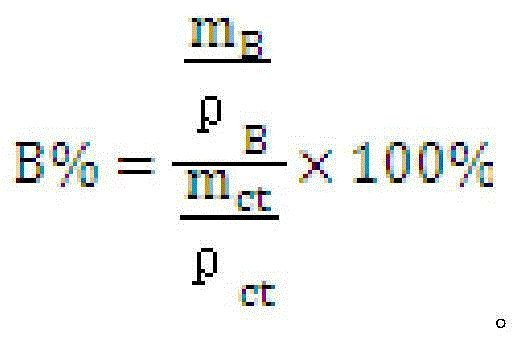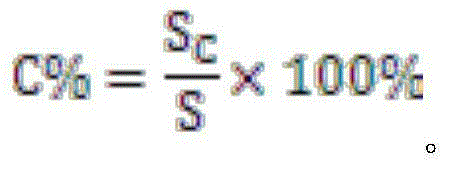Patents
Literature
507 results about "Porous thin films" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
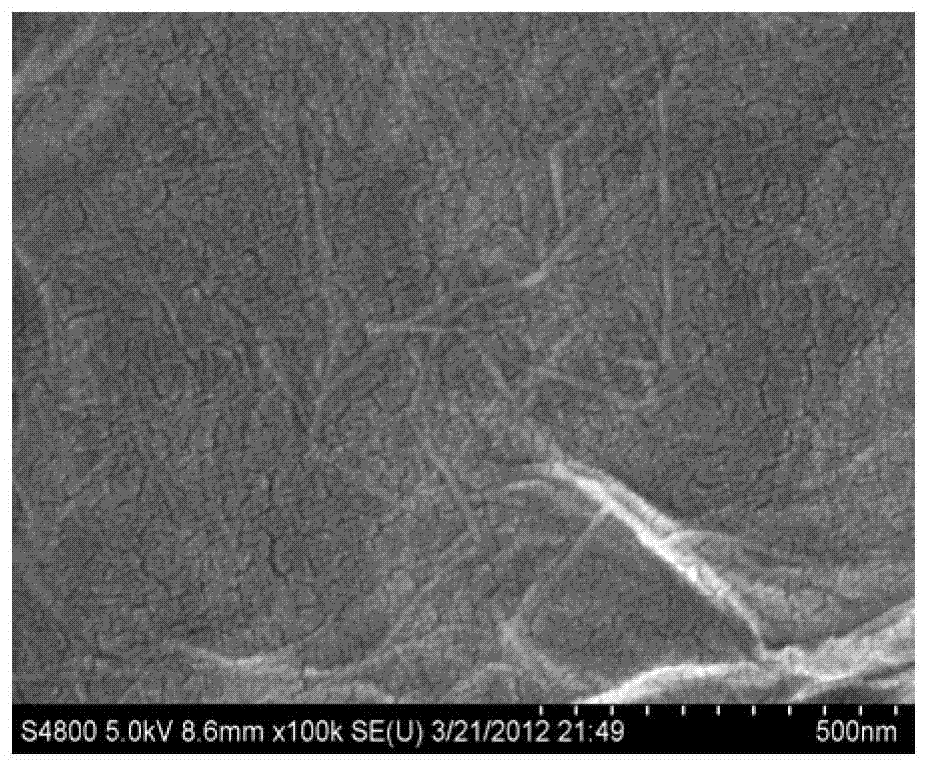
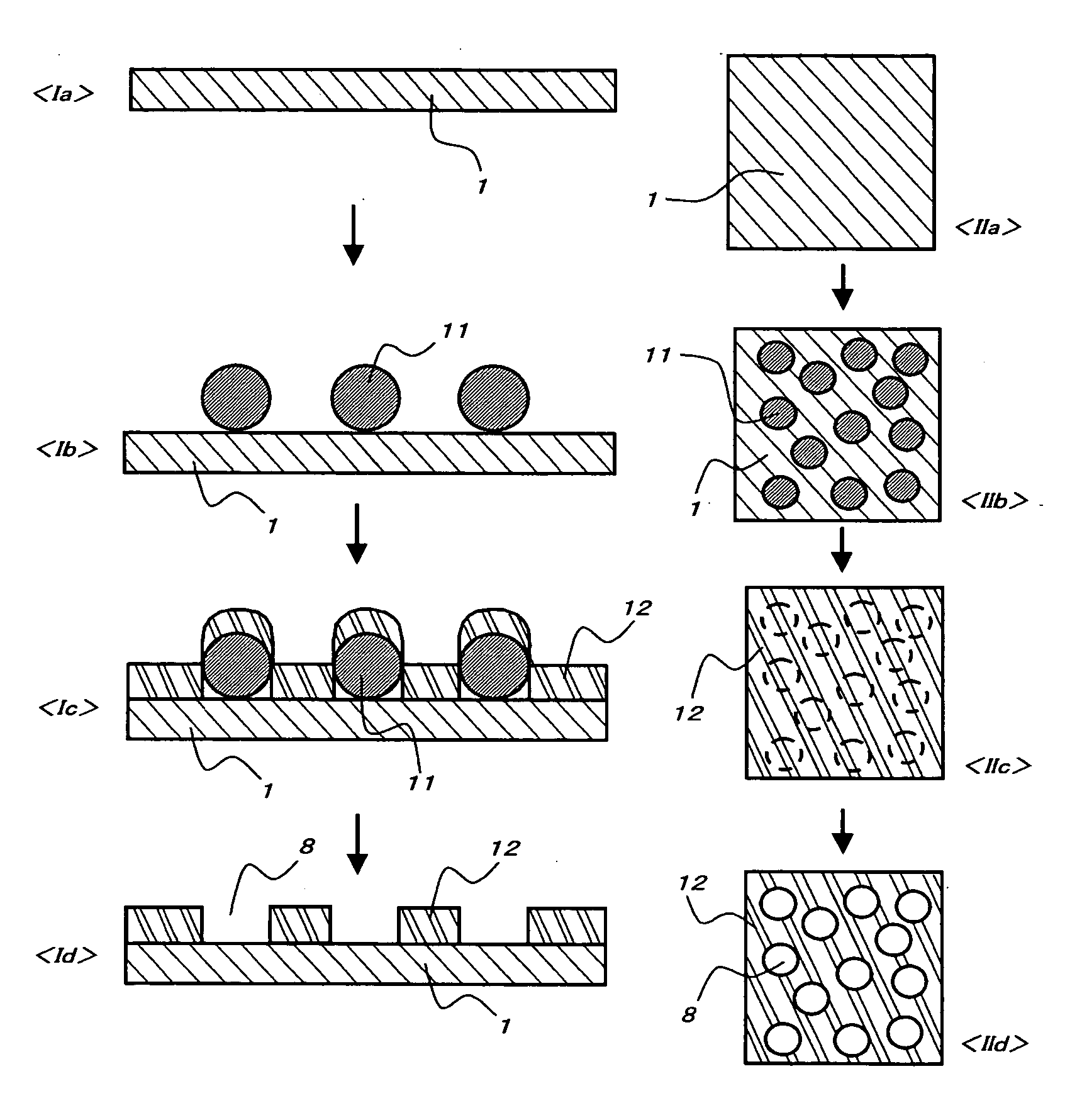
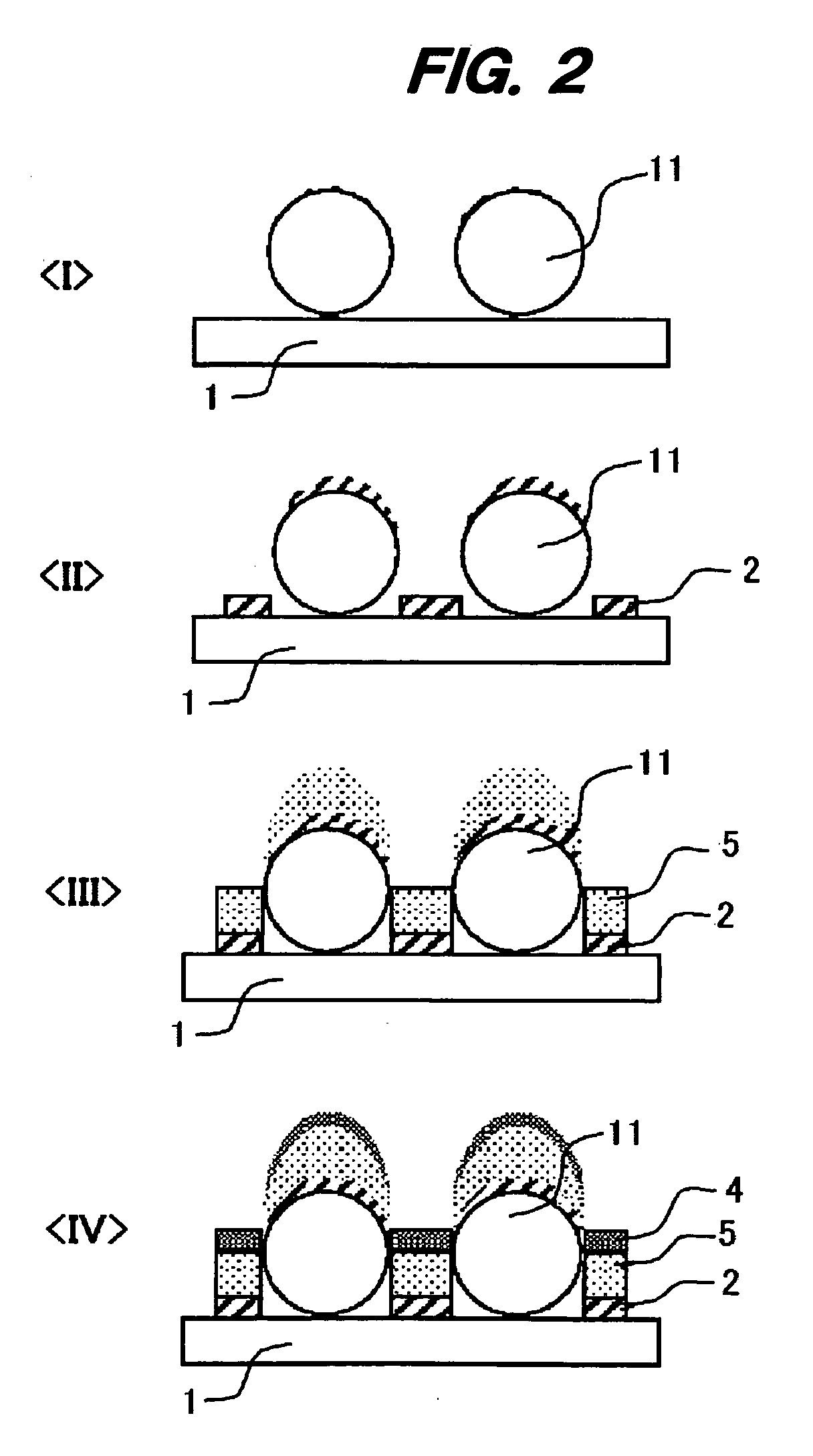
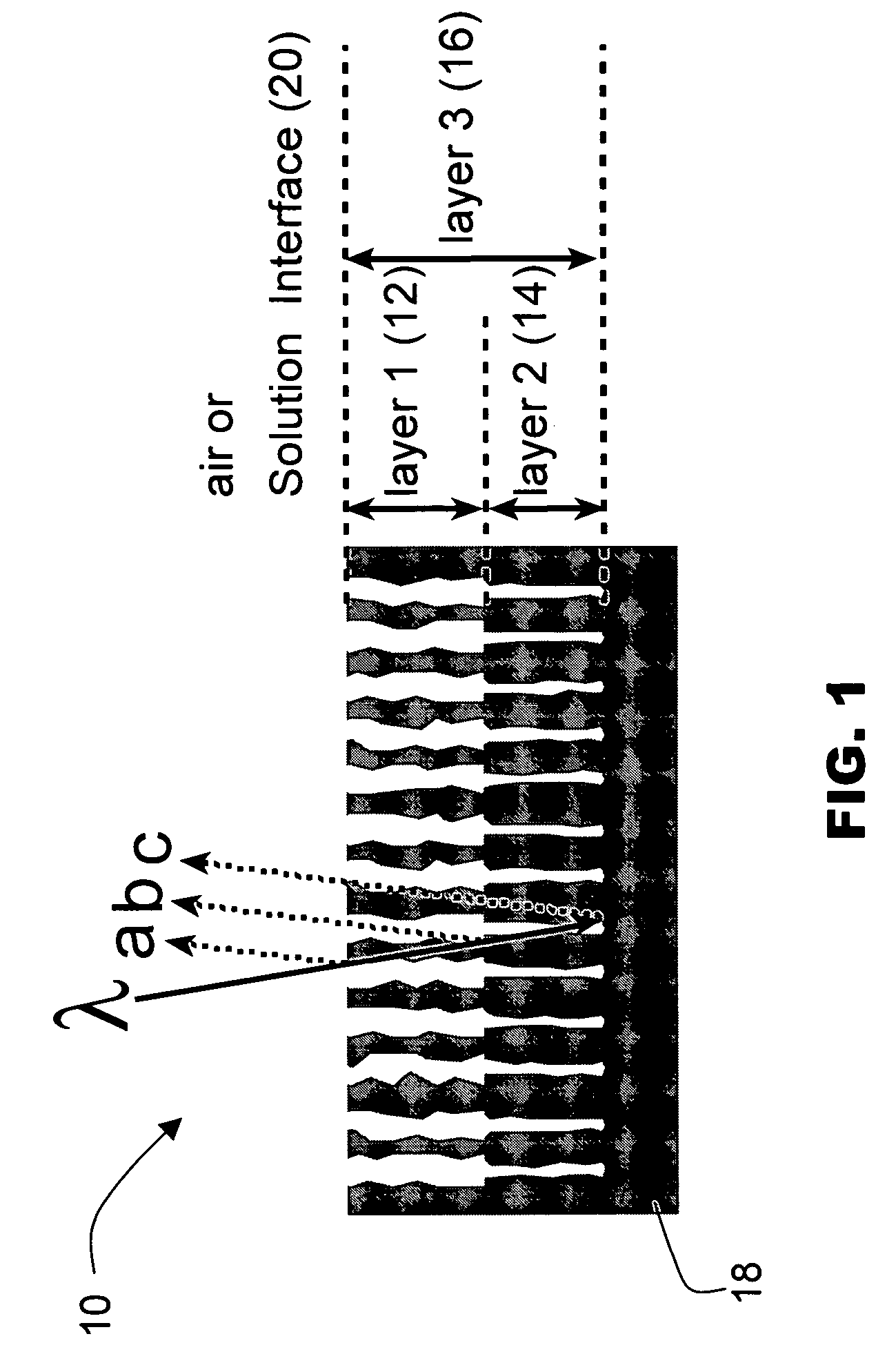
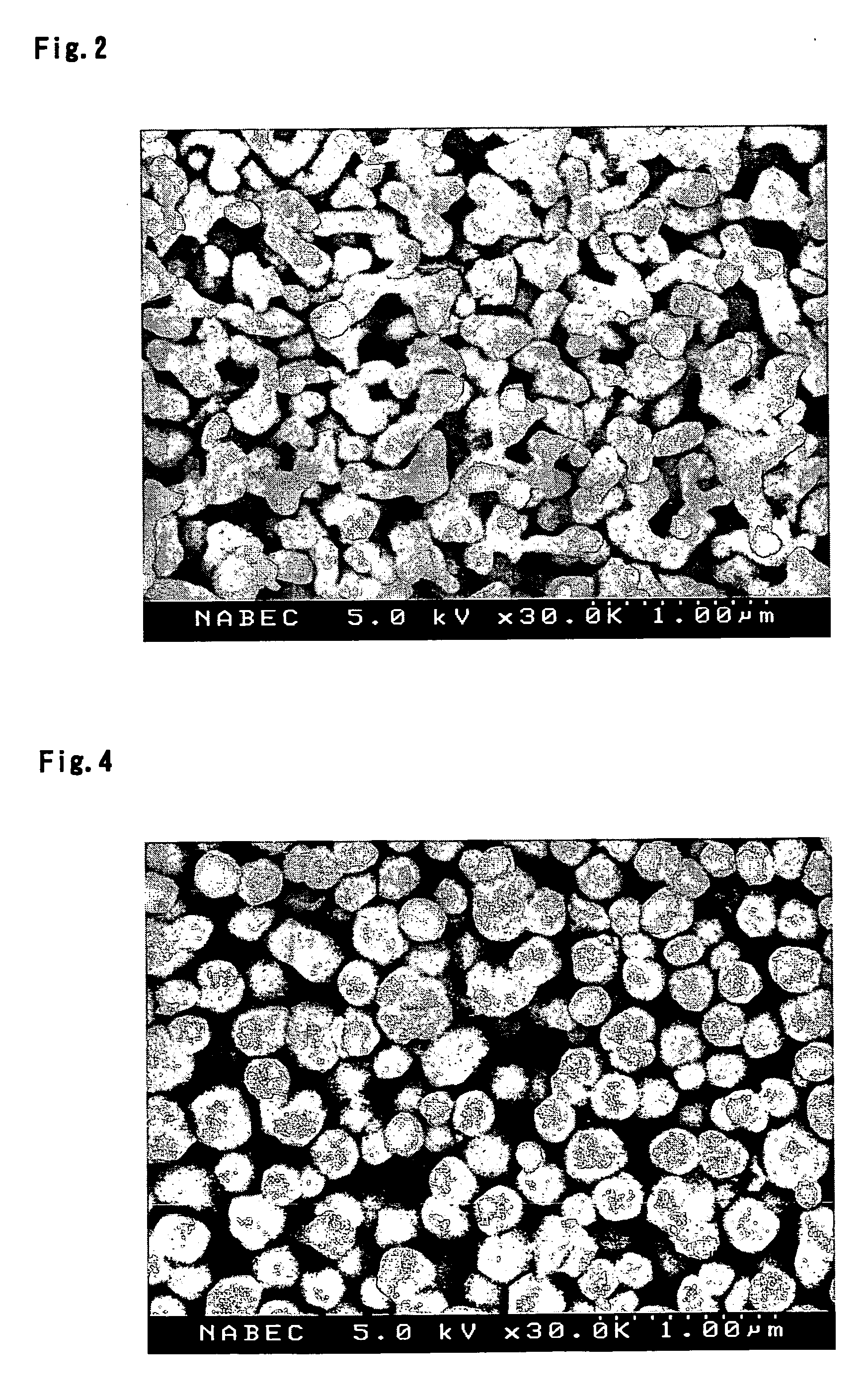
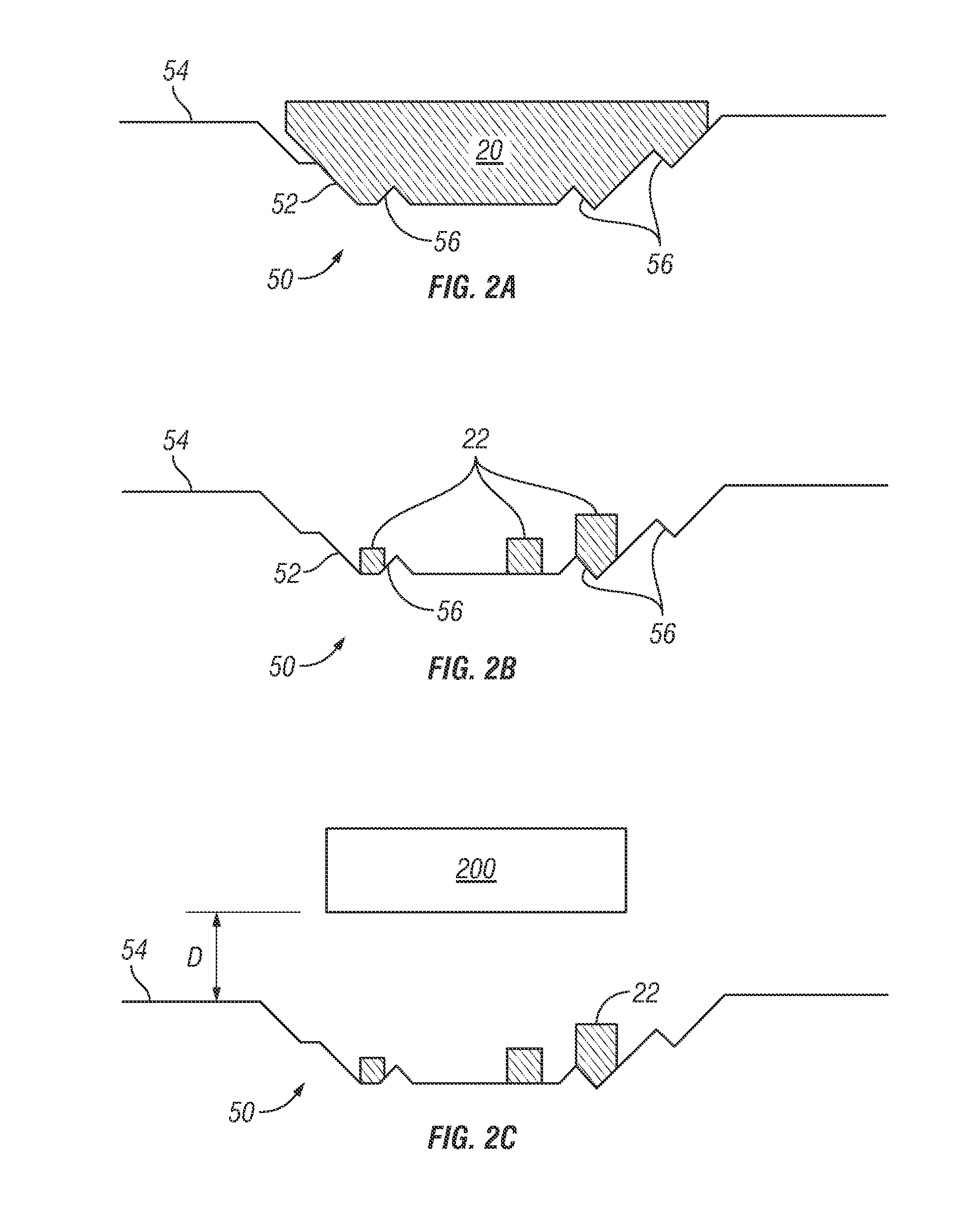
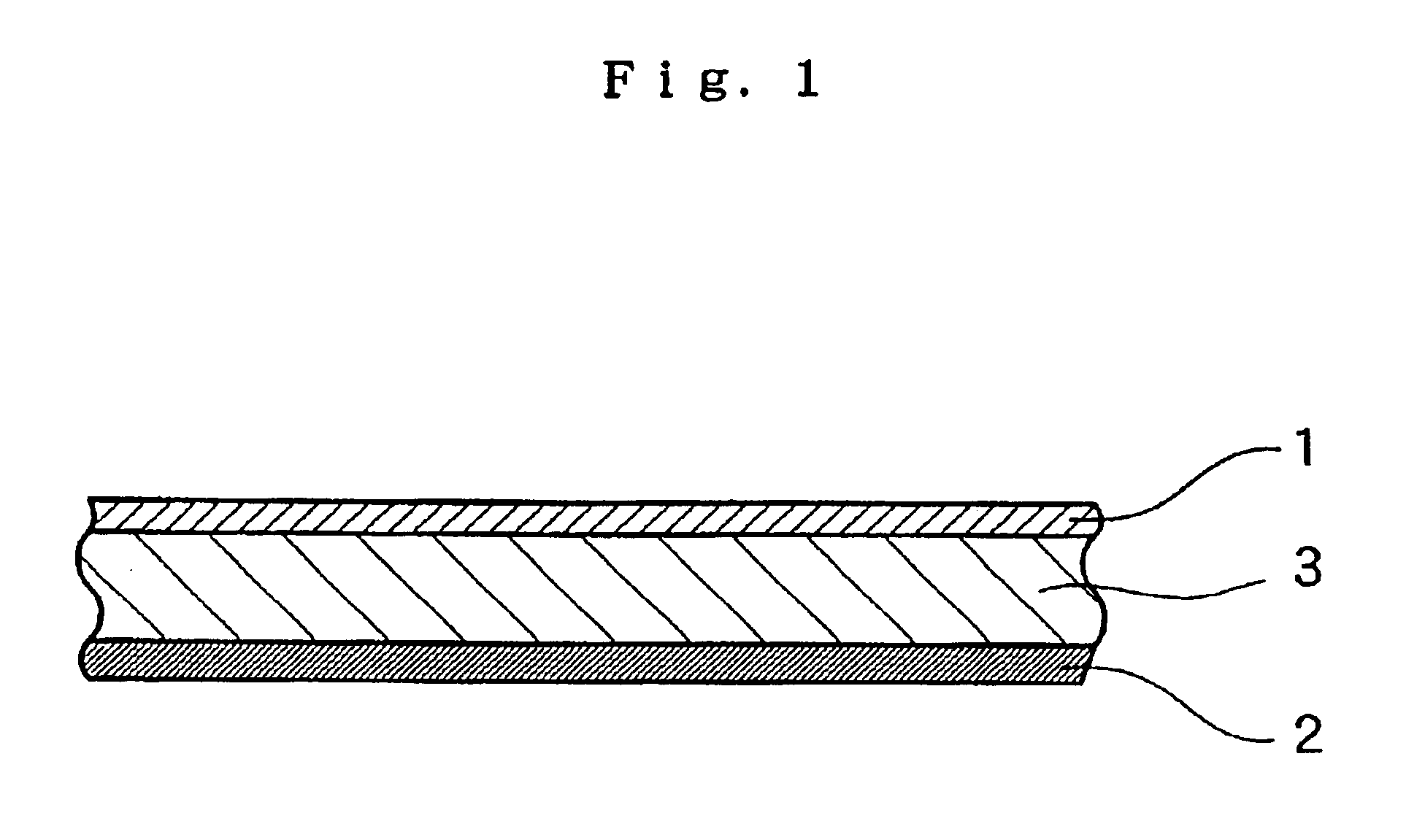
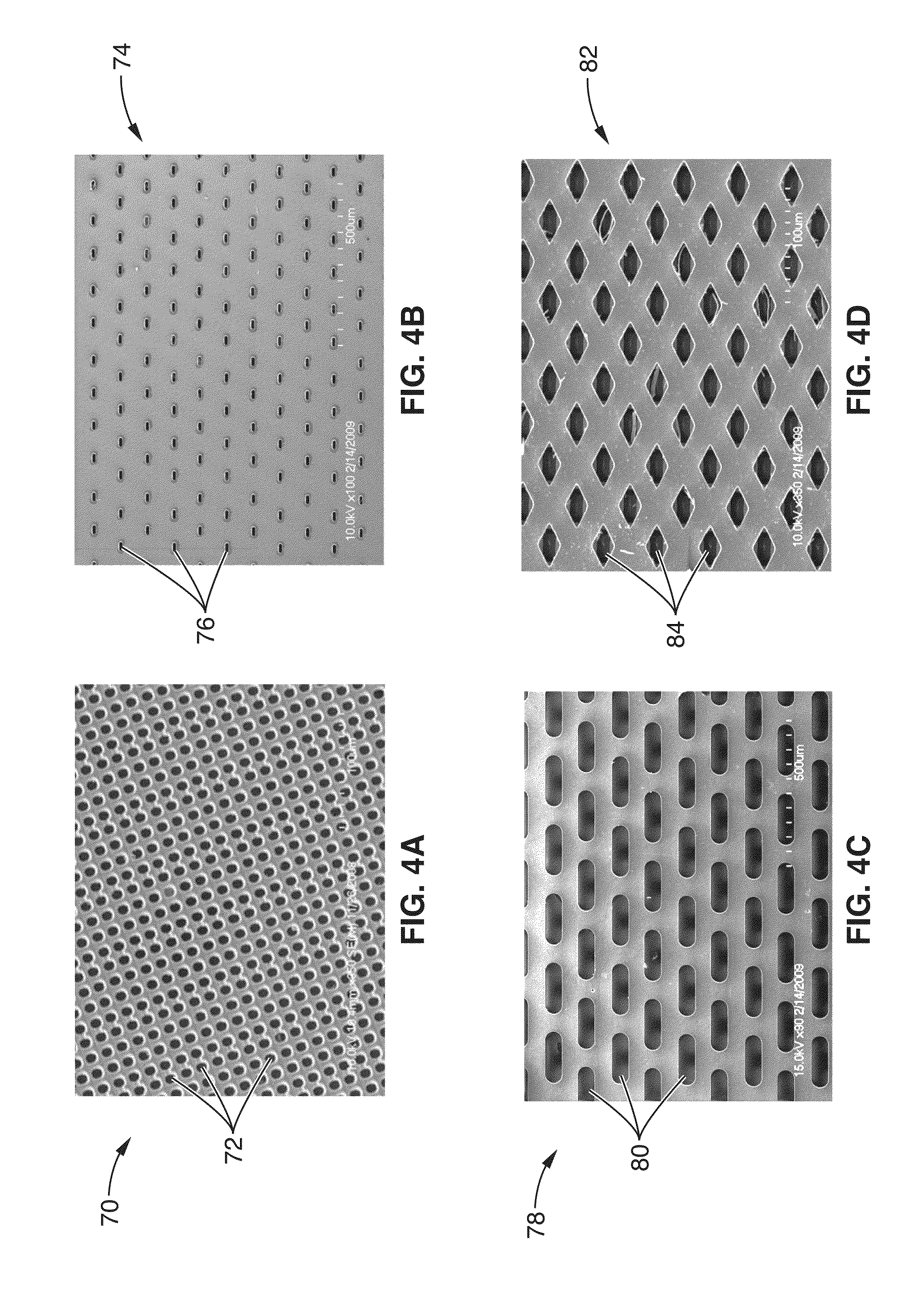
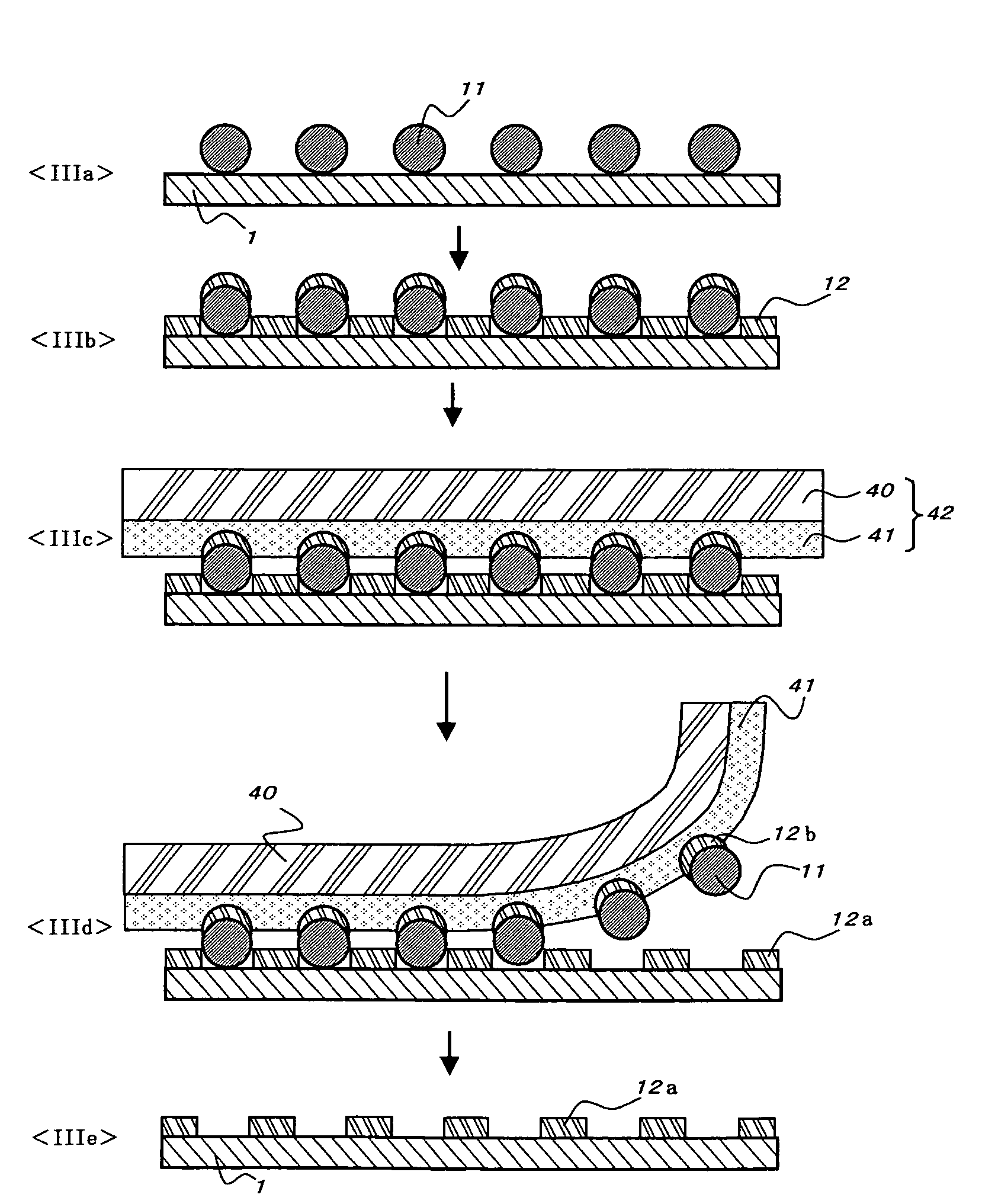
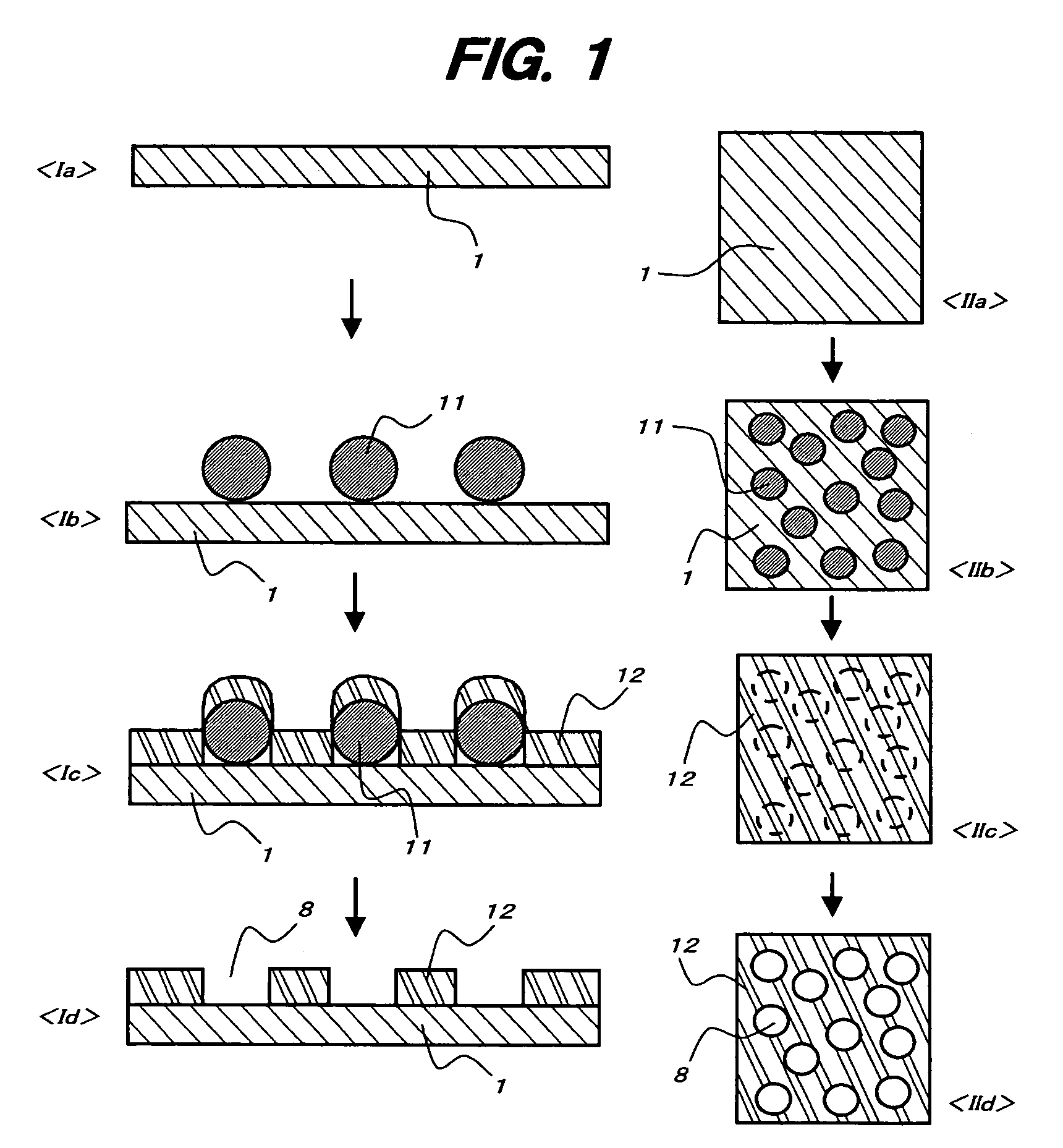
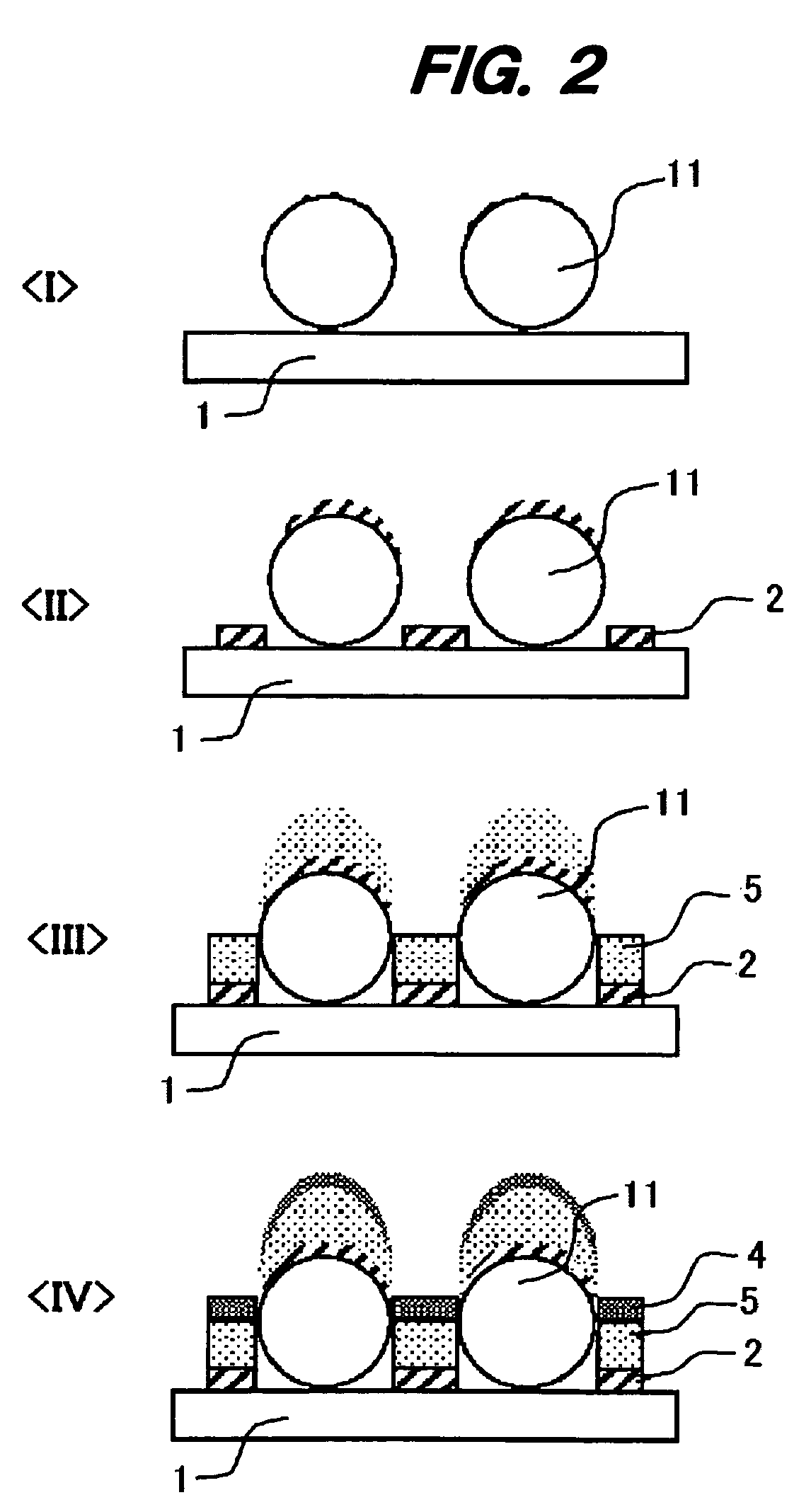
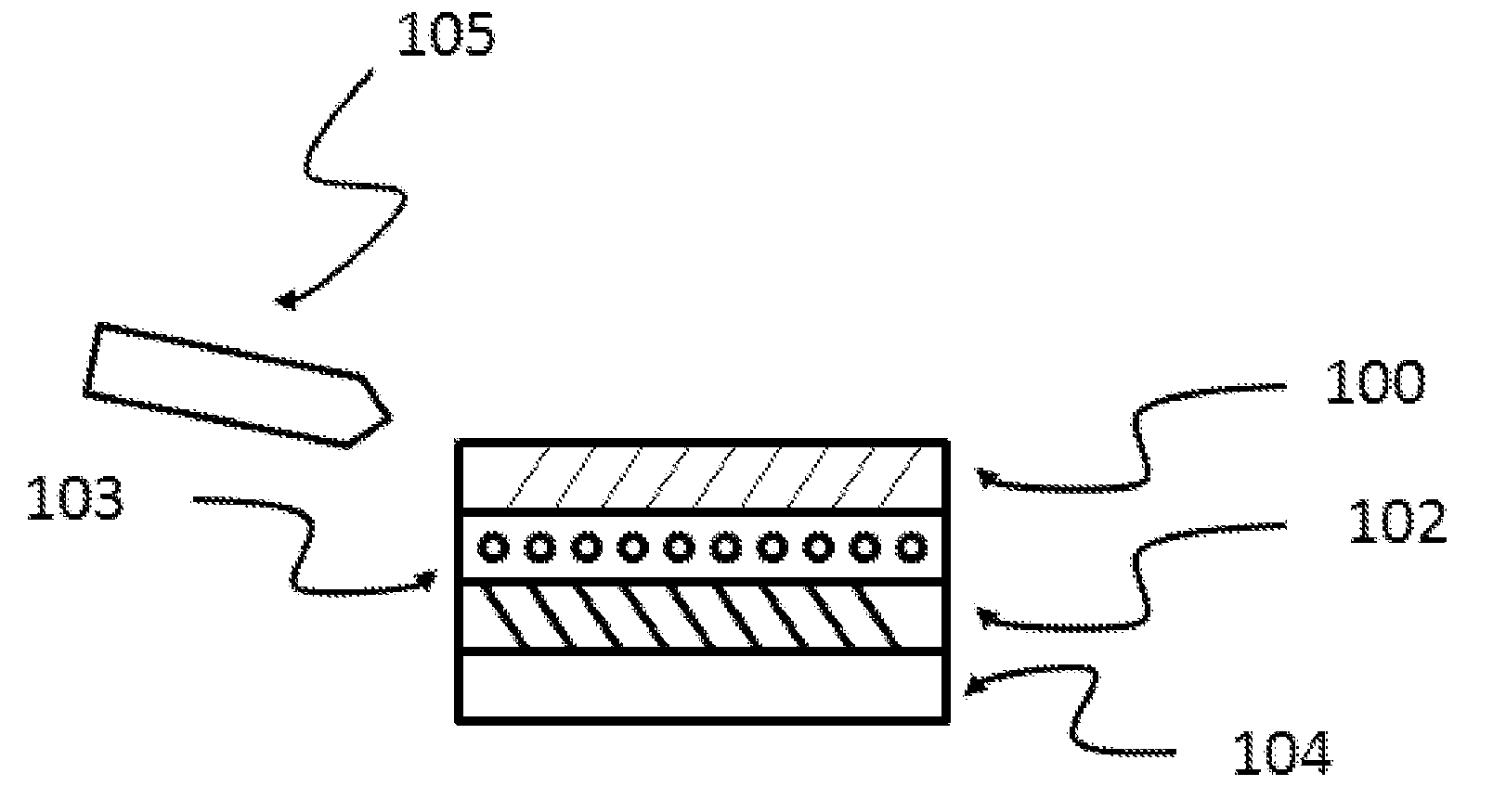
Porous thin-film-deposition substrate, electron emitting element, methods of producing them, and switching element and display element
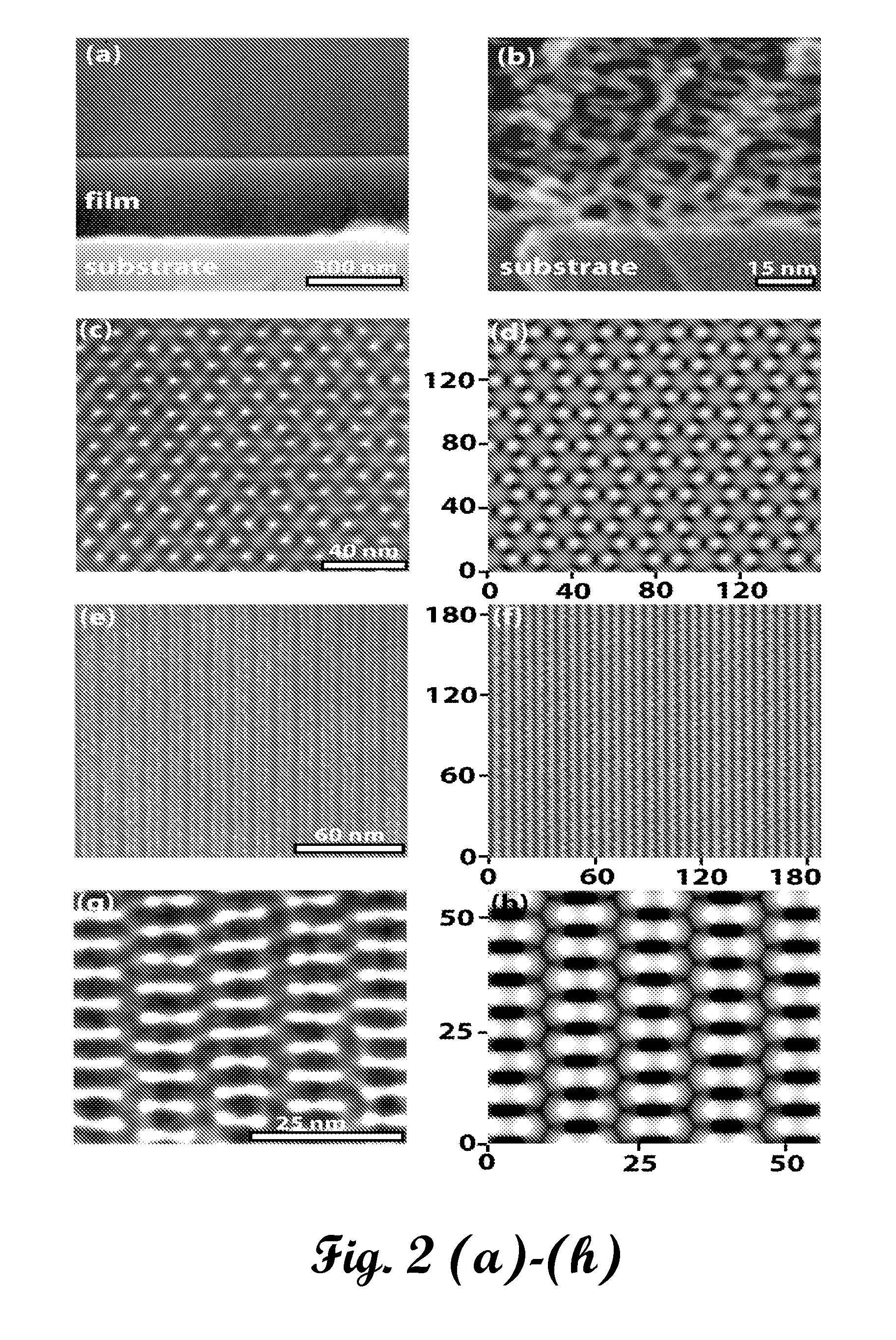
