Method for adjusting angle of oxide field plate in LDMOS transistor
A technology of oxides and transistors, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as impact and unsatisfactory effects, improve electrical performance, reduce characteristic on-resistance, and increase breakdown voltage Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
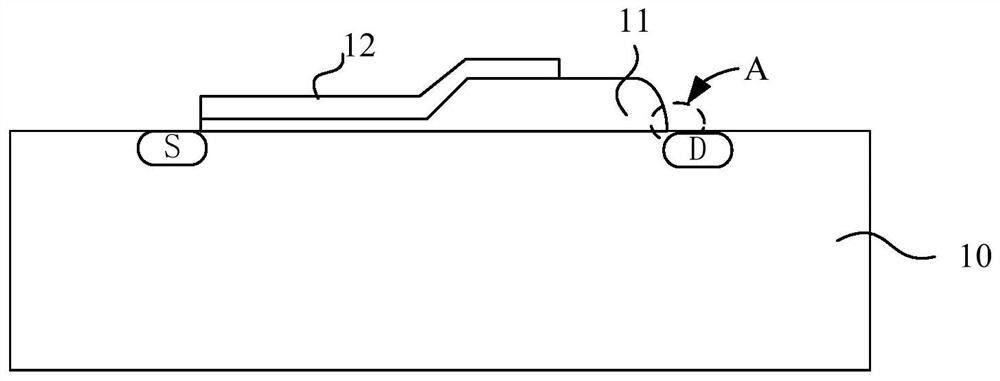
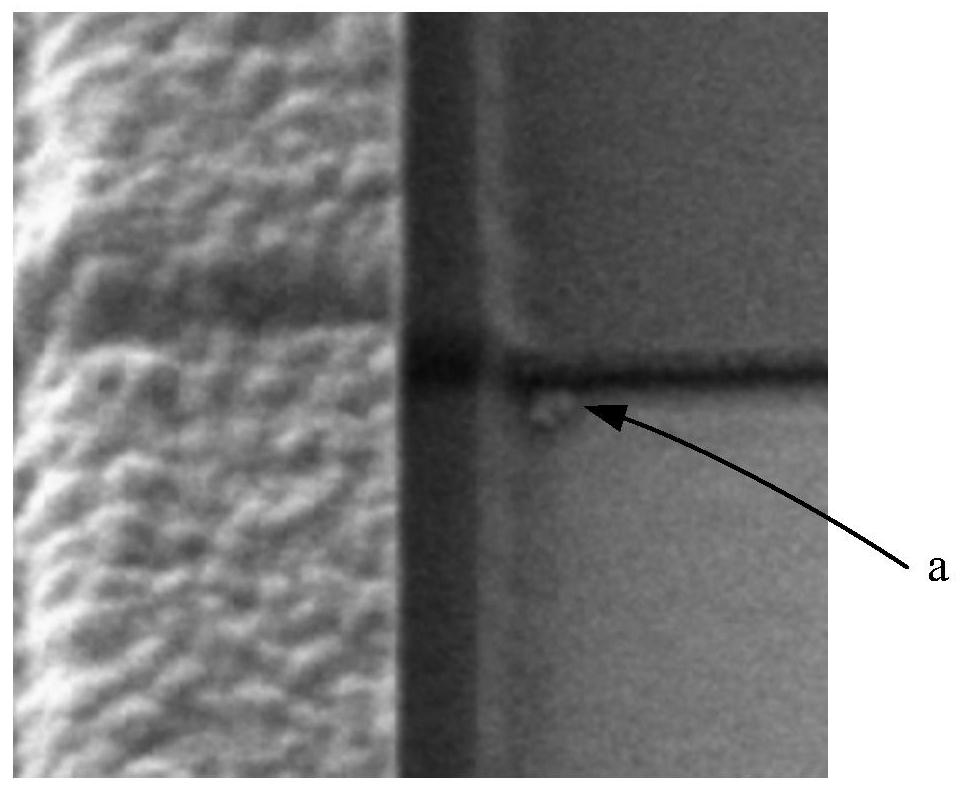
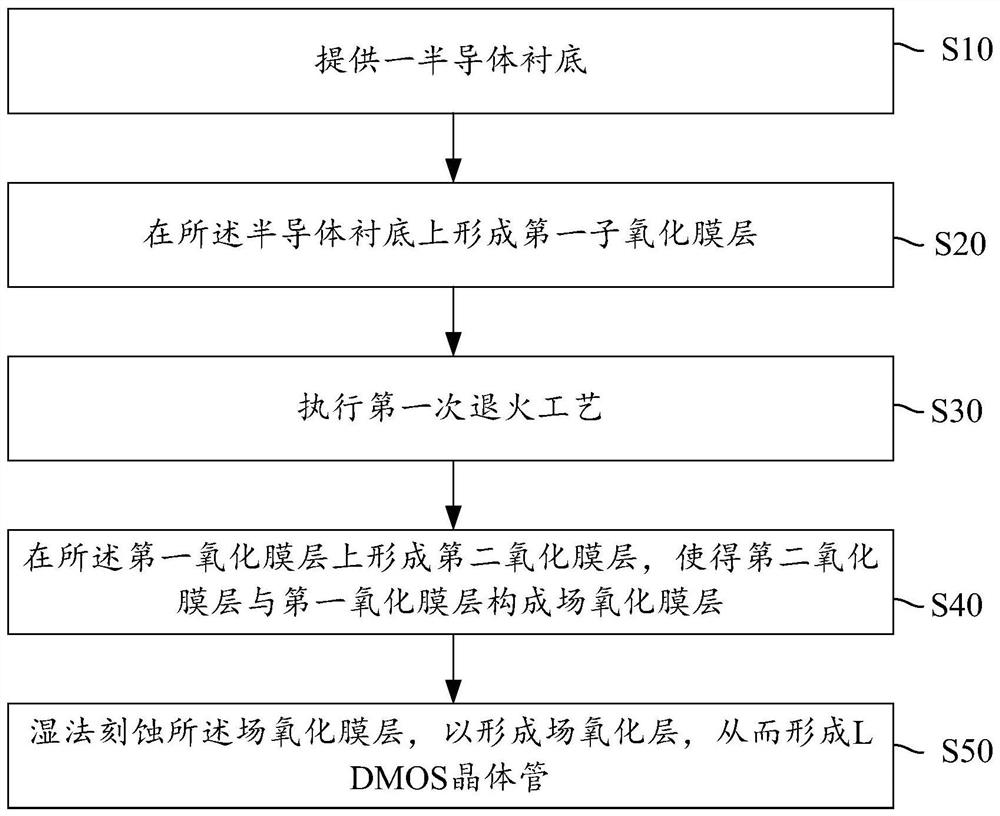
[0038] The core idea of the present invention is to provide a method for adjusting the angle of an oxide field plate in an LDMOS transistor, the method comprising the following steps: providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a first oxide film layer on the semiconductor substrate; performing the first annealing process; forming a second oxide film layer on the first oxide film layer, so that the second oxide film layer and the first oxide film layer form a field oxide film layer; and wet etching the field oxide film layer film layer to form an oxide field plate to form an LDMOS transistor. In the present invention, the first oxide film layer is first formed, and the first annealing process is performed on the first oxide film layer, and then the second oxide film layer is formed, so that the oxide field plate angle during wet etching is controllable That is, the included angle α is between 25° and 75° (preferably, the included angle α is 45°), and this included angle mak...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com