Method for stepwise detecting Cr(VI) and Cr(III) based on fluorescent carbon quantum dots
A carbon quantum dot, stepped technology, applied in the field of stepped detection of Cr and Cr based on fluorescent carbon quantum dots, can solve the problems of difficulty in rapid detection and daily detection, expensive instruments and equipment, and cumbersome detection process, and achieve excellent photoresistance. The effect of luminescence performance, simple method and wide detection range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: Preparation of fluorescent carbon quantum dots
[0038] (1) Dissolve 100 mg of ammonium citrate and 200 mg of bis-linked pinacol-based diborane (BPDB) in 5 mL of ultrapure water, mix well, and transfer to a PPL-lined hydrothermal autoclave , heated to 240°C, and kept for 10 h. After cooling to room temperature, a solution a containing pyrolysis products was obtained.
[0039] (2) The solution a obtained in step (1) was centrifuged at 8500 rpm for 10 min, and the sediment was discarded to obtain the supernatant. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to obtain a transparent light yellow solution, which emitted blue fluorescence under a 365 nm ultraviolet light, which was the stock solution of the CDs solution, and was stored at 4°C for later use.
[0040] (3) Dilute the stock solution of CDs solution with ultrapure water to a final concentration of 10 mg / L for later use.
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Construction of a fluorescence detection system
[0046] (1) At room temperature, mix 100 µL of the CDs solution prepared in Example 1 with 900 µL of ultrapure water to obtain a mixed system, and the concentration of the CDs solution in the mixed system is 10 mg / L.
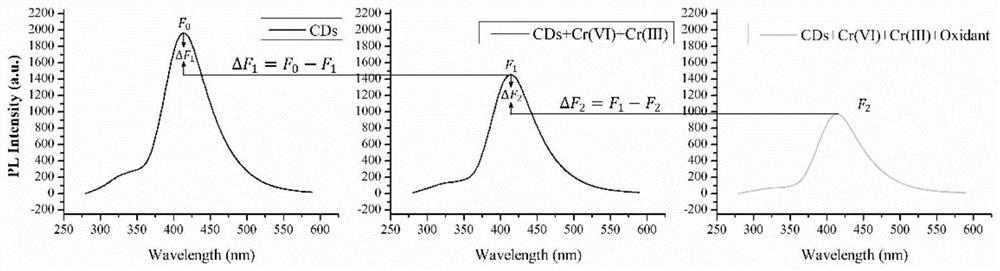
[0047] After the mixed system was left to stand for 10-30 min, the fluorescence peak intensity of the solution was detected by a fluorescence spectrophotometer at an excitation wavelength of 335 nm, recorded as .
[0048] (2) Prepare 10 mg / L Cr(Ⅵ) standard stock solution and 10 mg / L Cr(Ⅲ) standard stock solution, then mix the standard stock solution with ultrapure water to prepare different concentrations of Cr(Ⅵ) and Cr( Ⅲ) mixed solution, set aside.
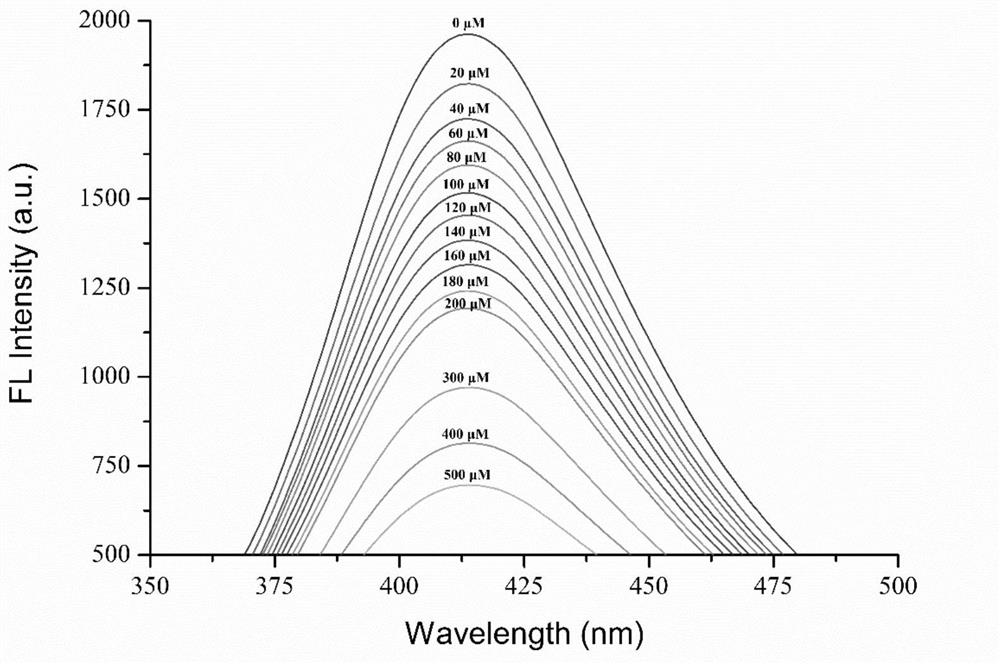
[0049] (3) Mix 100 µL of CDs solution with 800 µL of different concentrations of Cr(Ⅵ) and Cr(Ⅲ) mixtures and 100 µL of ultrapure water to obtain a mixed system. The concentration of CDs solution in the mixed system was 10 mg / L, and the final ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: Stepwise detection of Cr(Ⅵ) and Cr(Ⅲ) content and verification
[0060] Add a mixed solution of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) to the ultrapure water sample, so that the final concentrations of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) are both 100 μM, and use the fluorescence detection system established in Example 2 to detect Test samples and calculate the content of Cr(Ⅵ) and Cr(Ⅲ).
[0061] The calculated Cr(Ⅵ) and Cr(Ⅲ) contents were 104.2±5.1 μM and 98.7±6.5 μM, respectively, and the test results proved that the established method above could be used for the detection of Cr(Ⅵ) and Cr(Ⅲ) in ultrapure water. ) for step detection.
[0062] According to the 3σ / k principle (where σ represents the standard deviation obtained from 11 repeated detections of the blank solution, and k represents the slope of the standard curve), the detection limit (LOD) of this fluorescence detection system is 0.24 μM, which is much lower than that of other hexavalent Chromium detection method.
[0063] In thi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com