A method of producing a porous thin-film-deposition substrate, which has the steps of: placing onto a substrate that has an electrostatic charge on its surface, fine particles with a surface electrostatic charge opposite to the electrostatic charge of the substrate surface, depositing a thin film on the fine-particle-placed substrate, and then removing the fine particles to form fine pores in the thin film; further, a method of producing an electron emitting element, which has the steps of: adding a catalyst metal on a substrate, placing fine particles onto the catalyst-added substrate, depositing a thin film on the fine-particle-placed substrate, then removing the fine particles to form fine pores in the film, and growing needle-shaped conductors on the catalyst metal that is exposed on a bottom face of the fine pore.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
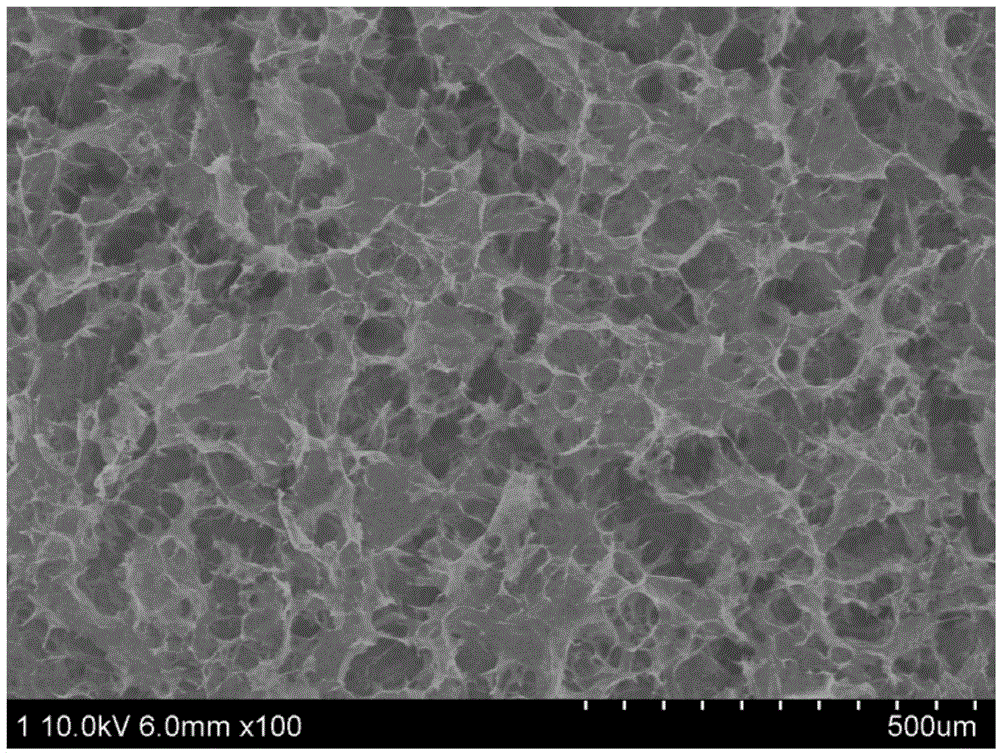
Porous film and preparation method of porous film
The invention discloses a porous film and a preparation method of the porous film, which can easily achieve high porosity and guarantee the formability during the preparation, and are simple and practical in preparation process. The thickness of the porous film is 200-1500[mu]m, the average aperture of the porous film is 0.05-100[mu]m, and the porosity of the porous film is 25-75%. The preparation method includes (1) acquiring a support film which has a porous first material, and forming primary pores in the first material; (2) preparing slurry containing a powder-like second material; (3) coating the support film with the slurry to prepare a base substrate; (4) sintering the base substrate, generating a porous third material through the reaction between the first material and the second material during the sintering, and further generating secondary pores communicated with the primary pores; and (5) cooling the base substrate to obtain the porous film after the sintering. The porous film at least contains the primary pores and the secondary pores, so that the porous film is easy to achieve high porosity.
