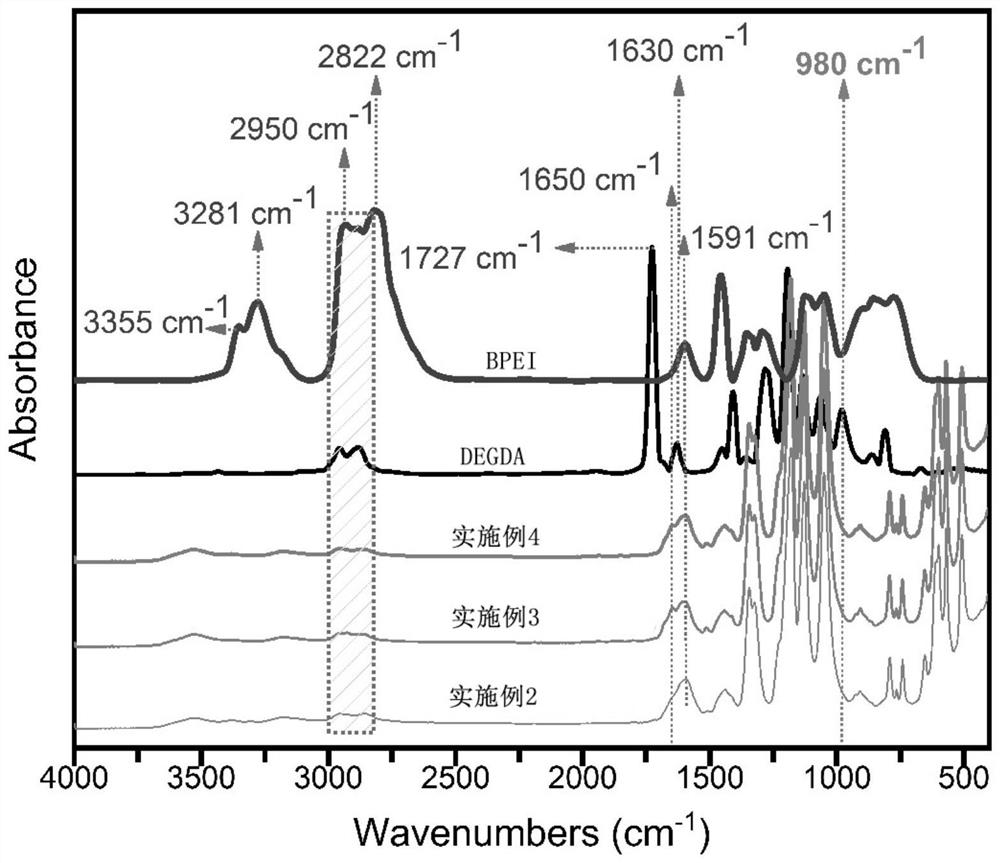
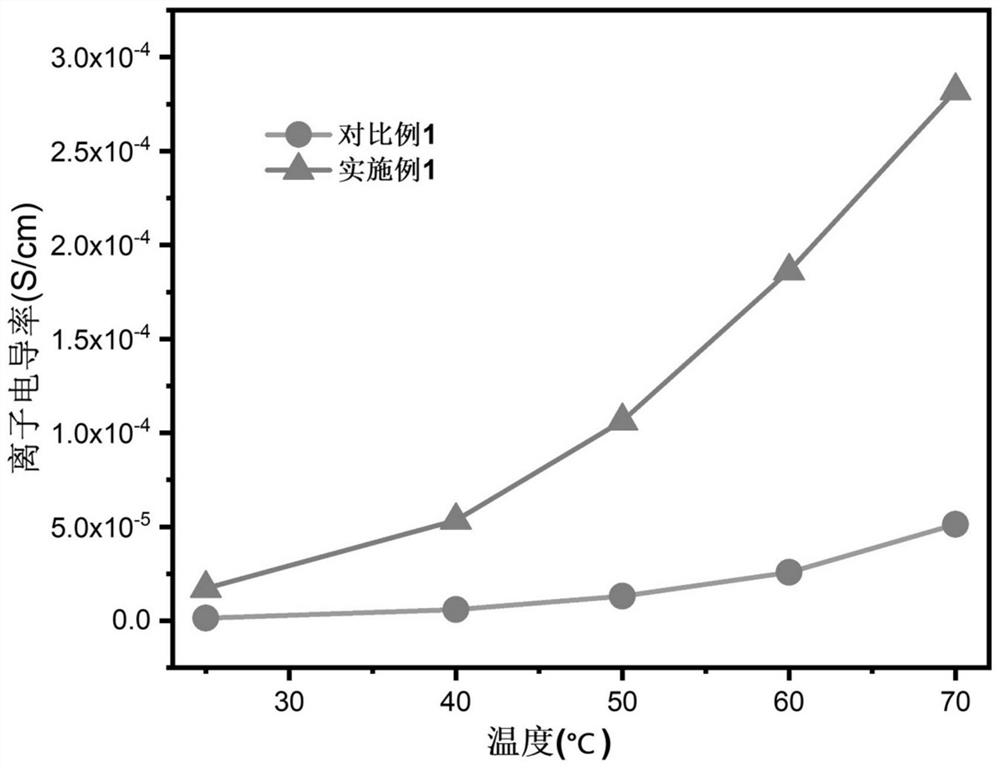
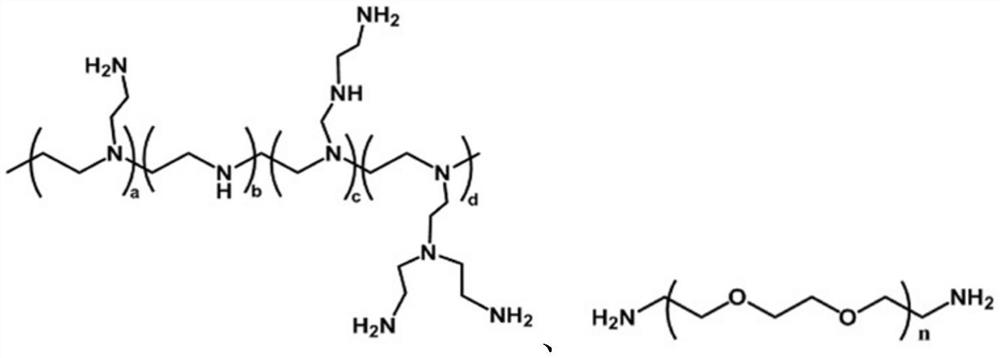
Method for preparing all-solid-state polymer electrolyte through in-situ thermal initiation and application
An all-solid polymer, thermally induced technology, applied in solid electrolytes, non-aqueous electrolytes, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, etc., can solve the problem that it is not suitable for direct in-situ preparation of polymer batteries, and improve the preparation cost and grafting rate of polymer electrolytes. Inability to precisely control problems such as reducing interface wetting and modification, improving interface compatibility and wide salt selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Components and parts by weight thereof in the mixed solution are as follows:
[0029] Branched Polyethyleneimine (BPEI) 40
[0030] Diethylene glycol diacrylate (DEGDA) 20
[0031] LiTFSI 20
[0032] Methanol 20
[0033] The in-situ reaction temperature is 60° C., and the reaction time is 1 h.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Components and parts by weight thereof in the mixed solution are as follows:
[0036]
[0037] The in-situ reaction temperature is 25°C, and the reaction time is 8h.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Components and parts by weight thereof in the mixed solution are as follows:
[0040]
[0041] The in-situ reaction temperature is 40°C, and the reaction time is 3.5h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com