Process for assisting in strengthening phosphorus removal and phosphorus recovery of phosphorus-containing wastewater
A waste water and process technology, applied in the direction of water pollutants, chemical instruments and methods, neutralized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of long reaction time, high treatment cost, limited phosphorus removal efficiency, etc., to reduce conductivity, Effects of increasing crystallization efficiency, accelerating nucleation rate, and crystal growth rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
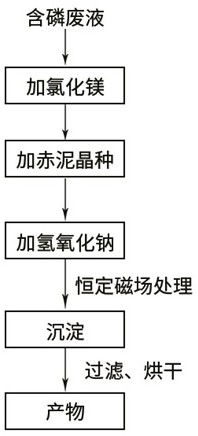
[0026] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of auxiliary strengthening phosphorus-containing waste water dephosphorization of the present invention and the technique of reclaiming phosphorus, concrete steps are: get waste liquid 200ml, add the magnesium chloride solution of 0.5mol / L, adjust N:Mg:P=1:1: 1; Add 1.6g of 60-mesh red mud seed crystals to it, start stirring, and the stirring speed is 150r / min; then add 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH of the solution to 9.5; adjust the constant magnetic field, and the magnetic induction intensity is 0.1T , the temperature is controlled at 60-70°C, the reaction time is 60 minutes, and it is left to stand for 30 minutes; finally, it is filtered and dried. After the reaction, the removal rate of nitrogen and phosphorus in the filtrate was detected, and the removal rate of phosphorus was 91%, and the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen was 85%.
Embodiment 2
[0028] Take 500ml of waste liquid, add 0.5mol / L magnesium chloride solution, adjust N:Mg:P=1:1.4:1; add 4g of 60-mesh red mud seed crystals to it, start stirring, and the stirring speed is 180r / min; then add 1.0mol / L sodium hydroxide, adjust the pH of the solution to 9.5; adjust the constant magnetic field, the magnetic induction intensity is 0.2T, the temperature is controlled at 70-80°C, the reaction time is 60min, and stand for 30min; finally filter and dry. After the reaction, the removal rate of nitrogen and phosphorus in the filtrate was detected, and the removal rate of phosphorus was 96.5%, and the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen was 90%.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Take 1L of waste liquid, add 1.0mol / L magnesium chloride solution, adjust N:Mg:P=1:1.8:1; add 80 mesh red mud seed crystals 8g to it, start stirring, and the stirring speed is 200r / min; then add 1.0mol / L sodium hydroxide, adjust the pH of the solution to 9.5; adjust the constant magnetic field, the magnetic induction intensity is 0.3T, the temperature is controlled at 80-90°C, the reaction time is 90min, stand still for 30min; finally filter and dry. After the reaction, the removal rate of nitrogen and phosphorus in the filtrate was detected, and the removal rate of phosphorus was 90%, and the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen was 92%.
[0031] From the concentration analysis of the wastewater treated in the above three examples, it can be seen that changing some reaction conditions will have some impact on the final result. But in general, the phosphorus removal rate is basically over 90%, the phosphorus removal rate is high, and the reaction time is short, which still ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com