Owner:CHENGDU INTERMENT TECH
Porous thin film and preparation method for porous thin film
The invention discloses a porous thin film and a preparation method for the porous thin film which are easy to achieve the high porosity, guarantee the possible formability in preparation and are simple and practical in preparation technology. The thickness of the porous thin film is 5-200Mum, the average pore size is 0.05-100Mum, and the porosity is 25-75%. The preparation method comprises the steps that 1, a support film is obtained, the support film is provided with a porous-shaped first material, and preliminary pores are formed in the first material; 2, a slurry is prepared, and the slurry contains a powdered second material; 3, the support film is coated with the slurry and then made into a rough-body; 4, the rough-body is sintered, auto-reaction happens to the second material in sintering, a porous third material is generated, and then secondary pores communicated with the preliminary pores are generated; 5, the porous thin film is obtained by cooling after the sintering. Due to the fact that at least the preliminary pores and the secondary pores are contained, the high porosity of the porous thin film is easy to achieve.
Owner:CHENGDU INTERMENT TECH
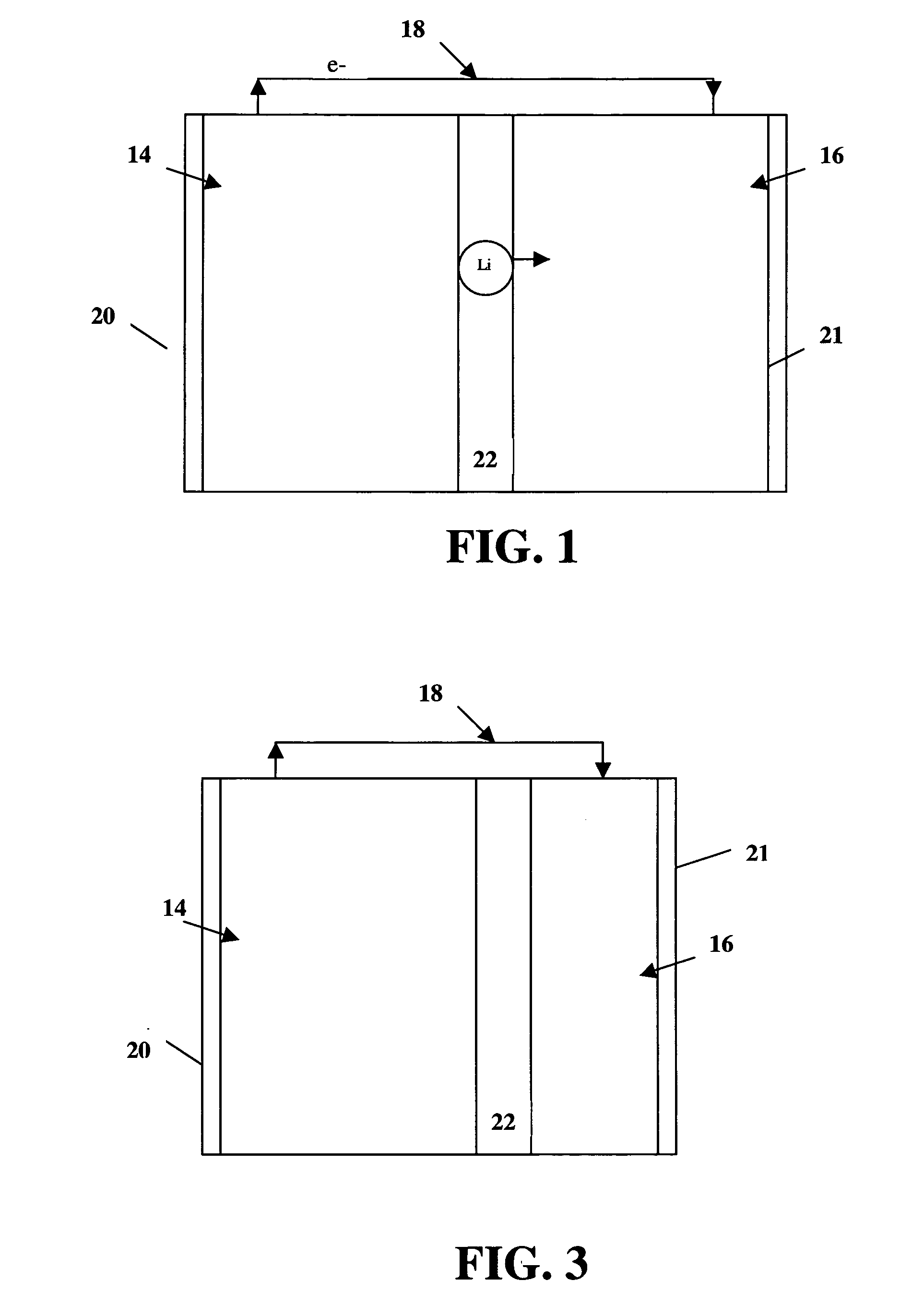
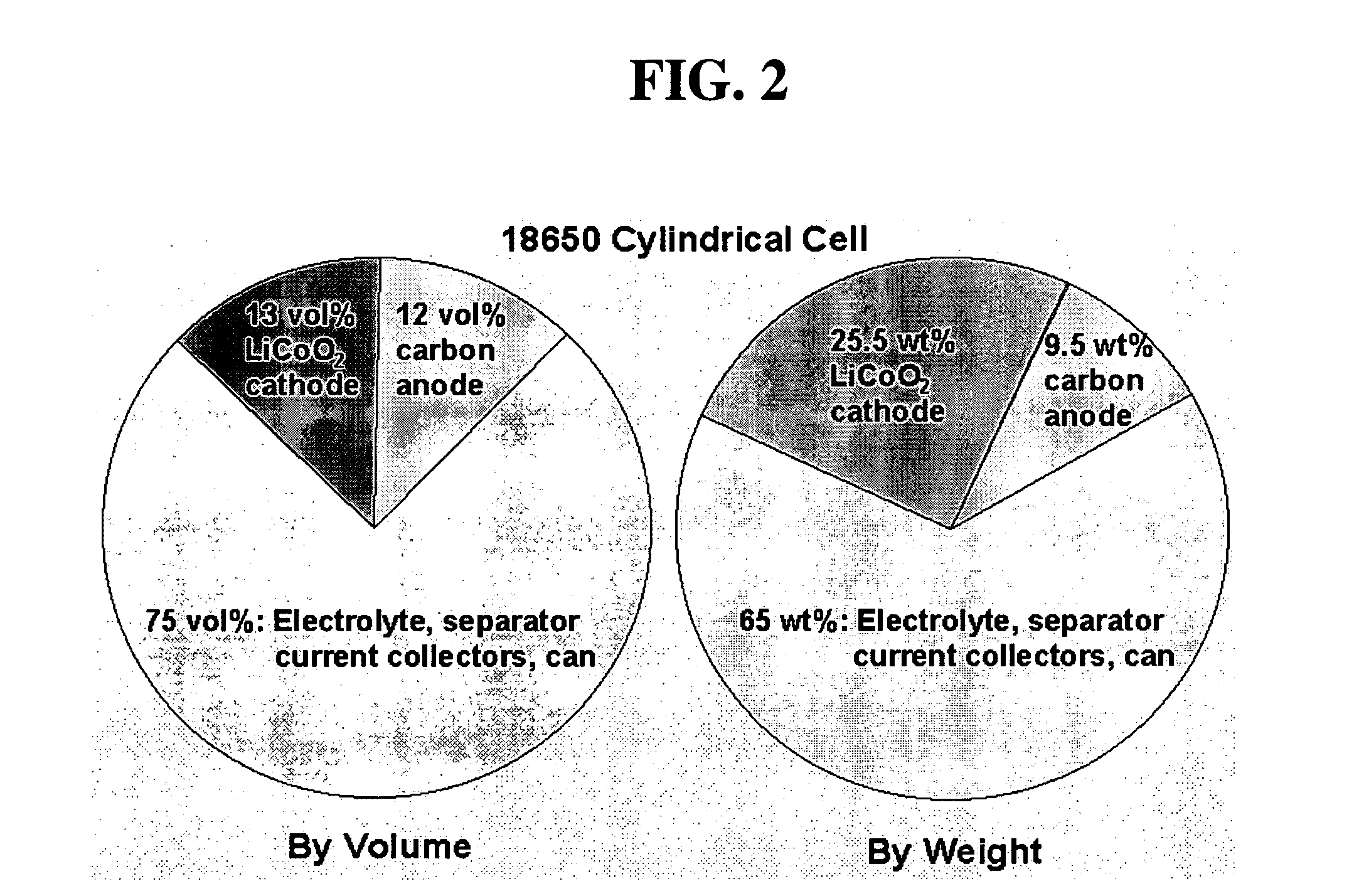
High energy and power density electrochemical cells
ActiveUS20060292444A1Improve electrochemical performanceExtreme safetyPhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesHigh energyMetalloid
The energy density of the entire cell may be improved while retaining high power density by use of an alkali metal transition metal polyanion compound as the cathode and a thin film metal or metalloid anode. The thin film anode may be initially unalloyed or partially unalloyed. During use, the thin film anode may be only partially unalloyed relative to the theoretical maximum. The high volumetric capacity of the metal anode makes it possible to use a dense or porous thin film anode in conjunction with a relatively thin particle-based cathode to thereby improve the energy density of the cell.
Owner:A123 SYSTEMS LLC
Surface-treated microporous membrane and electrochemical device prepared thereby
ActiveUS20090291360A1Improve adhesionAvoid breakingSecondary cellsCell component detailsPorous substrateElectrochemistry
Disclosed is a porous film comprising: (a) a porous substrate having pores; and (b) a coating layer formed on at least one region selected from the group consisting of a surface of the substrate and a part of the pores present in the substrate, wherein the coating layer comprises styrene-butadiene rubber. An electrochemical device using the porous film as a separator is also disclosed. The porous film is coated with a styrene-butadiene polymer, whose rubbery characteristics can be controlled, and thus provides improved scratch resistance and adhesion to other substrates. When the porous film is used as a separator for an electrochemical device, it is possible to improve the safety of the electrochemical device and to prevent degradation in the quality of the electrochemical device.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD +1
Mesoscopic solar cell based on perovskite-kind light absorption material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105405973AIncrease currentHigh voltageFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHole transport layerElectron blocking layer
The invention discloses a mesoscopic solar cell based on a perovskite-kind light absorption material. The mesoscopic solar cell comprises a glass substrate, a transparent conductive layer, a hole blocking layer, an electron transport layer and a back electrode; and the hole blocking layer is a compact layer, the electron transport layer is a porous thin film, a porous electron blocking layer is further disposed between the electron transport layer and the back electrode, and the electron transport layer and the electron blocking layer are filled with the perovskite-kind light absorption material. Or the mesoscopic solar cell comprises a glass substrate, a transparent conductive layer, a hole transport layer and a back electrode; and the hole transport layer is a porous thin film, a compact electron blocking layer is further disposed between the hole transport layer and the transparent conductive layer, and the hole transport layer is filled with the perovskite-kind light absorption material. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the mesoscopic solar cell. The cell has optimized structure, the filled perovskite material in mesoporous is more, morphology is good, charge transmission performance is improved, cell photoelectric conversion efficiency is greatly improved, and long-term illumination stability of the cell is substantially improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of fabricating porous film structure using dry processes and porous film structures fabricated by the same
InactiveUS20130052475A1Easy to controlSolve the real problemPaper/cardboard articlesThin material handlingAlloyOptoelectronics
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Pellicle and photomask assembly including the same
ActiveUS20170038676A1Improve productivityHigh resolutionNanotechnologyOriginals for photomechanical treatmentNanowireMaterials science
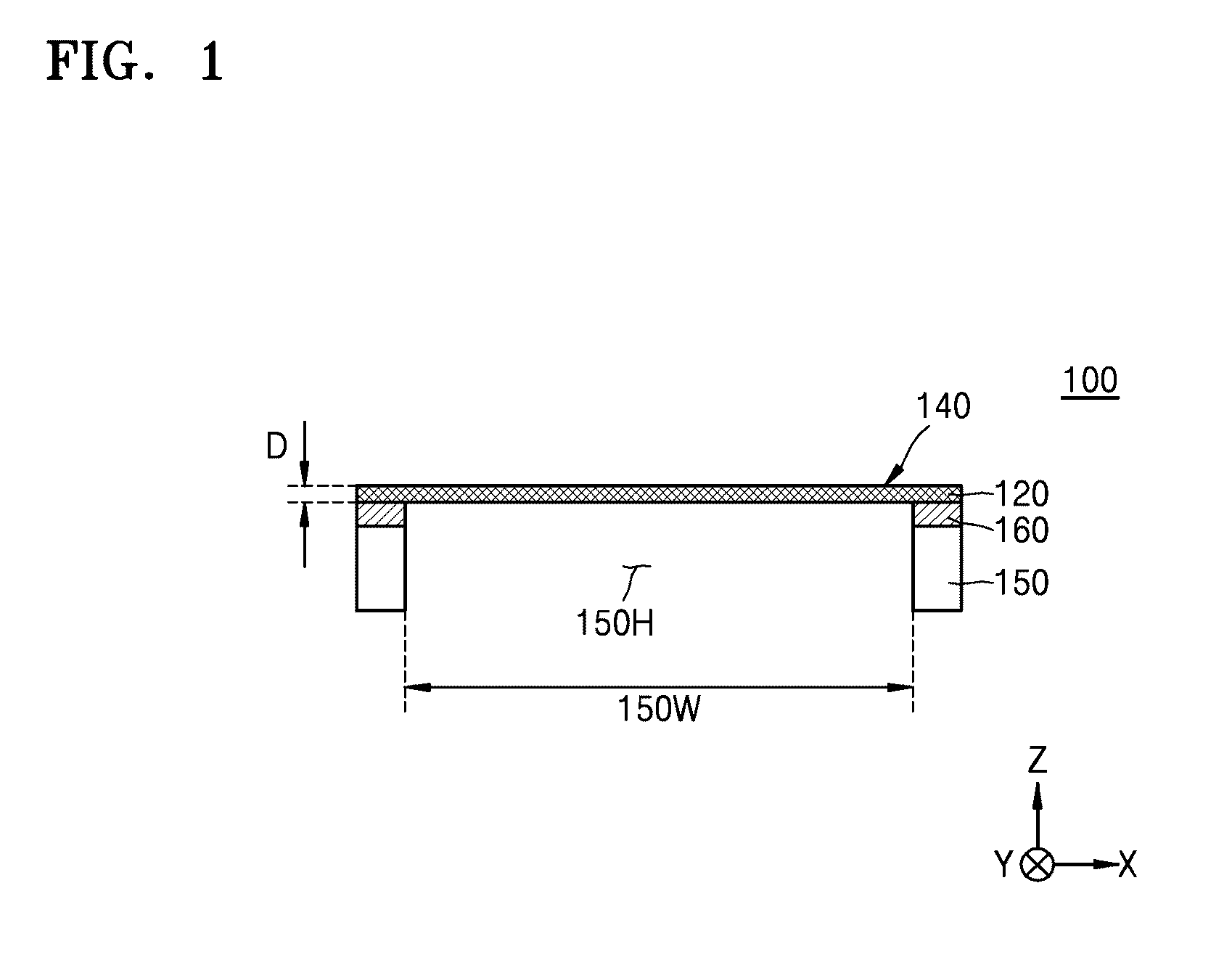
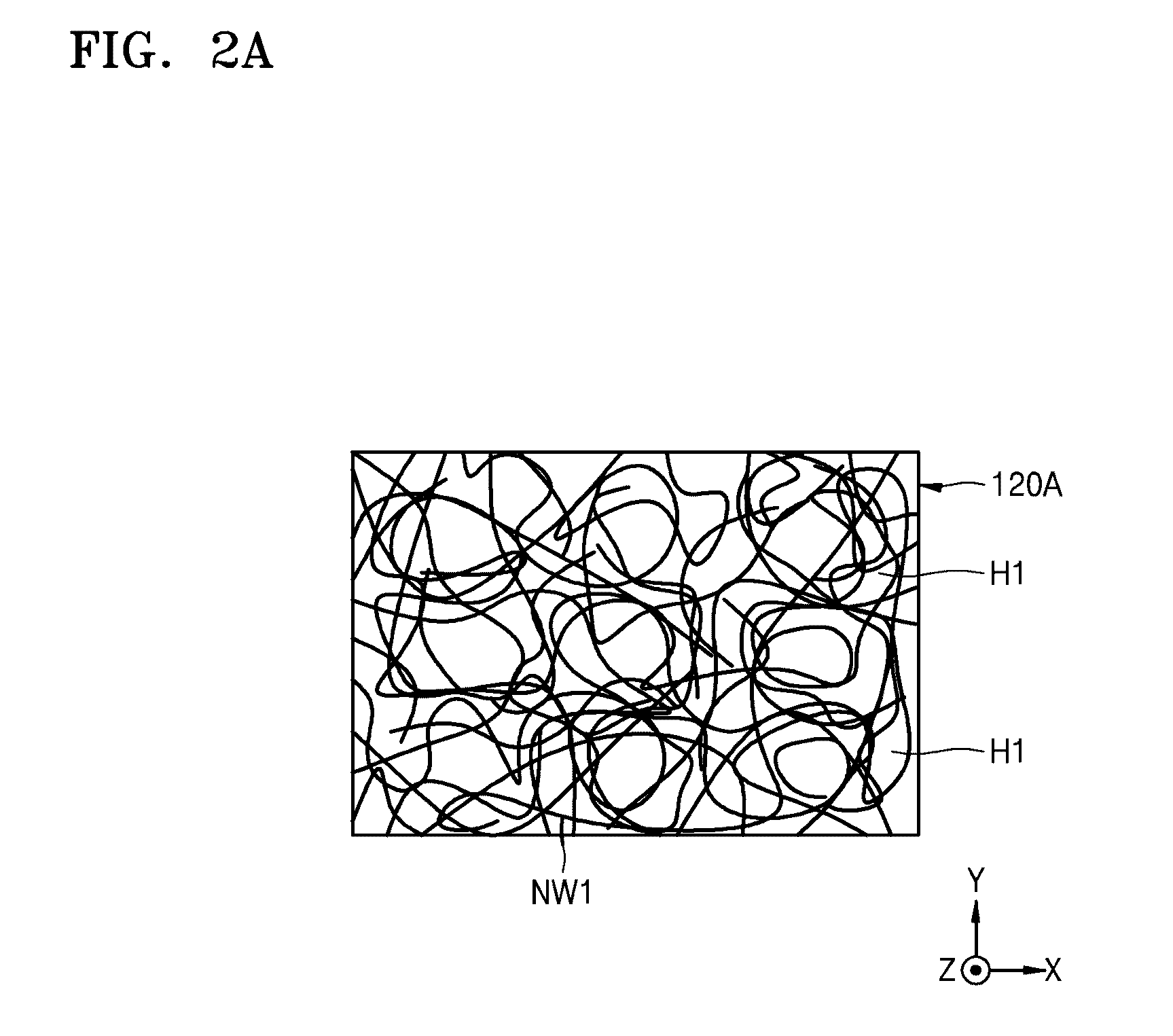
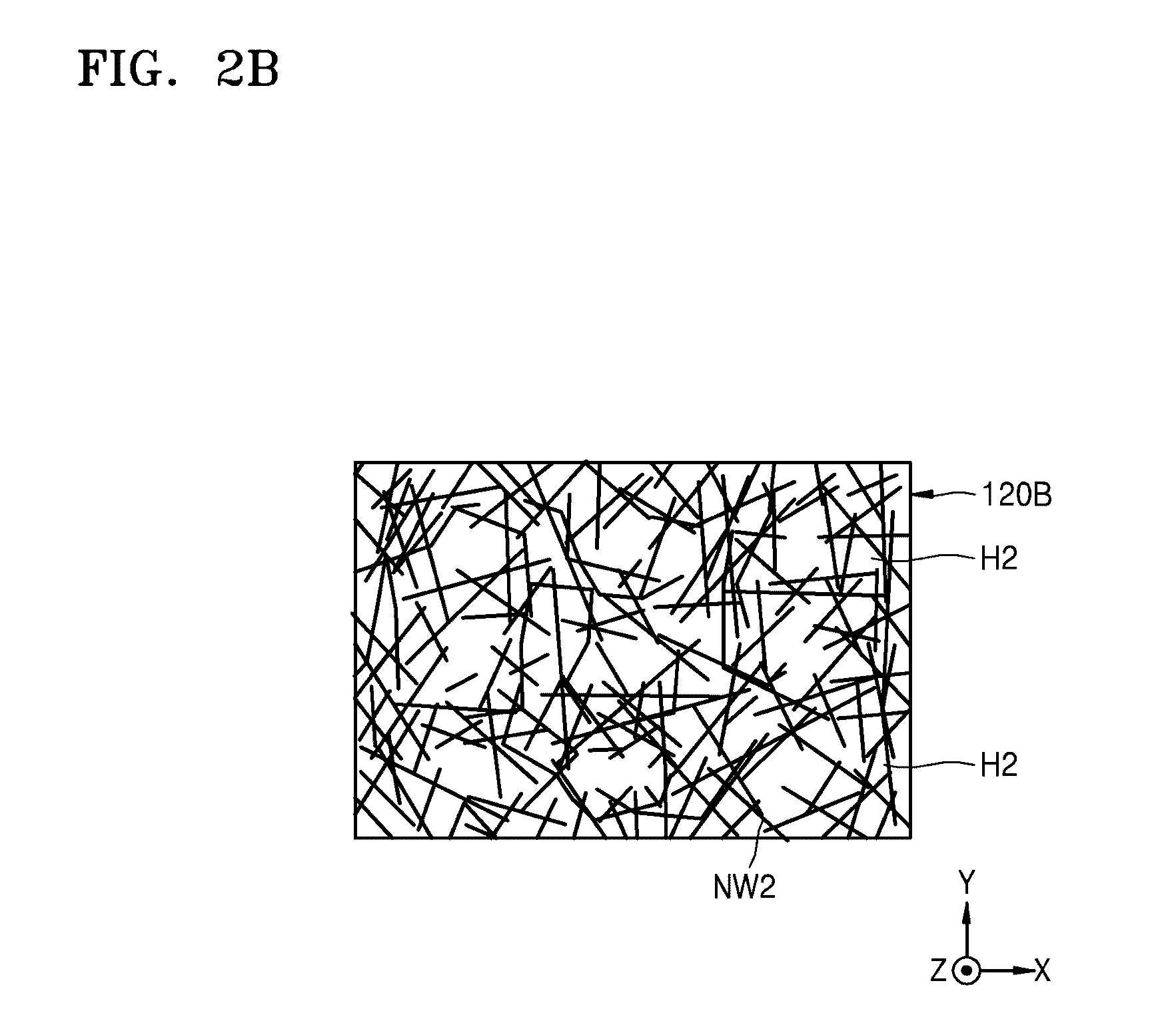
A pellicle includes a pellicle membrane, which includes a porous thin film. The porous thin film includes a plurality of nanowires, which are arranged across one another to form a net structure. A photomask assembly includes the pellicle and a photomask, wherein the pellicle is fixed to a surface of the photomask.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
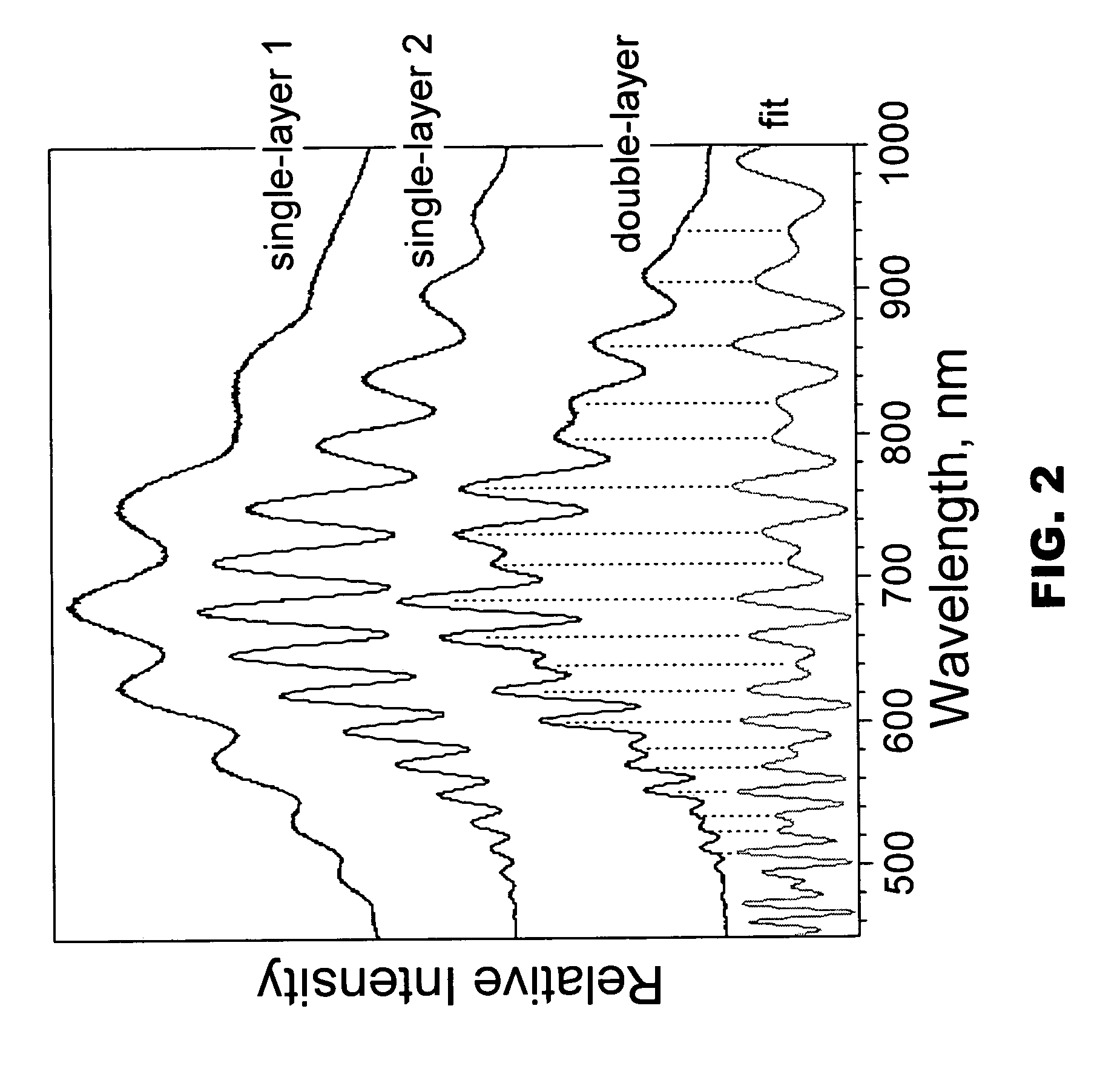
Porous microstructure multi layer spectroscopy and biosensing
