphate crystals
The invention relates to a preparation method of self-activation laser crystal phosphoric acid trisneodymium. Neodymium oxide and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate serve as raw materials, lithium carbonate-tungsten oxide serves as a fluxing agent, solute concentration is controlled to be 20-50wt%, a fluxing agent growth method is used for preparing, obtained neodymium phosphate crystals are monoclinic systems, and a space group is Cm. Prepared phosphoric acid trisneodymium crystals can serve as a laser operation material and be used for producing 1060nm and 1339nm laser output and be used for fields, such as medical treatment, scientific research and military affairs.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Cetagliptin salt crystal form and amorphism and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108383845AImprove solubilityHigh crystallinityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderP phosphateHypoglycemia
The invention relates to a salt of a compound in a formula (I) as shown in the specification. The salt is crystal or amorphous phosphate or crystal or amorphous oxalate. By salification screening andresearching on the compound in the formula (I), a novel salt form suitable for medicine development is discovered, and medicine solubility is improved. Especially, a phosphate crystal form B is high in crystallinity and stability, low in hygroscopicity, great in oral bioavailability, high in tolerance in long-term administration, less prone to causing hypoglycemia and great in serum DPPIV inhibition effect, and accordingly better options are provided for medicine subsequent development.
Owner:CGENETECH (SUZHOU CHINA) CO LTD
Dual-wavelength mould laser welding machine
InactiveCN103212811AGood welding effectImprove welding effectLaser detailsLaser beam welding apparatusPhosphate crystalsEngineering
The invention relates to a dual-wavelength mould laser welding machine, which comprises a main machine box, a laser generator, a laser welding arm and a wavelength switching module, wherein the main machine box, the laser generator and the laser welding arm are arranged on a main machine frame, the interior of the main machine box is provided with a main machine, the tail end of the laser welding arm is provided with a welding head provided with the laser generator, the laser generator comprises a laser resonance cavity, the wavelength switching module comprises a frequency-doubling crystal inserting device, the frequency-doubling crystal inserting device is arranged in the laser resonance cavity and is used for inserting a frequency-doubling crystal into the laser resonance cavity, and the frequency-doubling crystal is a potassium titanium oxide phosphate crystal. The wavelength switching module can generate a 532NM laser, and the 532NM laser together with a 1064NM laser can be acted on the surface of the welded workpiece. Particularly for the high-reflecting material of which the original single wavelength laser is difficultly processed, the dual-wavelength common processing method is adopted, so the good welding effect is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN TONGFA LASER EQUIP
Red and green laser based on laser crystal, frequency doubling crystal and self-frequency-doubling crystal
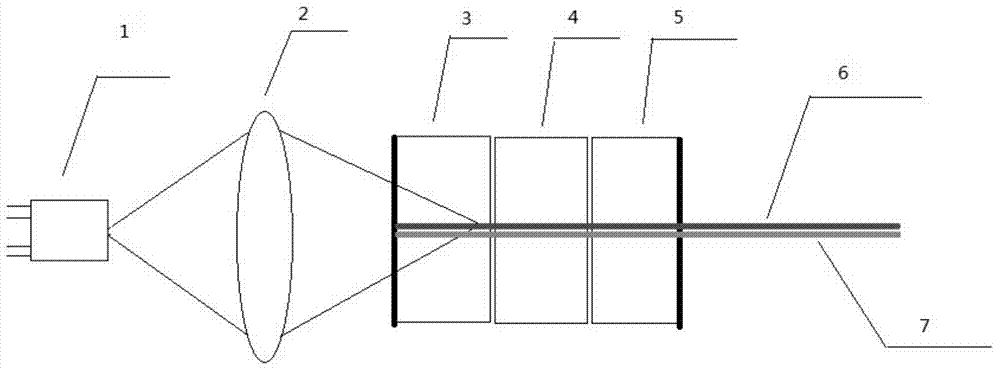
ActiveCN103762491ACompact structureImprove stabilityActive medium materialPhosphate crystalsGadolinium
The invention relates to a red and green laser based on a laser crystal, a frequency doubling crystal and a self-frequency-doubling crystal. The red and green laser comprises a dual-wavelength pumping source, a focusing lens, the laser crystal, the frequency doubling crystal and the self-frequency-doubling crystal, wherein the dual-wavelength pumping source, the focusing lens, the laser crystal, the frequency doubling crystal and the self-frequency-doubling crystal are sequentially arranged along an optical path. The light transmitting surface of the laser crystal, the light transmitting surface of the frequency doubling crystal and the light transmitting surface of the self-frequency-doubling crystal are plated with dielectric films, and the laser crystal, the frequency doubling crystal and the self-frequency-doubling crystal are sequentially combined together through the light transmitting surfaces. The laser crystal is a neodymium-doped yttrium vanadate crystal. The frequency doubling crystal is a potassium titanyl oxygenic phosphate crystal. The self-frequency-doubling crystal is a neodymium-doped yttrium calcium oxyborate crystal or a neodymium-doped gadolinium calcium oxyborate crystal, the self-frequency-doubling crystal is cut in the light transmitting direction, and the cutting direction is a self-frequency-doubling direction where 530 nm or 545 nm laser light is generated. The red and green laser is formed by gluing the dual-wavelength pumping source, the laser crystal, the frequency doubling crystal and the self-frequency-doubling crystal and is compact in structure and good in stability; in the optical path, red laser light and green laser light are output respectively and do not interfere with each other, and switching is convenient.
