Method for evaluating heavy metal reproductive toxicity resistance effect of traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharide extract
A technology for polysaccharide extraction and reproductive toxicity, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, pharmaceutical formulations, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of low reproductive protection effect, achieve short test period, low cost, and simple evaluation method Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] The cultivation and exposure of nematodes were carried out as follows:
[0086]In this embodiment case, the cultivation of nematodes can be a method well known to those skilled in the art, and the present invention is preferably: the wild-type strain Caenorhabditis elegans (N2) is grown with nematodes containing Escherichia coli (E.coli OP50) bacterium The culture medium (NGM) was cultured, and the temperature was set at 20°C. In order to obtain nematodes with approximately the same growth stage, lyse the nematodes with fertilized eggs with nematode lysis solution (containing 0.5M NaOH and 20% NaClO) to obtain the eggs in the body, and incubate the eggs in the buffer solution at 20°C for 16-24h , to obtain the L1 stage nematodes required for the experiment. In order to simulate the conservation effect of kudzu root as a food-based health product, L1 stage nematodes were exposed to a buffer solution containing 0 mg / L-200 mg / L PPS, and Escherichia coli was added as food ...
Embodiment 2
[0088] The method for measuring the number of offspring of nematodes in this implementation case: transfer the L4 nematodes to an agar plate with food to allow them to grow normally, and place one nematode per plate. The next day, count the offspring of nematodes under a microscope, including unhatched eggs and hatched larvae, and the parental adults are then transferred to fresh food plates. Repeat the operation of transferring plates and counting the number of offspring until the nematodes no longer produce offspring. 15 nematodes per group.
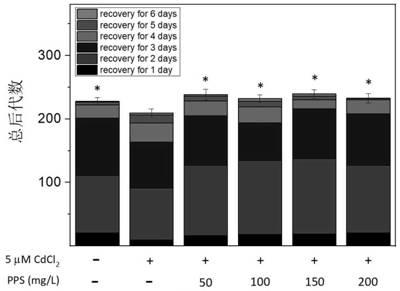
[0089] Attached from the manual figure 1 It can be seen from the results in that there is a significant difference between the total offspring number of Pueraria polysaccharides (50-200mg / L) and cadmium co-exposure group and the total offspring number of the control group (the symbol * represents a significant difference compared with the control group, P<0.05), the total progeny number of nematodes does not belong to the open interv...
Embodiment 3
[0091] The method for measuring the number of eggs conceived by nematodes in this example: pick a single nematode and place it in the droplet of lysate, after a few minutes the parent body of the nematode is lysed, leaving only undischarged eggs on the plate. The number of fecundated eggs of each nematode in each group was photographed and recorded, and 15 nematodes were tested in each group.
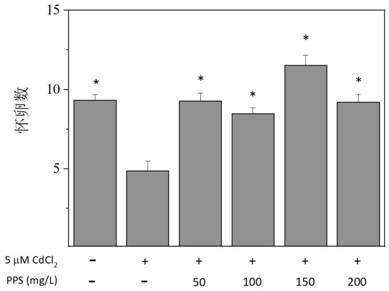
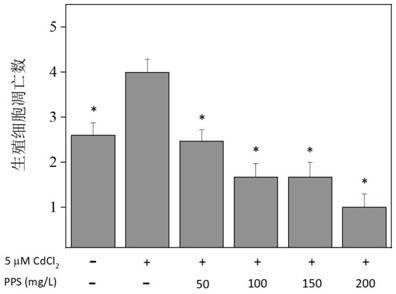
[0092] Attached from the manual figure 2 As can be seen from the results in the figure, there is a significant difference between the number of fertilized eggs in the pueraria polysaccharide (150mg / L) and cadmium co-exposure group and the control group (the symbol * represents a significant difference compared with the control group, P< 0.05), the number of fertile eggs of nematodes does not belong to the open interval formed by the number of fertile eggs of the blank group and the control group, and the total number of offspring is closer to the index value of the blank group. The re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com