InactiveUS20070108465A1Scattering properties measurementsSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionSpectroscopyPorous silicon
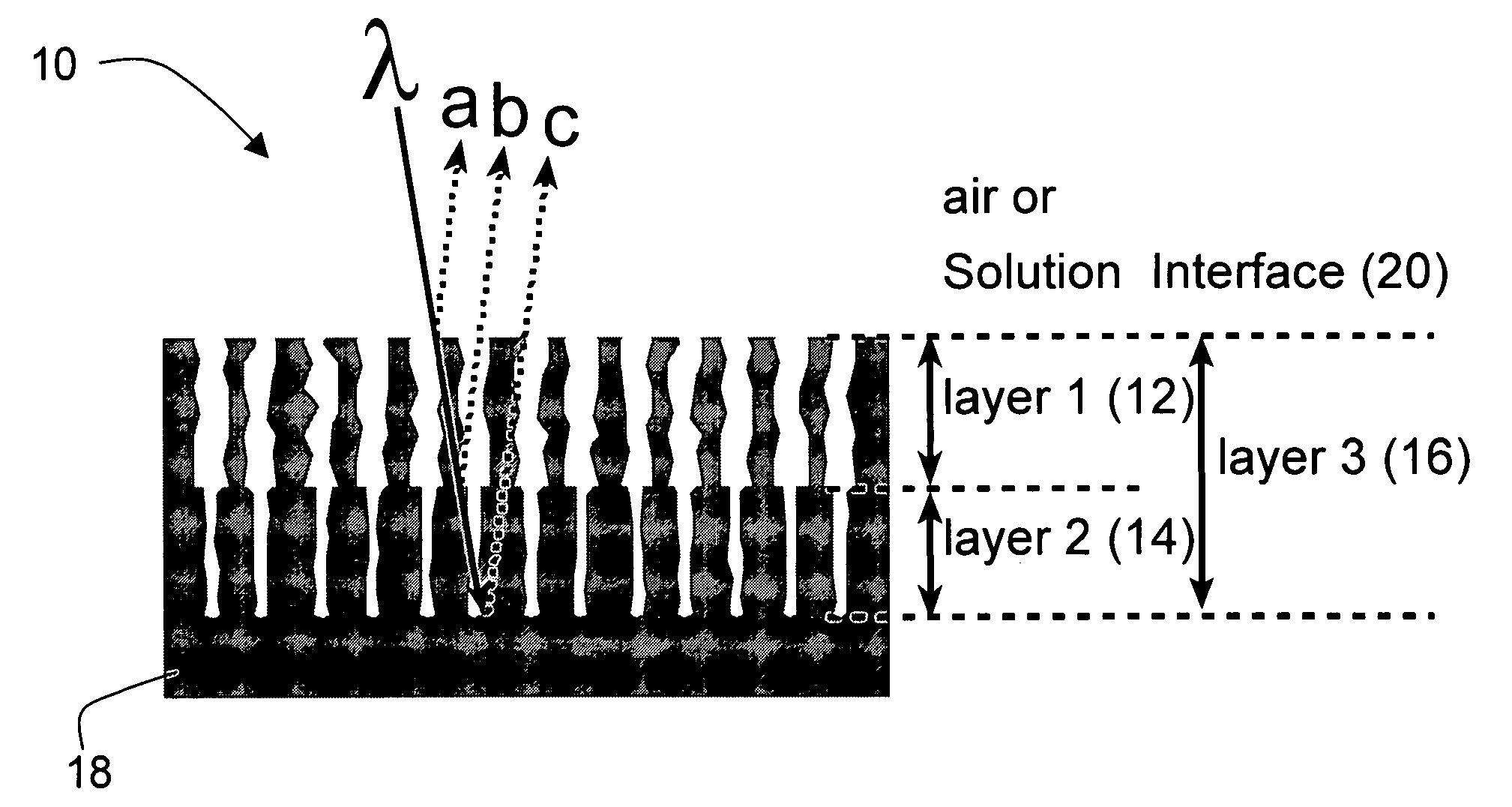
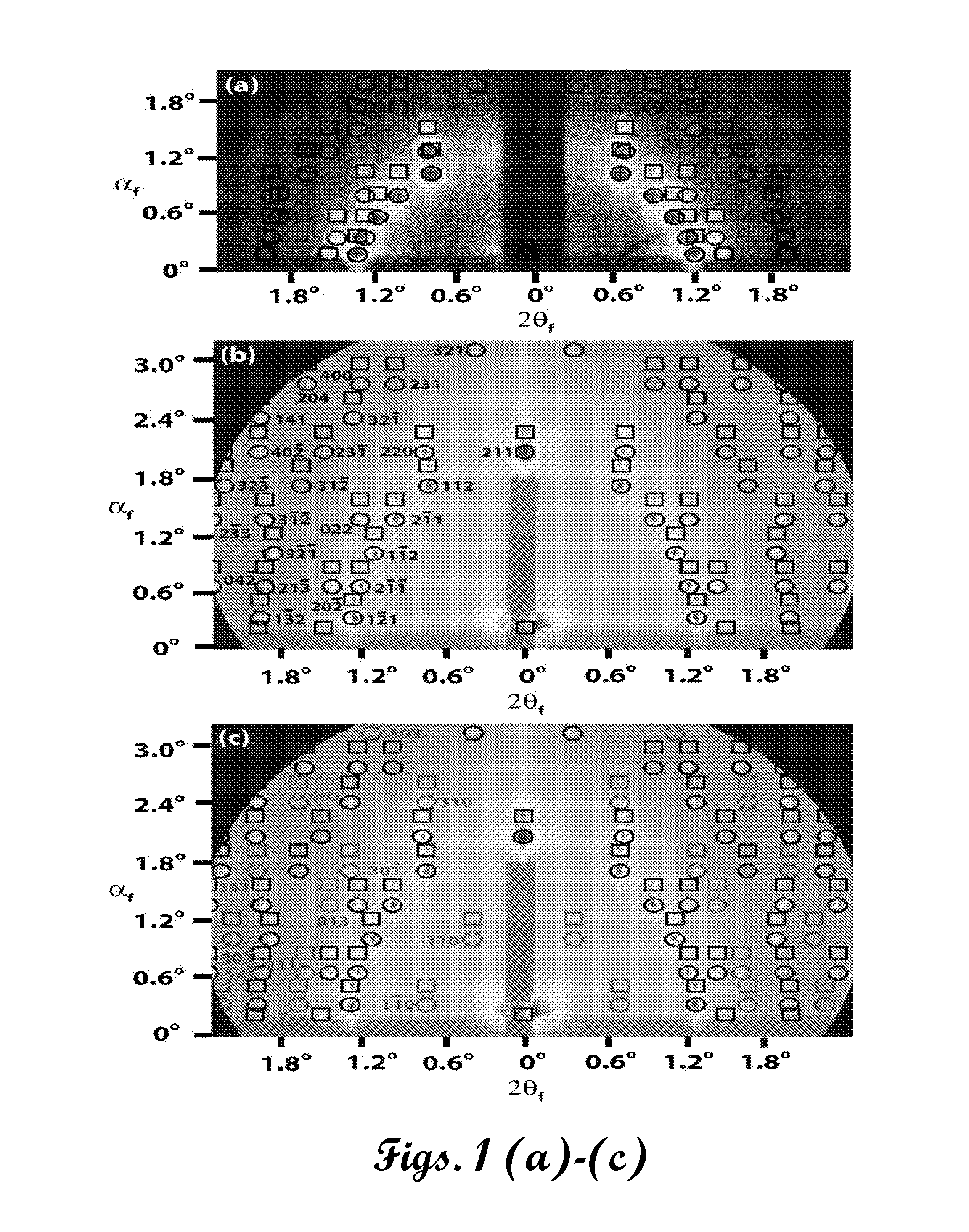
A preferred embodiment biosensor is a multi-layer micro-porous thin film structure. Pores in a top layer of the micro-porous thin film structure are sized to accept a first molecule of interest. Pores in a second layer of the micro-porous thin film structure are smaller than the pores in the top layer and are sized to accept a second molecule of interest that is smaller than the first molecule of interest. The pores in the second layer are too small to accept the first molecule of interest. The pores in the top layer and the pores in the second layer are sized and arranged such that light reflected from the multi-layer micro-porous thin film structure produces multiple superimposed interference patterns that can be resolved. In preferred embodiments, the multi-layer micro-porous thin film structure is a porous silicon thin film multi-layer structure formed on a silicon substrate, such as a silicon wafer. Specific and nonspecific binding can be detected with biosensors of the invention. The position of peaks in the Fourier transform of the reflection spectrum and the shift in peak amplitudes can be used to determine the presence and quantity of targeted biological molecules of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Secondary battery and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20060105245A1High porosityEasy to getAlkaline accumulatorsElectrode manufacturing processesSlurryBattery cell
In a secondary battery including a positive electrode, a negative electrode and a porous film bonded to the surface of at least one of the positive electrode and the negative electrode, the porous film includes ceramic particles and a binder, and the ceramic particles include polycrystalline particles obtained by mechanically crushing a fired material comprising a ceramic that is directly synthesized from a ceramic precursor. The porous film has a porosity of 40 to 80%, for example. The porous film can be formed by a method including the steps of: obtaining a fired material comprising a ceramic from a ceramic precursor; obtaining ceramic particles by mechanically crushing the fired material of the ceramic; obtaining a slurry including the ceramic particles and a binder; and applying the slurry onto the surface of an electrode, followed by drying.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Porous films by backfilling with reactive compounds
ActiveUS8277899B2Improve functionality and durabilityImprove propertiesSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesUltimate tensile strengthWear resistance
The invention provides methods for modifying one or more properties of porous thin films. In such methods, a formulation comprising a reactive species is applied to the porous thin film and allowed to crosslink. In some embodiments, the crosslinked network thus formed imparts increased mechanical strength and wear resistance to the porous thin films.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Methods of making lithium ion battery separators
ActiveUS8470898B2Promote formationImprove thermal stabilityCell component detailsNon solventPolymer science
A porous thin-film polymer separator for use in a lithium ion battery may be formed by a phase separation method in which hydrophobic-treated ceramic particles are used to help induce the formation of a tortuous, interconnected network of pores coextensively across the thickness of the separator. As part of the phase separation method, a wet thin-film layer is formed from a polymer slurry that comprises a polymer solvent in which a polymer material is dissolved and the hydrophobic-treated ceramic particles are dispersed. The wet thin-film layer is subsequently exposed to a polymer non-solvent to form a solvent-exchanged thin-film precipitated polymer layer which is then heated to produce the separator.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Non-flammable quasi-solid electrolyte-separator layer product for lithium battery applications
ActiveUS20150024248A1Reduce electrical conductivityLow ionic conductivityFinal product manufactureLi-accumulatorsGlass fiberCelsius Degree
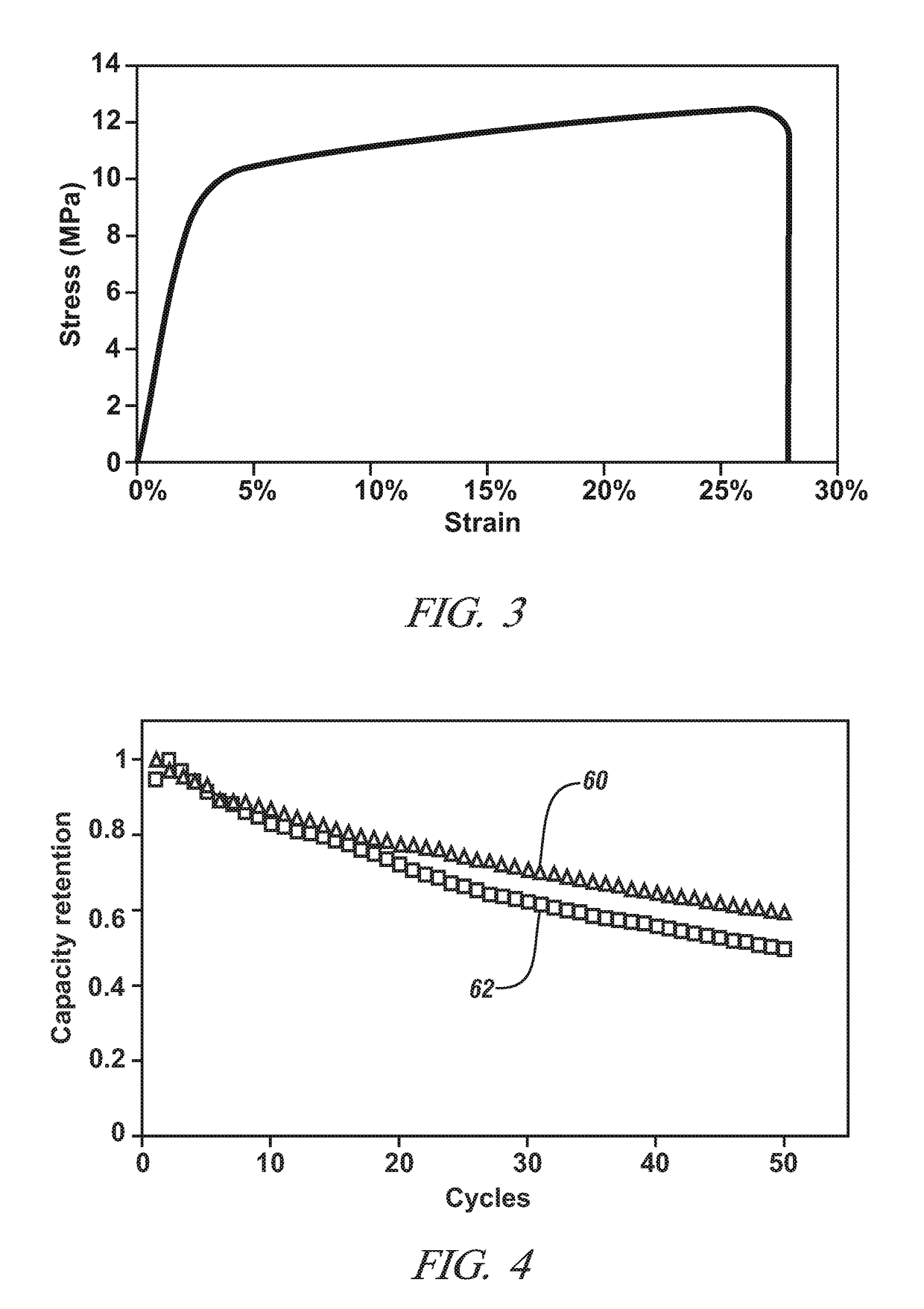
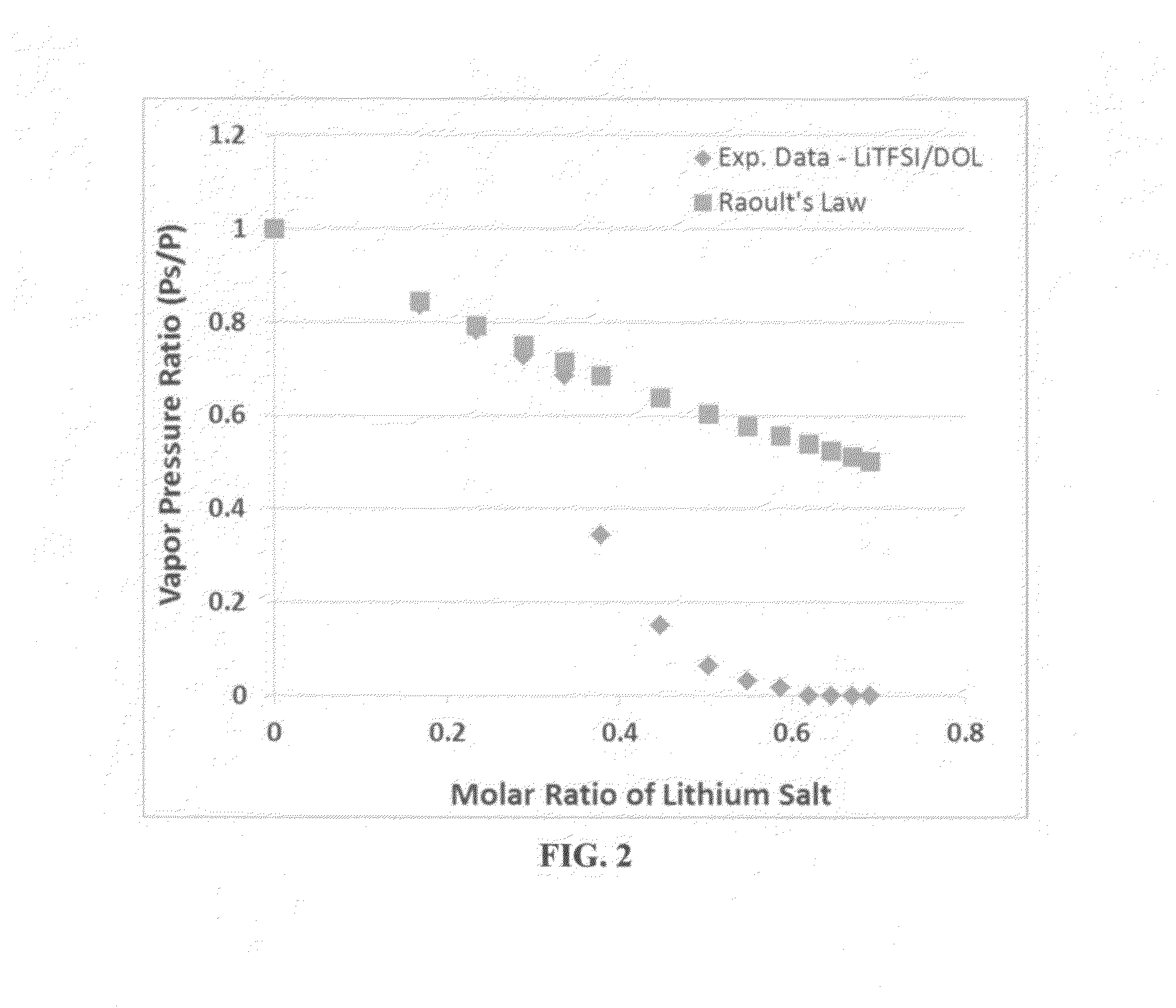
A separator-electrolyte layer product for use in a lithium battery, comprising: (a) a porous thin-film separator selected from a porous polymer film, a porous mat, fabric, or paper made of polymer or glass fibers, or a combination thereof, wherein the separator has a thickness less than 500 μm; and (b) a non-flammable quasi-solid electrolyte containing a lithium salt dissolved in a liquid solvent up to a concentration no less than 3 M; wherein the porous thin-film separator is coated with the quasi-solid electrolyte so that the layer product exhibits a vapor pressure less than 0.01 kPa when measured at 20° C., a vapor pressure less than 60% of the vapor pressure of the liquid solvent alone, a flash point at least 20 degrees Celsius higher than a flash point of the first liquid solvent alone, a flash point higher than 150° C., or no detectable flash point.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
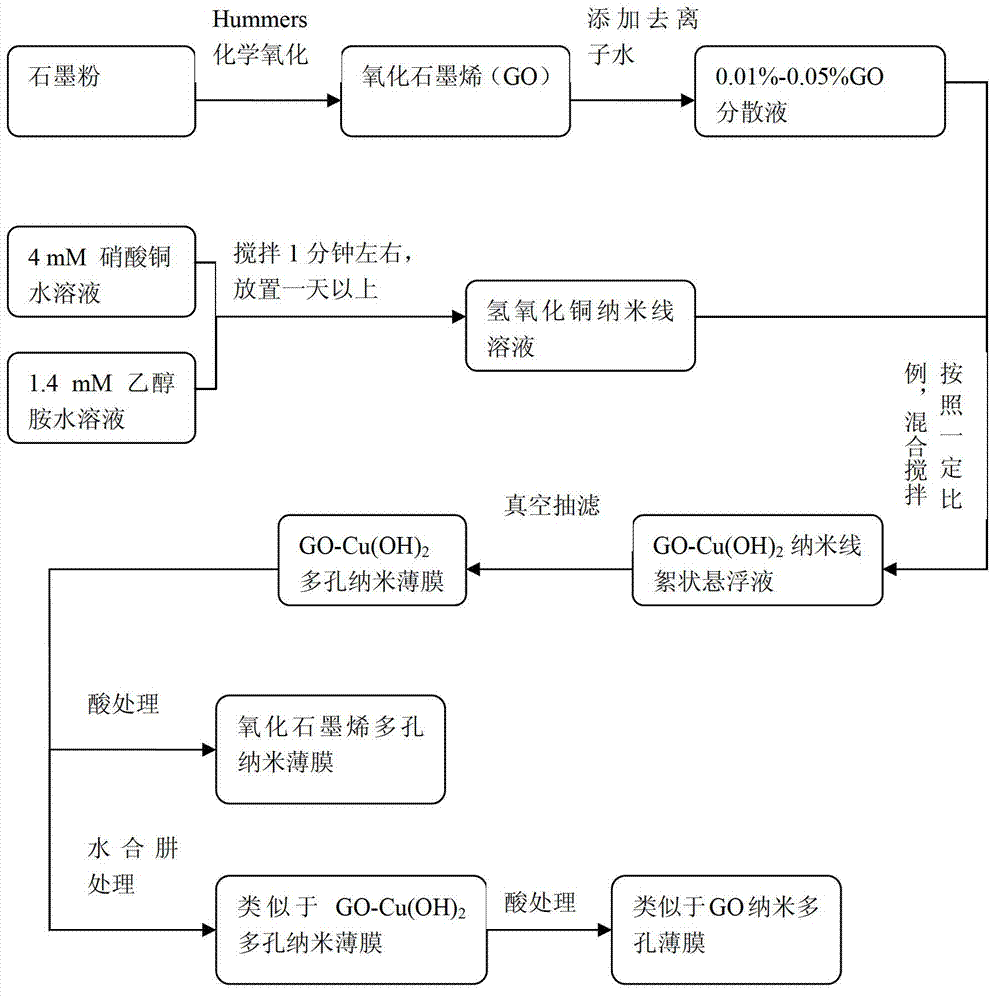
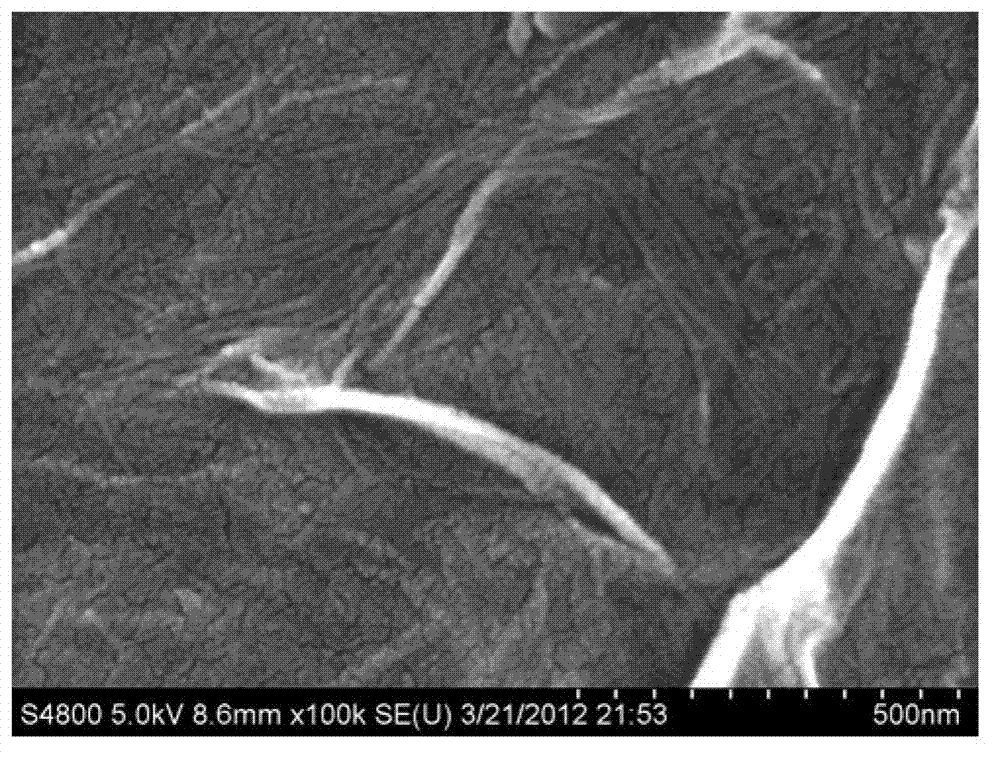
Method for preparing graphene oxide base porous film by using metal hydroxide nanowires and graphene oxide, and application of graphene oxide base porous film
InactiveCN102814124AImprove mechanical propertiesGood chemical stabilitySemi-permeable membranesCopper oxides/halidesEthylenediamineNanowire