Owner:青岛镭视光电科技有限公司 +1
Anode material with lithium ferrous phosphate being embedded in stereoscopic reticular electric conductor and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an anode material with lithium ferrous phosphate being embedded in a stereoscopic reticular electric conductor and a preparation method thereof. The anode material is a stereoscopic reticular conducting polyporous spherical particle, and the stereoscopic reticular conducting polyporous spherical particle is formed by embedding a nano lithium ferrous phosphate crystal particle in the electric conductor with a stereoscopic reticular structure. The preparation method of the anode material comprises the following steps: (1), mixing, grinding and dispersing a lithium source compound, a phosphorus source compound, an iron source compound and a conducting raw material to form a homogeneous solution or an emulsion; (2) granulating the homogeneous solution or the emulsion to prepare a spherical precursor including a nano particle; and (3) carrying out high-temperature pyrolysis on the spherical precursor in an inert atmosphere and / or a reducing atmosphere to form a stereoscopic reticular electric conductor skeleton, and then carrying out high-temperature crystallization to form the anode material with the nano lithium ferrous phosphate being embedded in a stereoscopic reticular electric conductor structure. The anode material provided by the invention has the characteristics of high charging / discharging specific capacity, long cycle life, stable preparation batch, excellent processing performance, good conductivity and safety, and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU LITHITECH CO LTD
Method for producing water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate by using extraction wet-process phosphoric acid
ActiveCN108383097ALess impuritiesRaw materials are cheap and easy to getAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersSolubilityWater insoluble
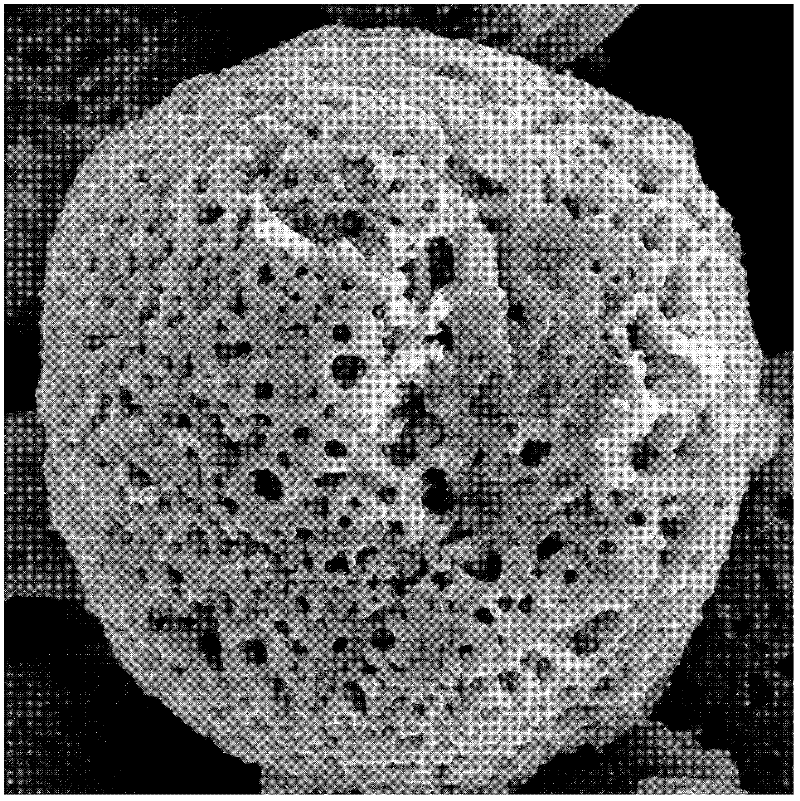
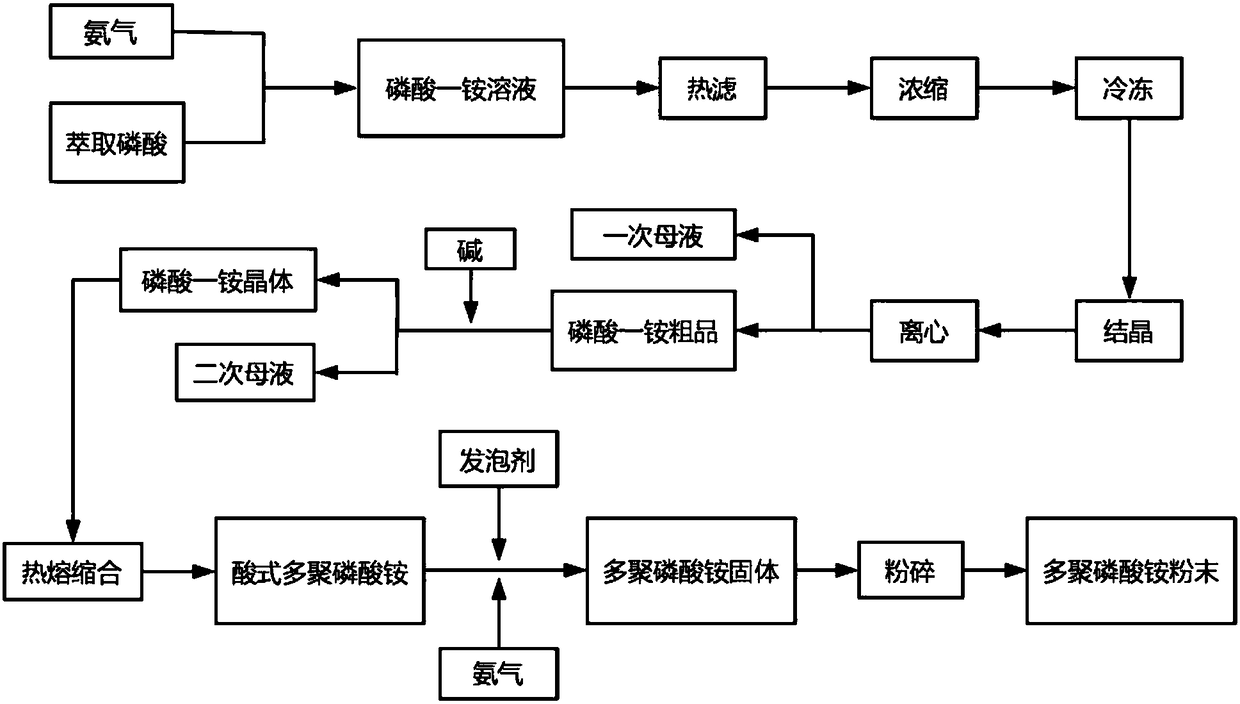
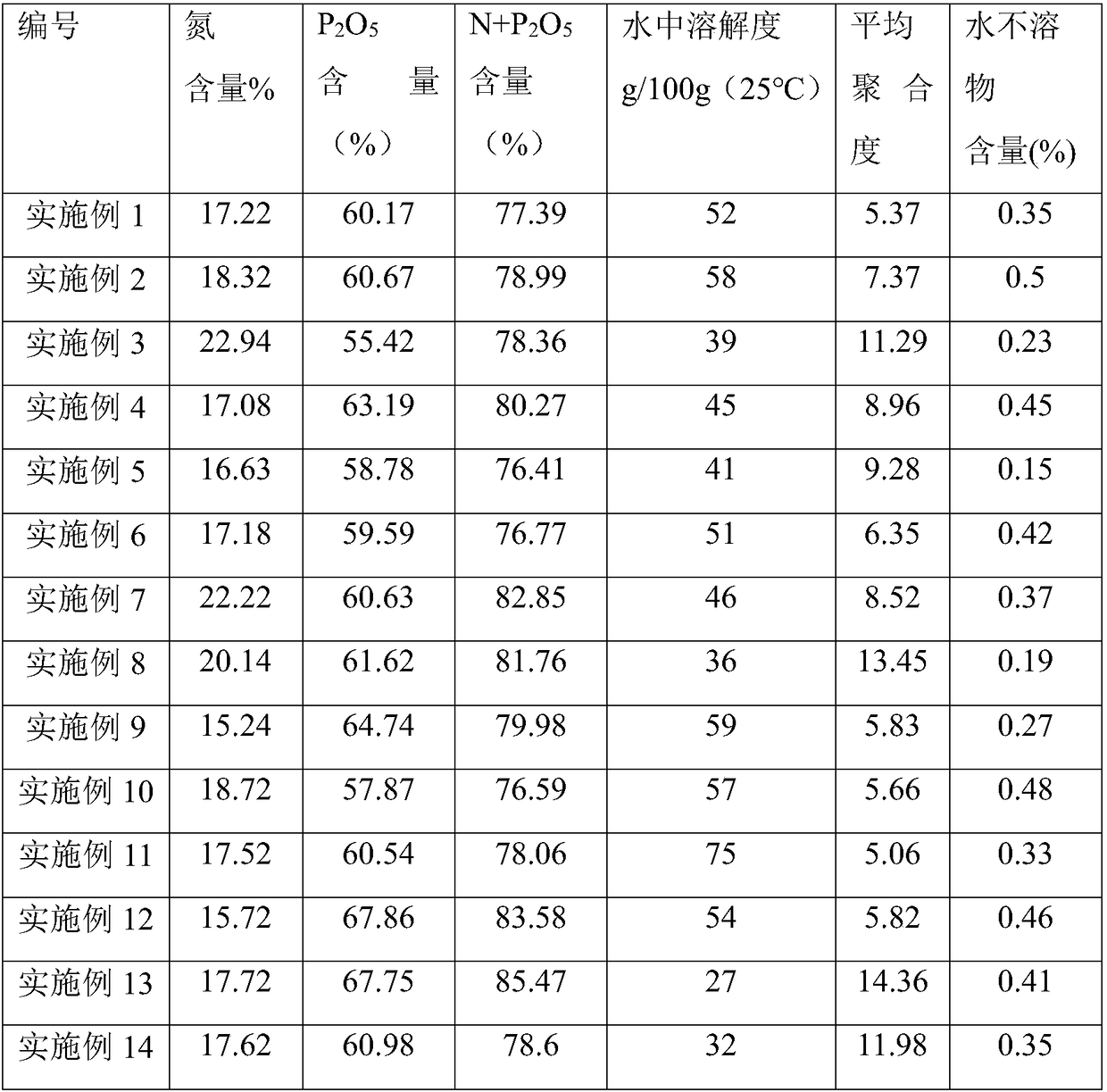
The invention discloses a method for producing water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate by using extraction wet-process phosphoric acid. The method comprises the steps that ammonia gas is continuously introduced into an extraction wet-process phosphoric acid reactor and reacts at the temperature of 80-110 DEG C to generate monoammonium phosphate, and heat filtration and concentration, freeze crystallization, centrifugal separation and washing with alkali liquor to obtain monoammonium phosphate crystals; then monoammonium phosphate is continuously added into a fixed bed reactor and melted and condensed into acid type ammonium polyphosphate at the temperature of 200-350 DEG C; finally, under the conditions that the temperature of an atomizing reactor is 150-250 DEG C and the ammonia gas partialpressure is 0.1-3 MPa, a mixture of the acid type ammonium polyphosphate melt and a foaming agent is continuously sprayed into the reactor for neutralization, and white water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate is generated. The nitrogen content of the ammonium polyphosphate product is 15-25%, the phosphorus pentoxide content is 50-65%, the content of N+P2O5 is larger than 76%, the solubility (25 DEG C) in H2O is in 25-75%, the average polymerization degree is 5-15, and the content of water-insoluble substances is less than 0.5%. The production process is low in cost, easy to operate and especiallysuitable for industrial production.
Owner:佳瑞科(武汉)国际贸易有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com