Microbial compositions for the prevention or reduction of growth of fungal pathogens on plants
A composition, microbial technology, applied in the direction of plant growth regulators, chemicals for biological control, fungi, etc., capable of solving problems that do not show plant or fungal specificity or effectiveness, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
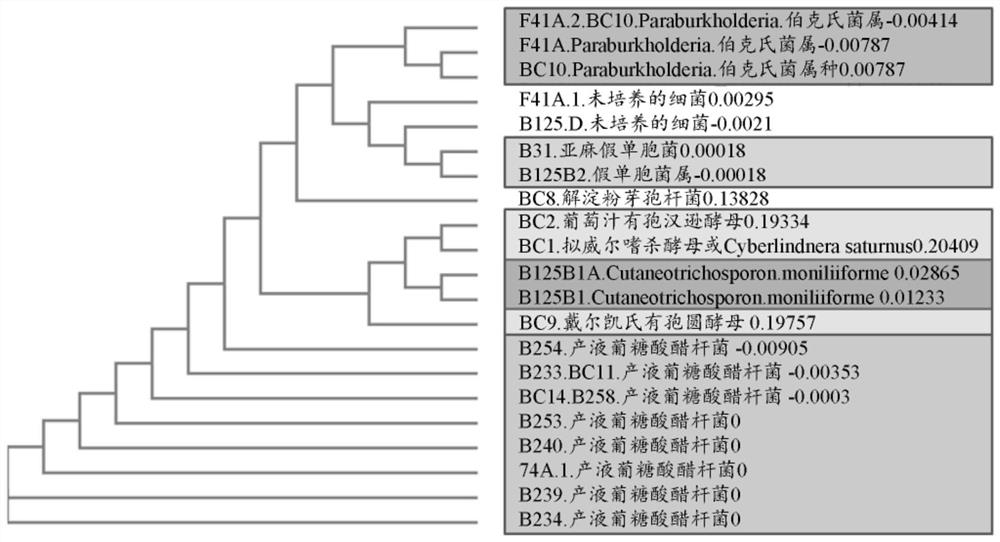
[0158] Example 1: Screening of microorganisms for antifungal activity
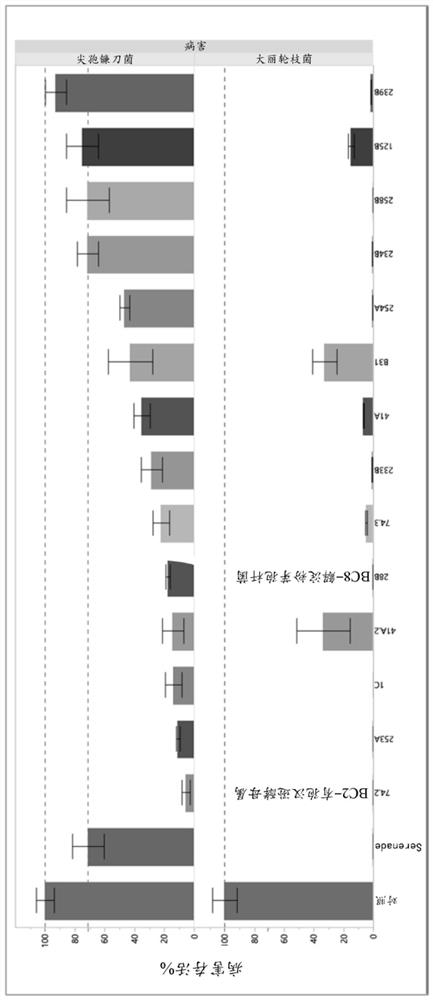
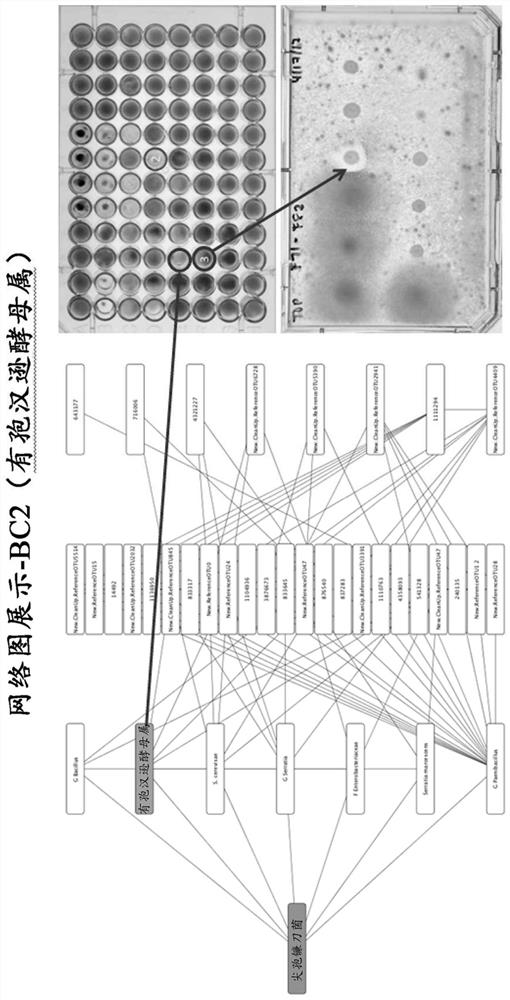
[0159] Screening of microorganisms for their ability to prevent the growth of the fungal diseases Verticillium dahliae and Fusarium oxysporum. Fourteen candidate microorganisms were identified as active in a primary screen that would form clearing zones on the fungal lawn (for example, see image 3 , on the identification of Hansenula vinespora for inhibition of Fusarium oxysporum). These fourteen candidate microorganisms were then screened in a secondary test designed to simulate a structured soil environment by using semi-solid agar. In this test, the growth of untreated fungi was set as 100% and the reduction relative to the growth of untreated fungi was determined. Serenade, a commercial product containing the active ingredient of the Bacillus subtilis strain QST713, was used as a control, which reduced the growth of Fusarium oxysporum by -25% and by >99% of the growth of Verticillium dahliae. Of th...
Embodiment 2
[0163] Example 2: Antifungal activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (strain 28B; BC8) supernatant against raspberries