The present invention discloses a method for preparing a graphene oxide base porous film by using metal hydroxide nanowires and graphene oxide, and an application of the graphene oxide base porous film. According to the present invention, a chemical oxidation ultrasonic dispersion method is adopted to prepare a diluent negatively charged graphene oxide (GO) dispersion liquid with a content of 0.01-0.05%; the GO dispersion liquid is mixed with a positively charged metal hydroxide nanowire solution with a concentration of 0.15-1.2 mM, wherein the diameter is nanometer scale, and the length is micrometer scale; stirring is performed for 5-30 minutes; vacuum suction filtration (negative pressure of 50-85 kPa) is performed on a polycarbonate porous film; a hydrazine hydrate treatment is performed for 5-60 minutes; and an acid (HCl, H2SO4, HNO3) or a complexing agent ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) is adopted to remove the metal hydroxide nanowires to obtain a nanometer GO porous separation film formed by the left pores through removing the nanowires, wherein molecules with a molecular weight of about 350 daltons can be effectively separated with the separation film. The graphene oxide base porous film prepared by the method of the present invention has a separation performance similar to a nanometer graphene oxide separation film, and further is a porous separation film with good separation efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Foam Dressing with Integral Porous Film
Wound dressings and wound inserts comprising a porous film layer and at least a channel, wound inserts of forming wound inserts comprising a porous film layer and at least a channel, and wound-treatment wound inserts.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
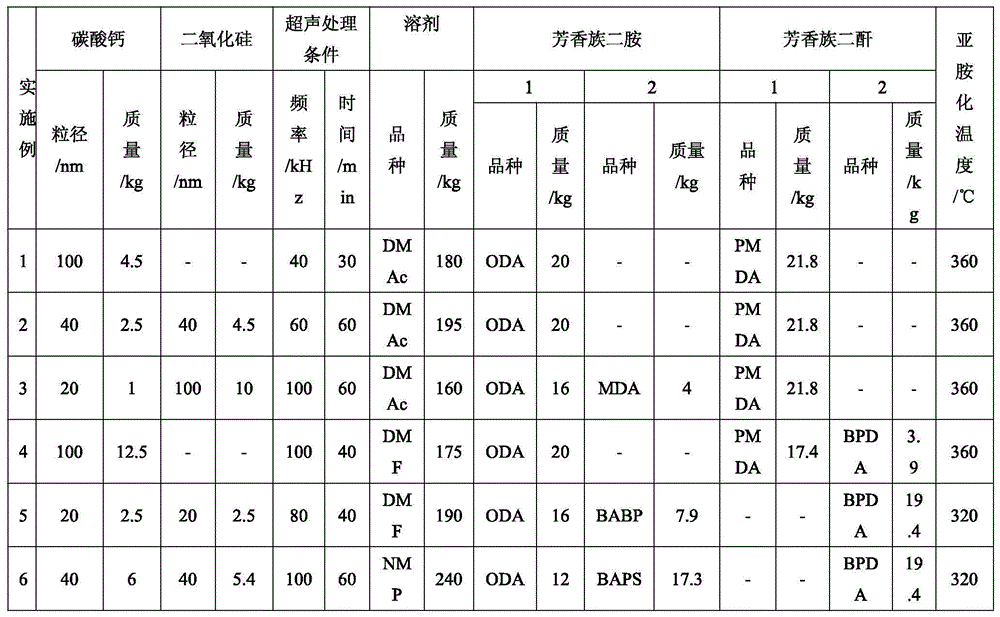
Preparation method of porous low-dielectric polyimide thin films
ActiveCN104910409AImprove performanceRaw materials are easy to obtainOrganic filmElectronic industry
The invention belongs to the organic film preparation field, and relates to a preparation method of porous low-dielectric polyimide thin films. The method includes the following steps: (1) preparation of a reinforcing filler suspension; (2) preparation of a polyamide acid compound solution; (3) preparation of polyimide thin films; and (4) obtaining of the porous polyimide thin films. Calcium carbonate is used as a pore-forming agent raw material, the calcium carbonate is removed by dilute hydrochloric acid to obtain the porous thin films, raw materials are simple and are easy to obtained, and complex operations are not needed; at the same time, the pore size and porosity of the thin films can be controlled directly through control of the particle size and content of the calcium carbonate, and various porous low-dielectric polyimide thin films with excellent performance are prepared, can be applied in substrate materials of electrician and electronic industries and are especially suitable for electronic materials of large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Resin composition for preparing micro-porous thin film and micro-porous thin film
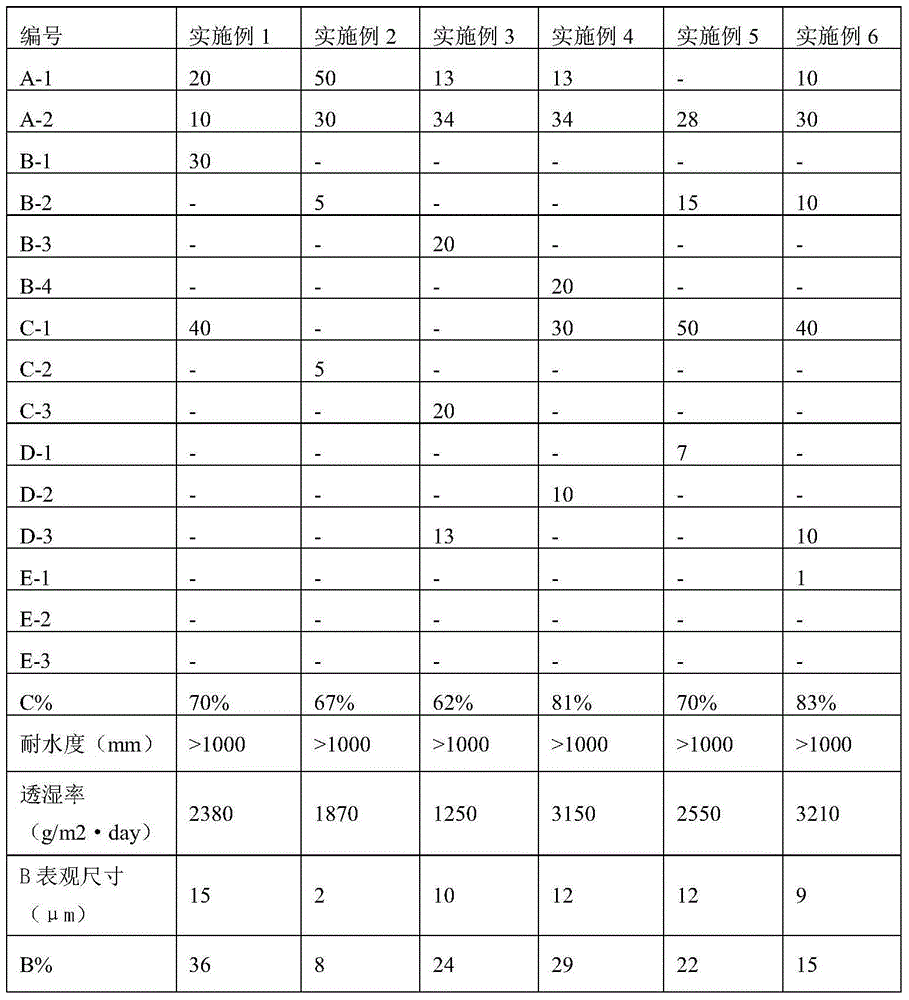
The invention relates to a resin composition for preparing a micro-porous thin film and the prepared micro-porous thin film. The composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-80 parts of polylactic resin A, 5-50 parts of a resin component B which is incompatible with polylactic acid and 5-50 parts of filler C, wherein the percentage by weight of the filler C which is fully in the phase B or partially in the phase B is as follows: C% is greater than (0.9*B%+10%) and B% is the volume percentage of B in the resin composition. The water vapor permeability of the micro-porous thin film prepared from the resin composition is higher than the water vapor permeability of a thin film where the filler is averagely distributed. The resin composition for preparing the micro-porous thin film provided by the invention can be used for preparing the micro-porous thin film and can be used in the field of hygienic products, building materials and the like.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
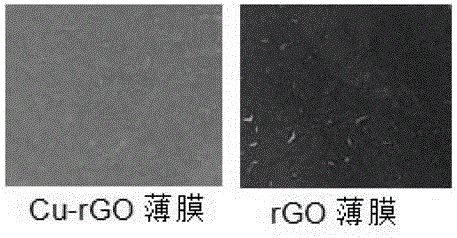
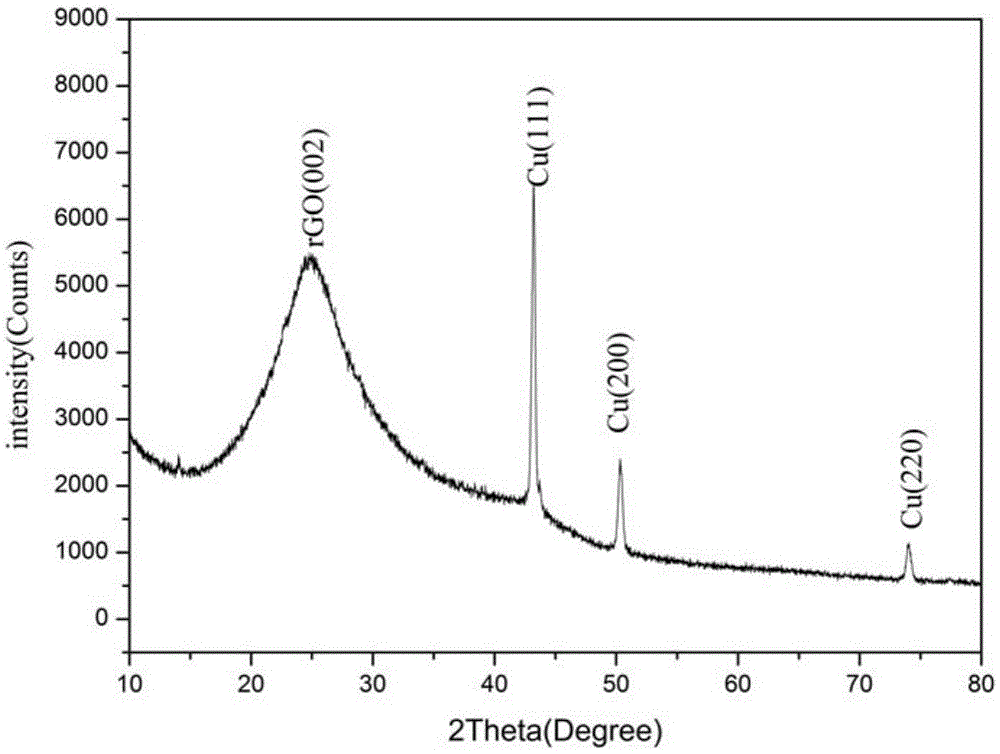
Preparation method and application of Cu nanowire-reduced graphene oxide three-dimensional porous film
InactiveCN105583408ALarge specific surface areaMild conditionsElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementComposite filmFiltration
The invention provides a preparation method of a Cu nanowire-reduced graphene oxide-PDMS composite strain sensor, and belongs to the field of reduced graphene oxide composite sensors. The preparation method comprises the steps that copper nanowires are added into graphene oxide containing ascorbic acid, Cu nanowire-reduced graphene oxide hydrogel is obtained after reducing, and a Cu nanowire-reduced graphene oxide film with the three-dimensional porous appearance is obtained through washing, stir-breaking and suction filtration film formation; and then liquid PDMS is poured, vacuum filtration is carried out to remove bubbles, the liquid PDMS is subjected to cross-linking and curing at the temperature of 70 DEG C, and finally the Cu nanowire-reduced graphene oxide-PDMS composite strain sensor is obtained. The composite film is large in specific surface area and excellent in electric conductivity and mechanical performance, and the preparation method of a Cu nanowire-reduced graphene oxide-PDMS composite is mild in condition, simple, practical, controllable in process parameter, low in cost and high in repeatability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Porous polypropylene film, process for producing the same, and absorbent article employing the film
InactiveUS6861132B2Improve breathabilityImprove textureOrganic chemistryFibre treatmentWater vapor permeabilityPolypropylene
