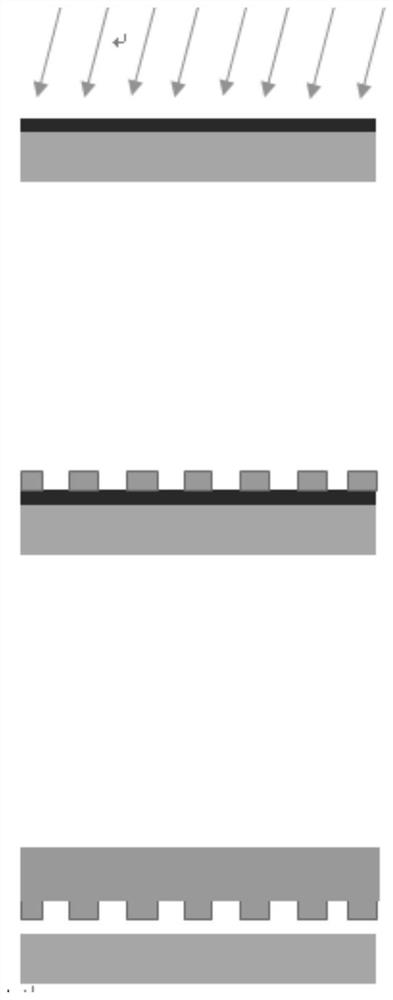
Method for transferring porous PDMS film in organ chip
An organ chip and thin film technology, applied in the field of micromachining, can solve the problems of complicated operation, increased experimental difficulty, low success rate, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation steps and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
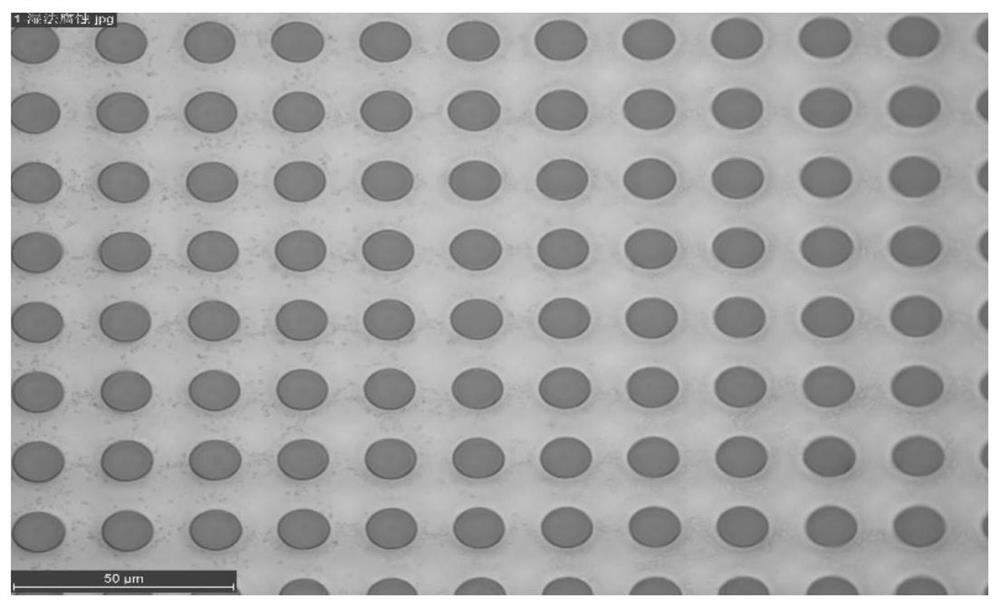
[0075] Firstly, the photoresist S1813 is spin-coated on the silicon wafer substrate, and the parameter is 3000rpm, 40s. It was then baked and cured at 115°C for 90s. Then use UV lithography SUSSMA6 for flood exposure, the exposure time is 1-2s longer than usual, and the photoresist with fully broken chain can be obtained by exposing for 9s with this equipment.
[0076] Surface O of the photoresist using a glue remover 2 Plasma treatment, O 2 The flow rate is 30sccm, the radio frequency power is 30w, and the surface treatment time is 2min, then the PDMS film is spin-coated with a thickness of 5μm, and baked and cured at 120°C for 40min. Then, the PDMS thin film is photolithographically patterned into a through-hole structure by using a microfabrication process.
[0077] The graphical process is: first use RIE to treat the PDMS surface with oxygen plasma, and the parameter is O 2 The flow rate is 30sccm, the radio frequency power is 200w, and the processing time is 2min. Th...
Embodiment 2
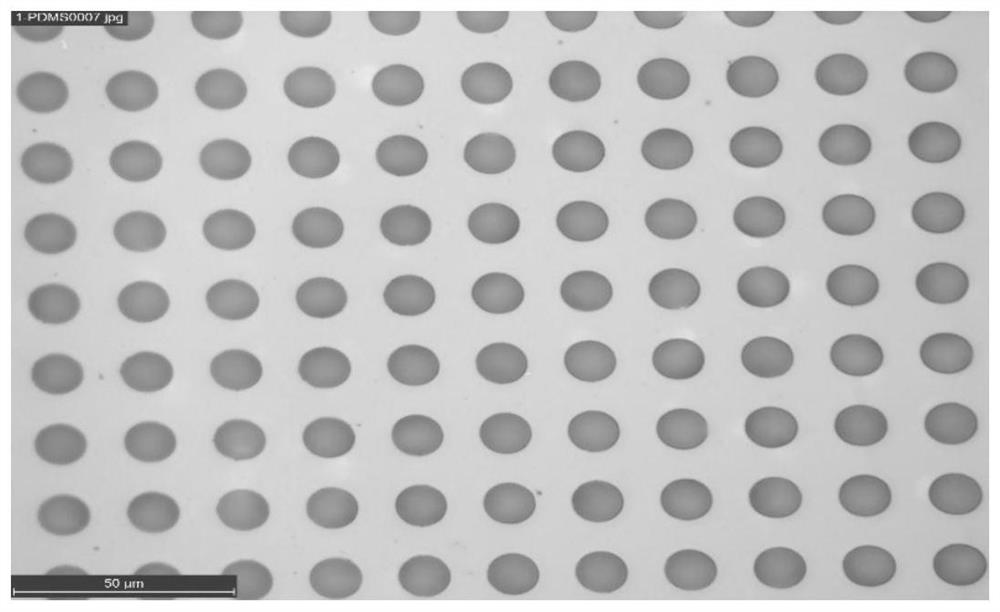
[0080] Firstly, the photoresist S1813 is spin-coated on the silicon wafer substrate, and the parameter is 3000rpm, 40s. It was then baked and cured at 115°C for 90s. Then use UV lithography SUSSMA6 for flood exposure, the exposure time is 1-2s longer than usual, and the photoresist with fully broken chain can be obtained by exposing for 9s with this equipment.
[0081] Surface O of the photoresist using a glue remover 2 Plasma treatment, O 2 The flow rate is 30sccm, the radio frequency power is 30w, and the surface treatment time is 2min, then the PDMS film is spin-coated with a thickness of 10μm, and baked and cured at 120°C for 40min. Then, the PDMS thin film is photolithographically patterned into a through-hole structure by using a microfabrication process.
[0082] The graphical process is: first use RIE to treat the PDMS surface with oxygen plasma, and the parameter is O 2 The flow rate is 30sccm, the radio frequency power is 200w, and the processing time is 2min. T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com