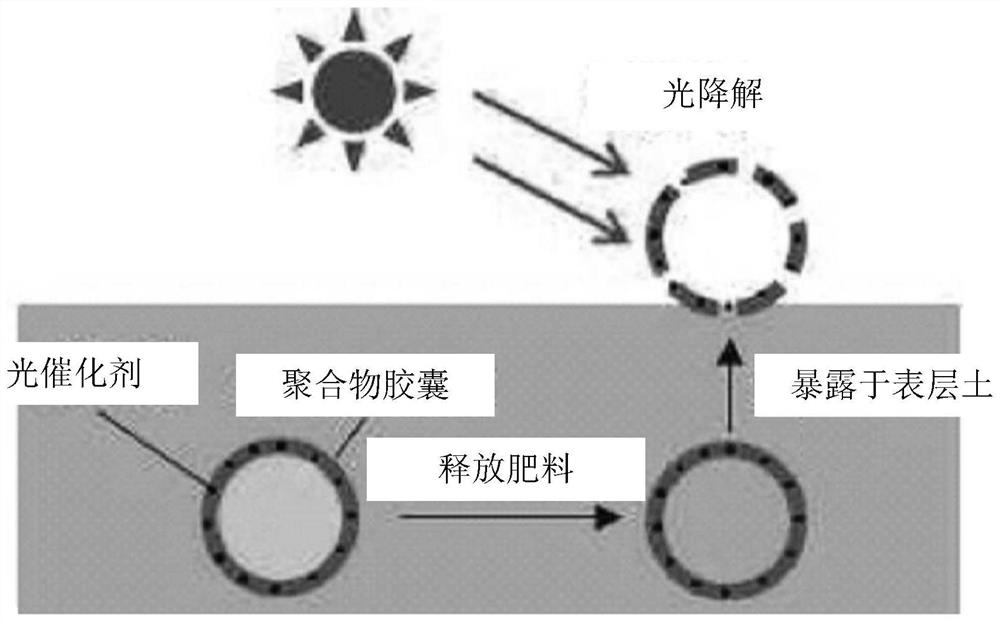
Controlled-release fertilizer
A technology for controlled-release fertilizers and fertilizers, applied in fertilizer mixtures, layered/coated fertilizers, solid/semi-solid fertilizers, etc., can solve problems such as being unsuitable for controlled-release fertilizers, and achieve excellent photodegradation efficiency, high compatibility, and uniformity. dispersion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to Embodiment 4
[0082] (1) Preparation of photocatalytic composites
[0083] 0.43 g of a (meth)acrylate compound containing an alkylene glycol repeating unit shown in Table 1 below was dissolved in tetrachloroethylene, and TiO in an amount shown in Table 1 below was mixed thereinto. 2 (Average particle diameter of primary particles: 21nm), and by applying 20,000s -1 Stir the mixture at high shear rate for 20 min.
[0084] Then, 0.015 g of a thermal polymerization initiator (AIBN) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred at 90° C. for 30 minutes under a nitrogen atmosphere. Thus, a dispersion in which a photocatalytic composite was bound to the surface and inside of an aggregate of a (meth)acrylate compound containing an alkylene glycol repeating unit and inorganic fine particles was prepared.
[0085] (2) Preparation of controlled release fertilizer
[0086] The dispersion solution of the photocatalytic composite prepared above, polyethylene [LDPE, MI (melt index, 190° C., load 2.16 ...
experiment example 1
[0093] Experimental example 1: Comparative experiment of photodegradation characteristics
[0094] Take 5g of the controlled-release fertilizer of each embodiment and the coated fertilizer of the comparative example, and make pinholes for each fertilizer granule. The degradation of the coating remaining after the complete release of the internal fertilizer was evaluated.
[0095] Using Suntest CPS+ device (ATLAS) at 50°C with 400W / m 2 The intensity of irradiates light with a wavelength of 300nm to 800nm onto the envelope.
[0096] Then, when light was irradiated for 224 hours under the above conditions, the degradation rate of the binder resin obtained from the weight change of the envelope was determined by the following general formula 1, and the results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0097] [Formula 1]
[0098]
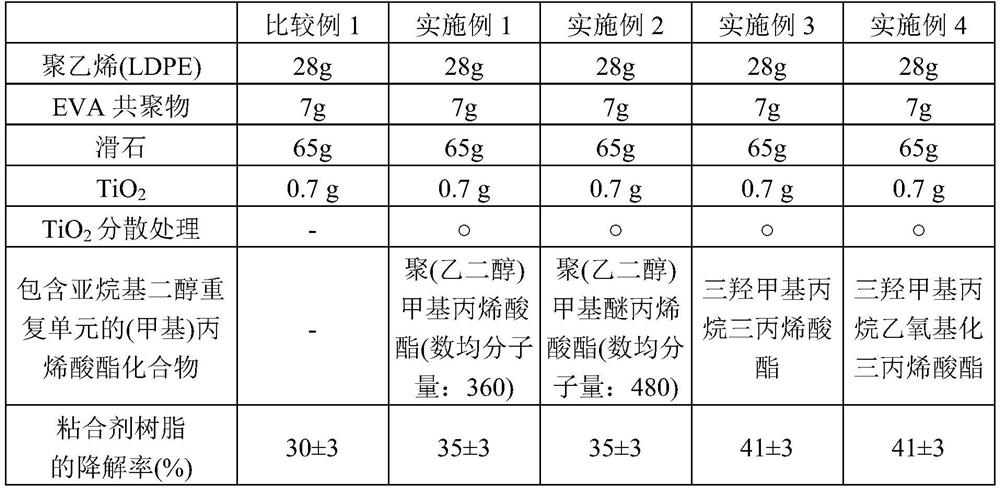
[0099] [Table 1]
[0100]
[0101] As shown in Table 1, it can be confirmed that when using light with a wavelength of 300nm to 800nm at 400W / m 2 W...
experiment example 2
[0102] Experimental example 2: TiO 2 Measurement of Z-average dispersed particle size
[0103] Use a dynamic light scattering instrument (Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS90) to measure the dispersion solution of the photocatalytic composite of embodiment 3 and the TiO-containing solution of comparative example 1 2 Dispersion of TiO in solution 2 The z-average dispersed particle size.
[0104] The results are shown in Table 2 below.
[0105] [Table 2] TiO 2 Z average dispersed particle size
[0106] Example 3 Comparative example 1 TiO 2 Z average dispersed particle size of TiO 2 (nm)
183 About 2.0×10 4
[0107] As shown in Table 2, it can be confirmed that the z-average dispersed particle diameter of the dispersion solution of the photocatalytic composite of Example 3 is about 183nm, therefore, the TiO used 2 The particles are uniformly dispersed and aggregates of inorganic fine particles having a relatively small average particle diameter a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com