Disclosed is a porous film made of a resin composition containing (I) (i) a propylene-ethylene copolymer or (ii) a polypropylene-based resin mixture containing a propylene-ethylene copolymer, each having an ethylene content of 3.0 to 7.0 wt. % and an MFR measured at 230° C. of 2.0 to 4.0 g / 10 min and (II) a β-crystal nucleating agent; the film having a porosity of 20 to 80%, a Gurley air permeability of 5,000 sec / 100 cc or lower as measured according to JIS P-8117, a water vapor permeability of 2,000 g / m2·24 h or higher as measured according to JIS Z-0208 and a water pressure resistance of 75 kPa or higher as measured according to JIS L-1092 using an aqueous surfactant solution; a process for producing the same; and an absorbent article employing the porous film as a backsheet.
Owner:NEW JAPAN CHEM CO
Method for preparing porous film by adopting high molecular weight polyolefin and product and application thereof
ActiveCN102153776AHigh mechanical strengthHigh temperature puncture strengthCell component detailsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The invention discloses a method for preparing a porous film by adopting high molecular weight polyolefin. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing soaking treatment on the high molecular weight polyolefin; (2) blending the soaked high molecular weight polyolefin and materials such as thermoplastic resin, auxiliary agent and the like to prepare blended master batch; (3) preparing the obtained blended master batch into a film material; and (4) extracting the film material to obtain the porous film. The porous film has the characteristics of high mechanical strength, high porosity, uniform aperture size, high ion permeability, excellent dielectric property and the like, can be used as a lithium ion battery diaphragm, and has better safety; and the method has simple process and easily controlled conditions, is suitable for mechanized large-scale production, and has low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:LIAOYUAN HONGTU LI ION BATTERY DIAPHRAGM TECH
Organic/inorganic composite porous thin film and electrochemical energy storing device using same
InactiveCN102969473AHigh mechanical strengthImprove heat shrink resistanceSecondary cellsCell component detailsOrganic basePhosphate
The invention discloses an organic / inorganic composite porous thin film and an electrochemical energy storing device using the same. The organic / inorganic composite porous thin film comprises a porous organic base material and an active layer attached on the porous organic base material, wherein the active layer comprises inorganic particles and a binder, and the inorganic particles are one or mixture of sulfate, phosphate, metal fluoride and lithium salt. The organic / inorganic composite porous thin film is adopted as an isolating film for the electrochemical energy storing device. Compared with the prior art, the organic / inorganic composite porous thin film takes substances which do not react with hydrofluoric acid as the inorganic particles of the active layer, and therefore, the electrochemical energy storing device adopting the organic / inorganic composite porous thin film has the advantages of good circulating storage performance, high voltage resistance performance and safety performance.
Owner:CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECH CO
Double gyroid structure nanoporous films and nanowire networks
A method of forming a nanoporous film is disclosed. The method comprises forming a coating solution including clusters, surfactant molecules, a solvent, and one of an acid catalyst and a base catalyst. The clusters comprise inorganic groups. The method further comprises aging the coating solution for a time period to select a predetermined phase that will self-assemble and applying the coating solution on a substrate. The method further comprises evaporating the solvent from the coating solution and removing the surfactant molecules to yield the nanoporous film.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Ultra-low fractional area coverage flow diverter for treating aneurysms and vascular diseases
InactiveUS20140249620A1Low profileWithout productionStentsPaper/cardboard articlesIn vivoPseudo aneurysm
A flow diverter is described and fabricated using ultra-thin porous thin-film Nitinol, and is configured for implantation to a treatment site within a vessel for significant reduction in an intra-aneurismal flow velocity and vorticity. Using small size pores in a coverage area of only 10%, a 90% reduction in flow velocity into a pseudo-aneurysm can be achieved, with an almost immediate cessation of flow into an anatomical feature such as aneurysm sac in vivo. The size of the holes can be tailored to be any shape and range in size from 1-400 μm using photolithography and from 5-1000 nm using ebeam lithography.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and method for manufacturing thin film electrode of hydrous ruthenium oxide
InactiveUS20040013799A1Electrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufactureEngineeringElectric field
An apparatus and a method are provided for manufacturing an electrode of hydrous ruthenium oxide thin film. The apparatus comprises an injector for introducing a precursor solution and spraying the precursor solution; a substrate having the precursor solution sprayed thereon; a substrate-supporting base for supporting the substrate and including a halogen lamp therein for heating the substrate; a direct current power supply connected to the substrate-supporting base and the injector; a distance adjuster for adjusting the distance between the substrate-supporting base and the injector; and a temperature controller for controlling the substrate-supporting base. Under a strong electric field, the ruthenium precursor solution is sprayed, to yield a porous thin film electrode having very fine particles. The electrode prepared by the method which is advantageous in terms of simplified preparation process and shorter period of time required for preparation, compared to conventional methods, has more excellent properties than those of a conventional ruthenium oxide electrode for super capacitor or a composite electrode of ruthenium oxide and activated carbon.
