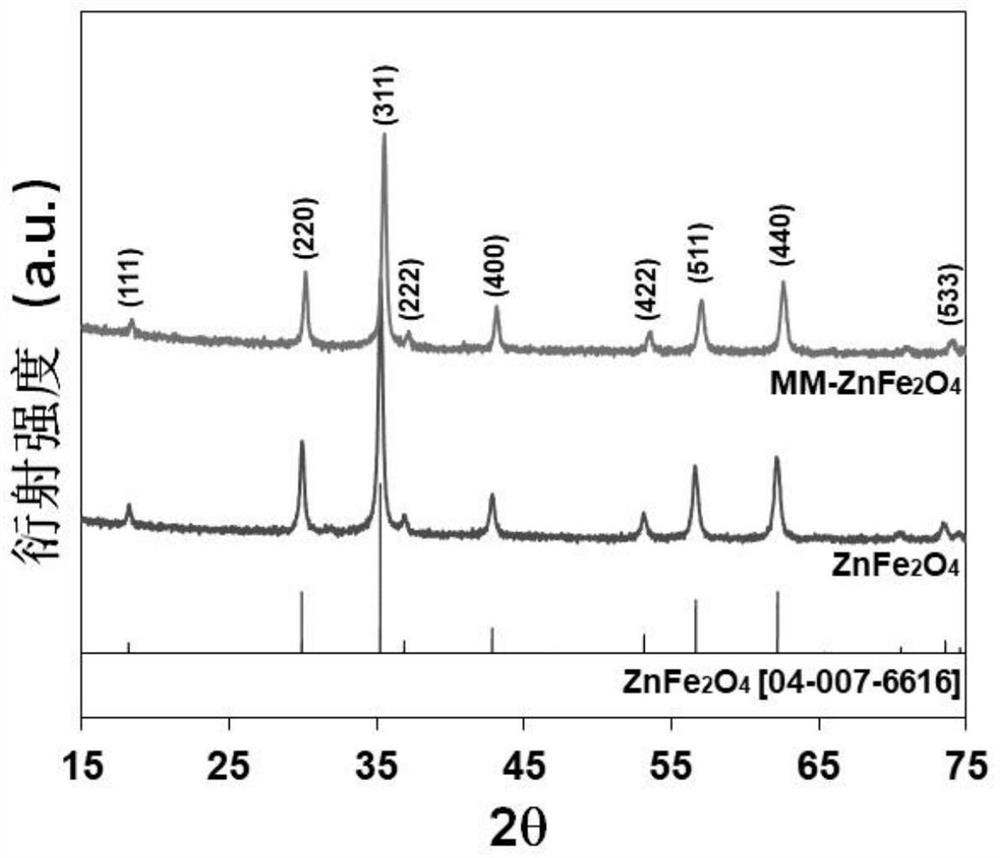
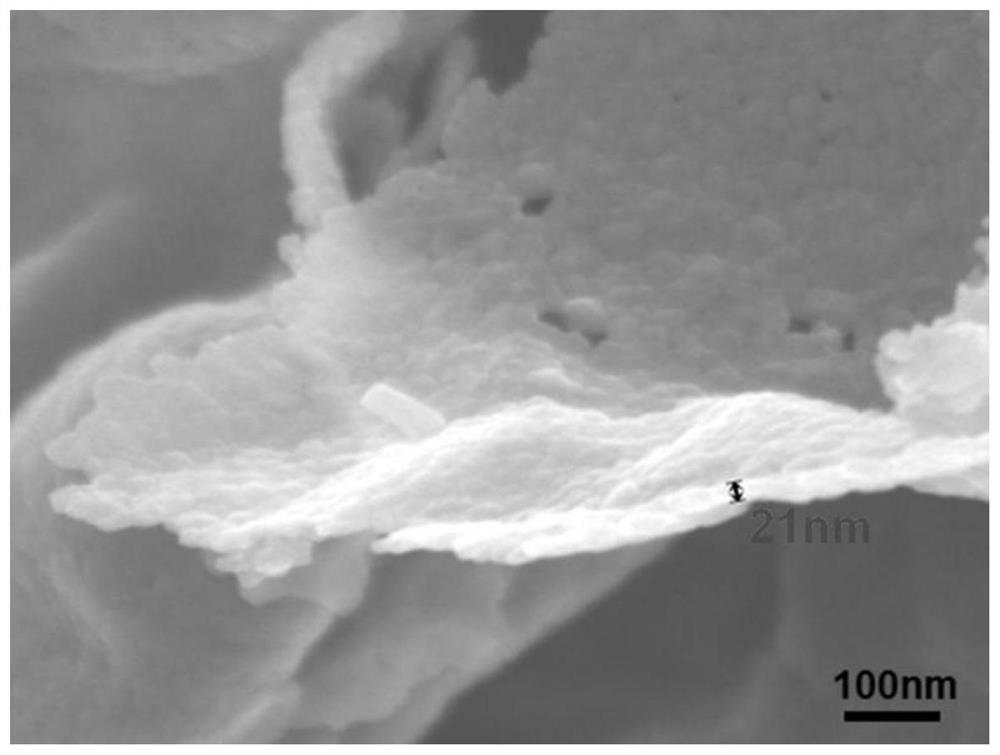
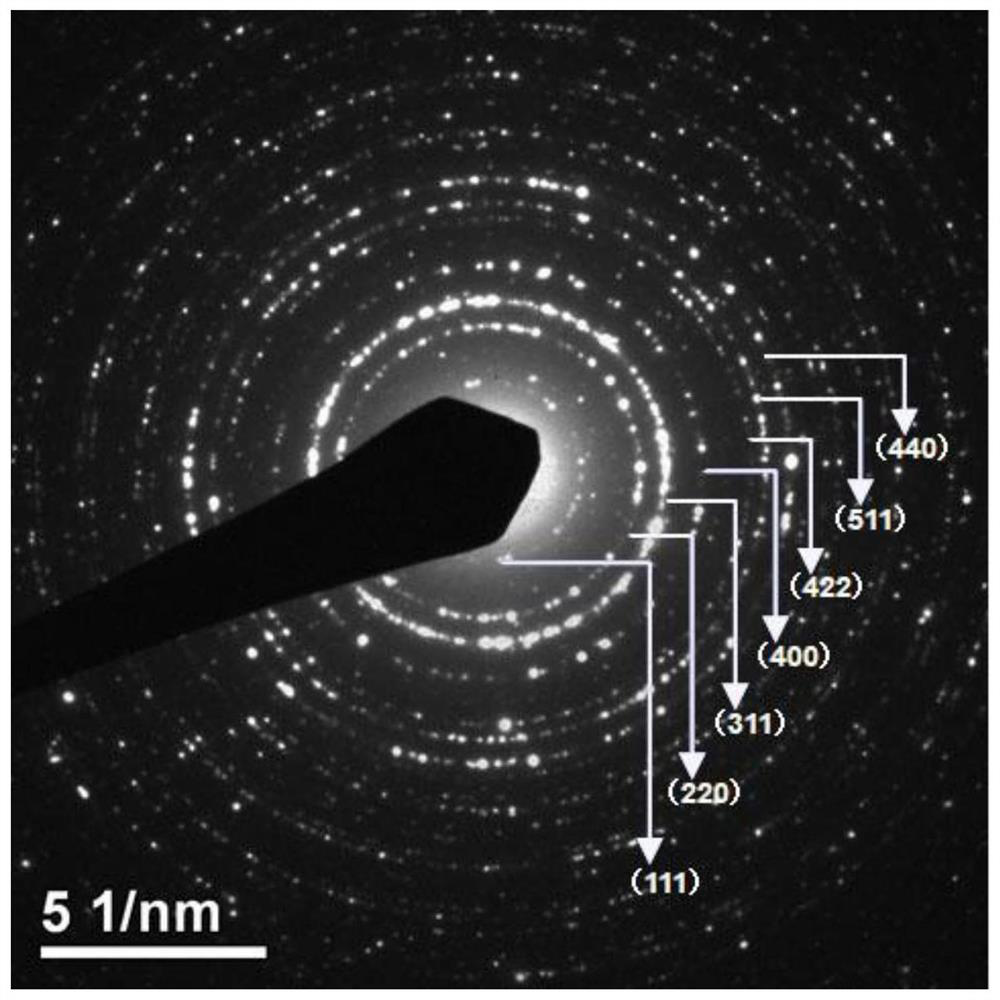
Method for treating organic pesticide by activating sulfate radicals based on iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst
A technology for organic pesticides and catalysts, which is applied in the directions of heterogeneous catalyst chemical elements, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable carcinogenicity, and achieve the effect of accelerating transformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst activates PMS to efficiently degrade thiacloprid
[0028] Preparation of iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst, the steps are as follows:
[0029] 1) Add 0.275g Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O, 0.237g Mg(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O, 0.223g Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O and 0.331g Mn(NO 3 ) 2 (50% by weight aqueous solution) mixed and stirred to form a mixed metal salt A for subsequent use. Mixed metal salt A and 2.987g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2Dissolve O together in 10mL water to form metal salt solution B for later use; weigh 2.13g citric acid and dissolve it in 10mL water to configure aqueous solution C; add aqueous solution C to metal salt solution B under stirring, and react in the resulting mixed solution to form multinuclear Zn / Mg / Cu / Mn / Fe-citrate complex;
[0030] 2) Slowly add 4.2mL of ammonia water with a concentration of 25~28% by weight to the mixture obtained in step 1) under rapid stirring, adjust the pH value to 7, then add 2mL of...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2 The iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst activates PMS to efficiently degrade isoproturon.
[0051] The preparation process of the catalyst in this embodiment 2 was repeated in embodiment 1.
