Cascaded optical frequency converter based on monolithic phosphate crystal and application of cascaded optical frequency converter
A phosphate crystal and frequency converter technology, applied in the field of laser and nonlinear optics, can solve the problems of inconvenience and low efficiency, and achieve the effects of improved conversion efficiency, low raw material cost, and easy growth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
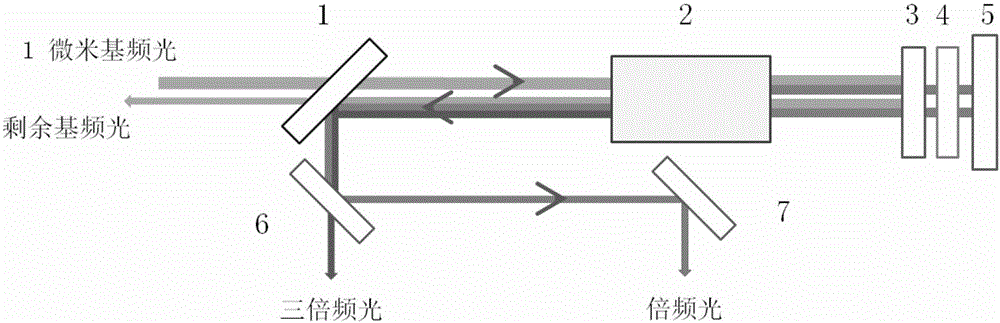
[0057] Such as Figure 1-3 shown.
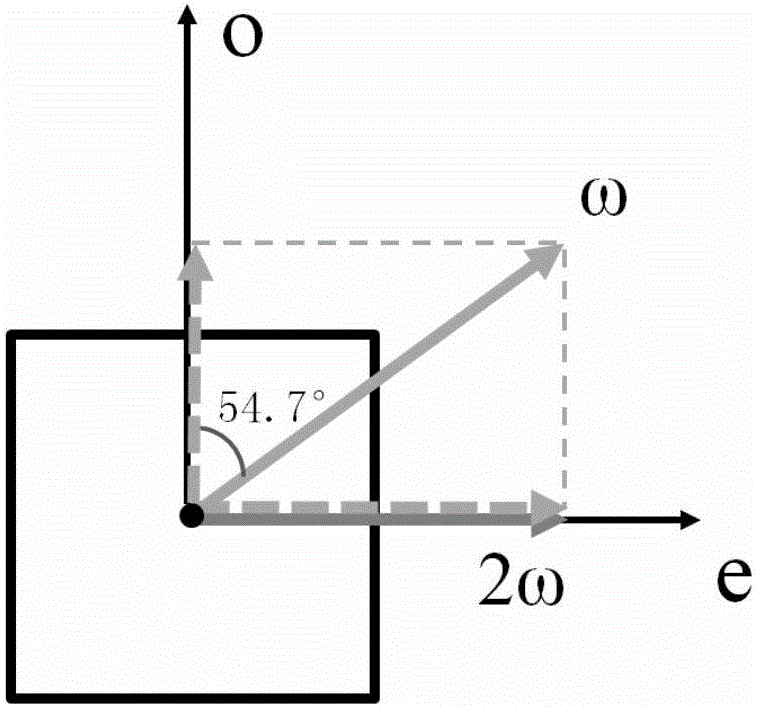
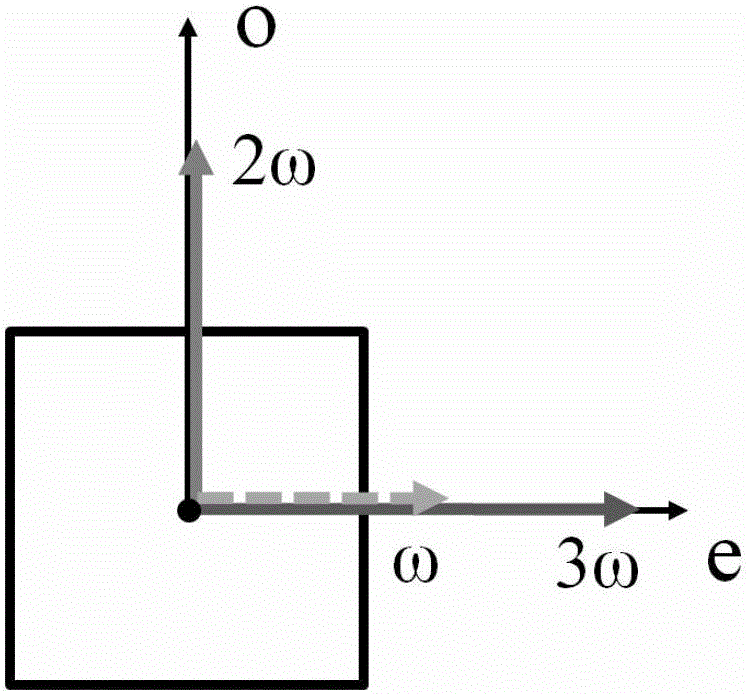
[0058] A cascaded optical frequency converter of 1064nm nanosecond laser based on a single phosphate crystal, including a first beam splitter, a phosphate crystal, a polarization conversion module, a second beam splitter and a third beam splitter arranged along the direction of the optical path mirror. The phosphate crystal is a KDP crystal; the polarization conversion module includes a first reflection mirror, a quarter-wave plate and a second reflection mirror arranged along the direction of the optical path. The second mirror is coated with a dielectric film with high reflection to 532nm laser. Phosphate crystals are cut along the direction of Class II frequency doubling phase matching; the direction of Class II frequency doubling phase matching is θ=58.9°, φ=0°; the angle of Class II triple frequency phase matching is θ=58.4°, φ=0 °; The transparent surface of the phosphate crystal is coated with a dielectric film for anti-reflection ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The cascaded optical frequency converter based on a single phosphate crystal as described in Example 1 is different in that the phosphate crystal is an ADP crystal; the phase-matching direction of the class II frequency multiplication is θ=61.6°, φ=0° ; Class II triple frequency phase matching angle is θ=60.0°, φ=0°.
[0062] ADP crystals are grown by an aqueous solution method, and large-size single crystals with high optical quality can be obtained by traditional cooling methods or rapid cooling methods. The raw material is cheap, the growth cost is low, and the crystal growth process, orientation, cutting, polishing, coating and other processes are relatively mature.
Embodiment 3
[0064] The cascaded optical converter based on a monolithic phosphate crystal as described in Example 1 is different in that the angle between the direction of the optical axis of the quarter-wave plate and the bisector of the angles of the o-light and e-light angles of the phosphate crystal is 0°. The frequency-doubled light passes through the quarter-wave plate twice, which is equivalent to passing through a half-wave plate. The linear polarization direction is rotated by 90°, and the polarization state of the relative frequency conversion crystal is changed from e light to o light, which meets the type II sum frequency phase matching condition . The quarter-wave plate is a 532nm quarter-wave plate made of quartz, and the transparent surface is coated with a dielectric film for anti-reflection of 532nm laser. The first mirror is coated with a dielectric film with high reflection to 1064nm laser and high transparency to 532nm laser.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Center wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com