[0164] The antifungal activity of culture supernatants of an isolated strain of Bacillus amylocii (strain 28B; BC8) was determined against Botrytis cinerea on raspberries. After 120 hours, raspberries treated with the supernatant of the B. amyloliquefaciens strain showed similar fungal growth to the negative control raspberries (not infected with Botrytis cinerea), covering less than 5% of the surface area of the raspberries. In contrast, after 120 hours, positive control raspberries (which had been infected with Botrytis cinerea) showed about 90% of their surface area covered by fungal growth ( Figure 4 ; Figure 5A-Figure 5C ).
Embodiment 3
[0165] Example 3: Evaluation of the efficacy of BC8 against blight caused by Botrytis cinerea and A. aureus anthracnose on blueberry crops.
[0166] The efficacy of BC8 was evaluated against flower rot caused by Botrytis cinerea and A. aureus anthracnose in blueberry crops. Blueberry bushes were treated with BC8 or a control treatment. As control treatments, shrubs were left untreated or treated with Lifegard (Certis; active ingredient: Bacillus mycoides), Stargus (Marrone; active ingredient: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain F727) and Nufilm (Fertrell, terpene polymer and emulsifier), or a combination of BravoWeatherstik (Syngenta; active ingredient: chlorothalonil (tetrachloroisophthalonitrile) 54%), Captevate (Arysta; active ingredient: fenhexamid, captan) and Treatment was carried out with continuous application of Pristine (BASF; active ingredients: pyraclostrobin, bosclid). All treatments also receive standard commercial fertility and pesticide programs. Treatment pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com