[0052] The iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst prepared in Example 2 cooperates with PMS to form a multiphase system (MM-ZnFe 2 o 4 / PMS system) is applied to the control of organic pesticides, the specific process is as follows:
[0053]S1: Prepare an aqueous solution of isoproturon with a concentration of 2.5 mg / L. Take 50mL of the prepared 2.5mg / L isoproturon aqueous solution, add 0.0025g of the iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst prepared in Example 2, ultrasonically disperse the catalyst in the solution for 2 minutes, and then place the mixed solution under mechanical stirring Under low temperature, the temperature of the mixed solution is controlled at room temperature 25°C through a low-temperature constant temperature tank, 400 microliters of 50mM P...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3 The iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst activates PMS to efficiently degrade 2,4-dichlorophenol.
[0056] The preparation process of the catalyst in Example 3 was repeated in Example 1.
[0057] The iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst prepared in Example 3 cooperates with PMS to form a multiphase system (MM-ZnFe2O4 / PMS system) and is applied to the treatment of organic pesticides. The specific process is as follows:
[0058] S1: Prepare an aqueous solution of 2,4-dichlorophenol with a concentration of 2.5mg / L. Take 50mL of the prepared 2.5mg / L 2,4-dichlorophenol aqueous solution, add 0.0025g of the iron-based polyatomic coupling catalyst prepared in Example 3, ultrasonically disperse the catalyst in the solution for 2 minutes, and then dissolve the mixed solution Under mechanical stirring, the temperature of the mixed solution was controlled at room temperature 25° C. by a low-temperature thermostat, and 400 microliters of 50 mM PMS solution was added...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com