Owner:KIM WOO SIK
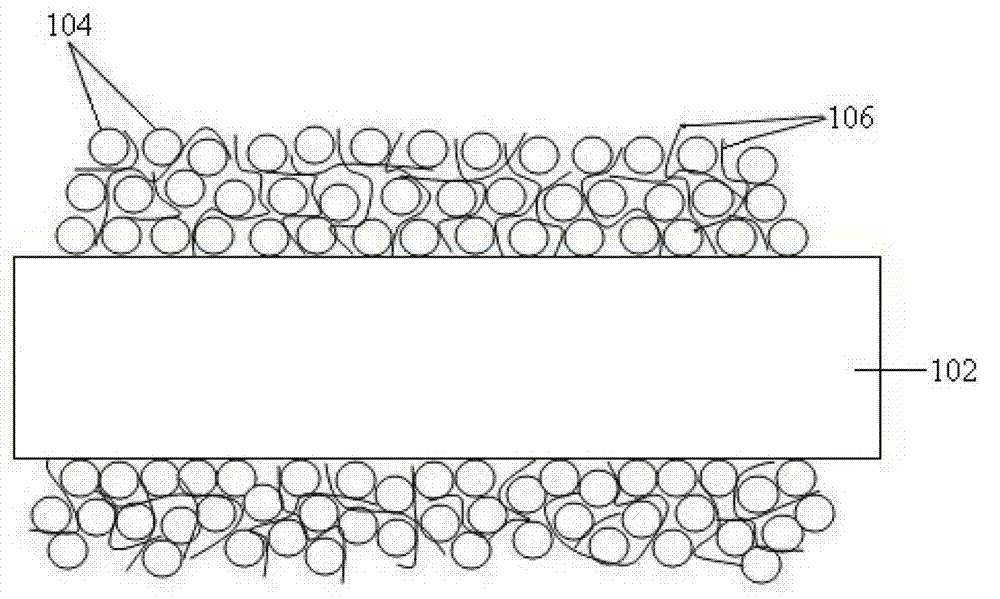
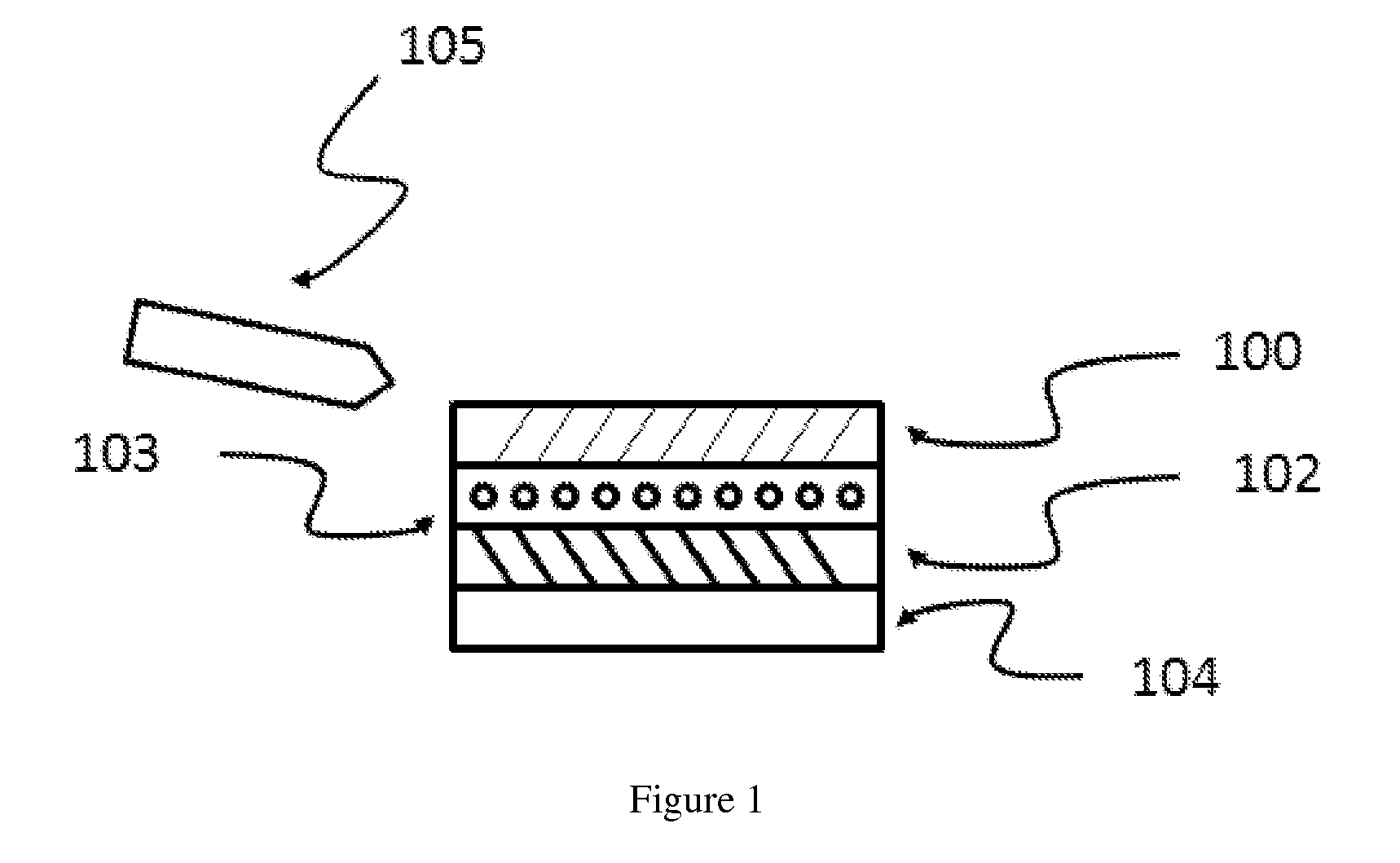
Porous thin-film-deposition substrate, electron emitting element, methods of producing them, and switching element and display element
A method of producing a porous thin-film-deposition substrate, which has the steps of: placing onto a substrate that has an electrostatic charge on its surface, fine particles with a surface electrostatic charge opposite to the electrostatic charge of the substrate surface, depositing a thin film on the fine-particle-placed substrate, and then removing the fine particles to form fine pores in the thin film; further, a method of producing an electron emitting element, which has the steps of: adding a catalyst metal on a substrate, placing fine particles onto the catalyst-added substrate, depositing a thin film on the fine-particle-placed substrate, then removing the fine particles to form fine pores in the film, and growing needle-shaped conductors on the catalyst metal that is exposed on a bottom face of the fine pore.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Preparation method of porous film
ActiveCN106000123AControl pore structureHigh porosityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesChemical reactionAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a porous support body; (2) preparing a thick size containing raw material powder, a binder, a dispersant and a pore forming agent; (3) loading the size onto the porous support body, and drying to make a film billet; (4) sintering the film billet to make a porous film precursor; (5) removing the pore forming agent from the precursor to obtain a porous film with the thickness of 5-3,000 [mu]m, the average aperture of 0.05-100 [mu]m and the porosity of 40-90%. The preparation method has the following advantages: firstly, no chemical reaction occurs between the pore forming agent and the raw material powder, so that the ingredients of the porous film cannot be damaged; secondly, the pore forming agent is excellent in thermal stability and always occupies a certain space (place) in the sintering process; after sintering, the pore forming agent is removed, holes or pores are generated in situ; therefore, the whole technological process is simple, the hole structure of the porous film is easy to control, and the porosity is remarkably improved.
Owner:CHENGDU INTERMENT TECH
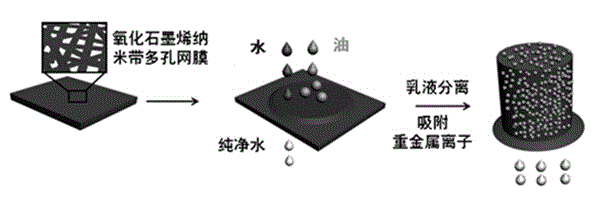
Preparation method of multifunctional oil-water separation material based on graphene oxide nanobelt
ActiveCN104815608AGood superhydrophilic underwater superoleophobic low adhesion propertiesLow costFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesOther chemical processesThin membraneOil water
The invention discloses a preparation method of a multifunctional oil-water separation material based on graphene oxide nanobelts, wherein the preparation method includes following steps: (1) cutting functionalized graphene oxide nanobelts in an oxidizing manner; and (2) preparing a graphene oxide nanobelt porous thin film through a vacuum-suction filtering method. The porous screen multifunctional oil-water separation thin film is 38 + / - 2 cm<2> in area and is 5-200 nm in pore size. The multifunctional oil-water separation material screen film can simultaneously perform oil-water separation and heavy metal adsorption to a mixture containing oil and water and heavy metal ions and the like components which are insoluble to each other. The integrated water-purifying renewable film has very important significance on protecting environment and maintaining ecologic system balance.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Polyurethane porous film and its preparing method
The porous polyurethane film has thickness of 80-120 micron, tensile strength of 10-20 MPa, elongation at breaking of 100-350 %, pore size in the outer surface contacting with solidifying agent of 5-20 micron, pore size in the inner surface contacting with mold of 30-80 micron, humidity transmission rate of 900-1800 g / m in 2.24 hr, water absorption of 30-300 wt% and porosity of 40-100 %. Its preparation process includes two-step solution polymerization to synthesize polyurethane solution, adding proper solvent, core creating agent, etc. into the solution, diluting the solution into film forming liquid in certain concentration, and wet coating to form the film. The present invention has the advantages of simple technological process, low cost, compact outer surface of the film and loose and porous inner surface.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite electrolyte of sandwich structure and preparation method thereof
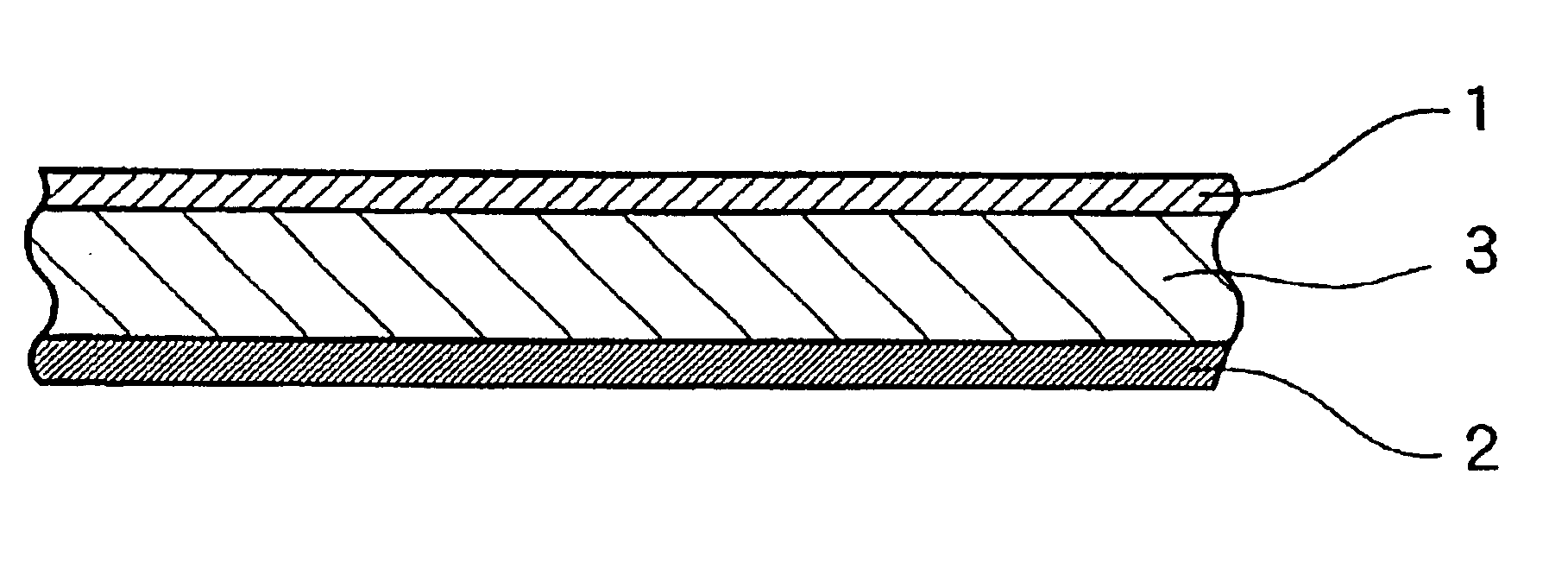
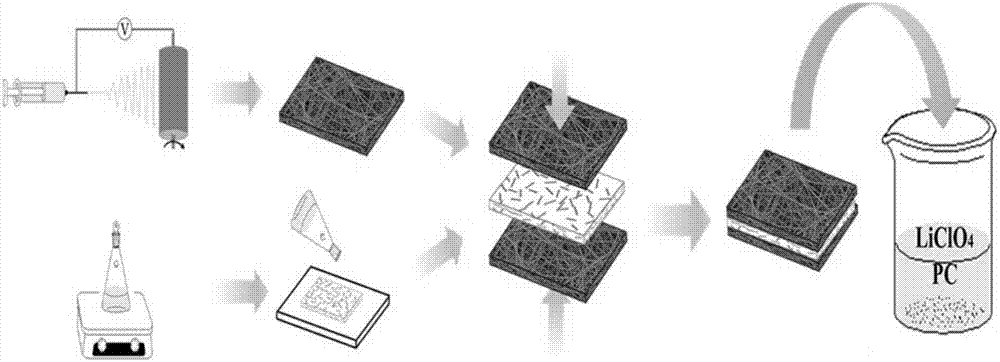
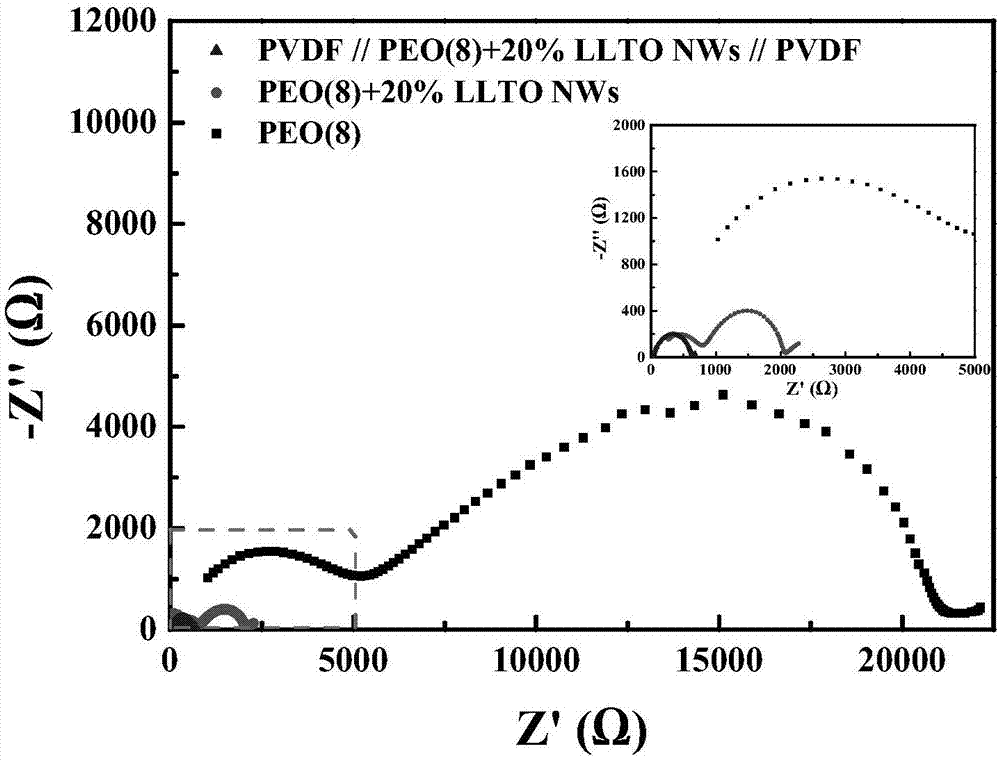
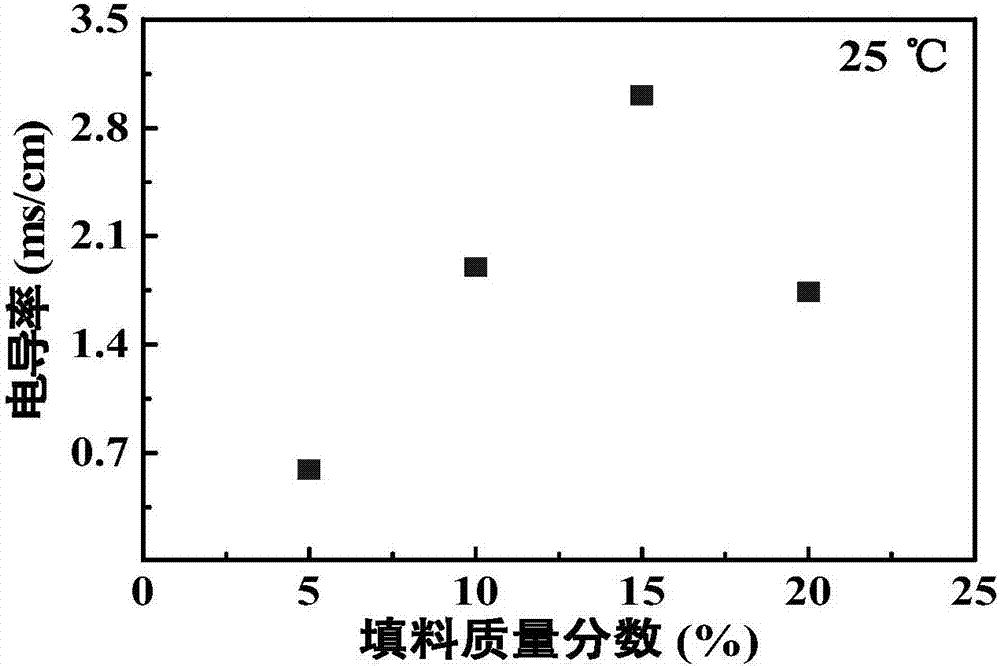
InactiveCN107369848AHas shapeSize andSolid electrolytesSecondary cellsSolid state electrolyteComposite electrolyte
The invention relates to a composite electrolyte of a sandwich structure and a preparation method thereof. The technical problems of poor interface performance and low conductivity of the existing all solid electrolyte are solved. The composite electrolyte comprises a porous thin film and a composite solid electrolyte material, the porous thin film is adhered on two sides of the composite solid electrolyte material, the porous thin film is composed of a high-molecular polymer, and the porous thin film adsorbs liquid electrolyte. The invention further provides a preparation method of the composite electrolyte. The composite electrolyte can be widely applied to the field of preparation of electrolyte.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Porous films by backfilling with reactive compounds
ActiveUS20120148829A1Increased durabilityImprove functionalitySynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesWear resistanceUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides methods for modifying one or more properties of porous thin films. In such methods, a formulation comprising a reactive species is applied to the porous thin film and allowed to crosslink. In some embodiments, the crosslinked network thus formed imparts increased mechanical strength and wear resistance to the porous thin films.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com