Fluorescence derivation analysis method based on photocatalysis
An analytical method and photocatalytic technology, applied in the field of fluorescence analysis, can solve the problems affecting the accuracy of analytical results, separation, and high instrument requirements, and achieve the effects of controllable derivatization process, simple derivatization operation, and high derivatization efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Fluorescence derivatization process: Add 1 mL of a certain concentration of folic acid solution, 1 mL of 0.1 mol L -1 NaAC-HAC buffer solution, pH 4.2, 100 μL 1 g L -1 Nano-TiO 2 suspension and 7.9 mL deionized water (the final concentration of photocatalyst is 0.01 g / L). The mixed solution was magnetically stirred under a 20W UV lamp for 2 min. Filter the mixture through a 0.22 μm filter membrane at room temperature. With the excitation wavelength of 280 nm, the fluorescence intensity of the filtrate at 440 nm was measured.
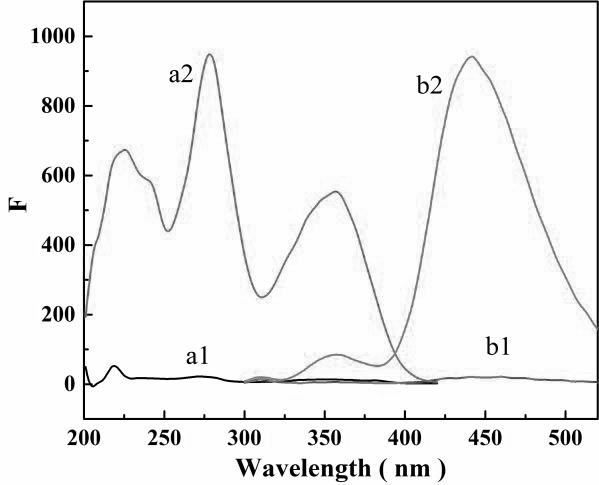
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, the fluorescence excitation and emission spectra before and after photocatalytic oxidation of folic acid, where a1 and a2 are the excitation spectra before and after folic acid oxidation, and b1 and b2 are the emission spectra before and after folic acid oxidation respectively. It can be clearly seen from the figure that The fluorescence intensity of the excitation spectrum and emission spectrum of folic ac...
Embodiment 2
[0034] This embodiment applies the analysis method of folic acid in the embodiment 1 to the detection of folic acid in the tablet:
[0035] Pretreatment of folic acid tablets: Grind a piece of folic acid into powder, dissolve it in distilled water and dilute to 100 mL, sonicate at room temperature for 10 min, filter with a separatory funnel, and take the supernatant after standing for a period of time Store in the refrigerator as a sample solution for later use. The entire operation process is carried out under low light.
[0036] Fluorescence derivatization process: Add 1 mL of the above folic acid sample solution, 1 mL of 0.1 mol L -1 NaAC-HAC buffer solution, pH 4.2, 100 μL 1 g L -1 TiO 2 suspension, and 7.9 mL deionized water. The mixed solution was magnetically stirred under a 20W UV lamp for 2 min. Filter the mixture through a 0.22 μm filter membrane at room temperature. With the excitation wavelength of 280 nm, the fluorescence intensity of the filtrate at 440 nm ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] This embodiment provides a fluorescence analysis method based on photocatalytic oxidation derivation for detecting terephthalic acid, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0040] Fluorescence derivation process: Add 1.00 mL of a certain concentration of terephthalic acid solution, 1 mL of 0.004mol L -1 Sodium hydroxide solution, 1 mL 1 g L -1 Tin oxide suspension and 7 mL deionized water (the final concentration of photocatalyst is 0.1 g / L). The mixed solution was magnetically stirred under a 150W UV lamp for 30 min. A hydrogen on the benzene ring is replaced by a hydroxyl group, and a fluorescence peak appears at 425 nm. Filter the mixture through a 0.22 μm filter membrane at room temperature. With the excitation wavelength of 315 nm, the fluorescence intensity of the filtrate at 425 nm was measured.
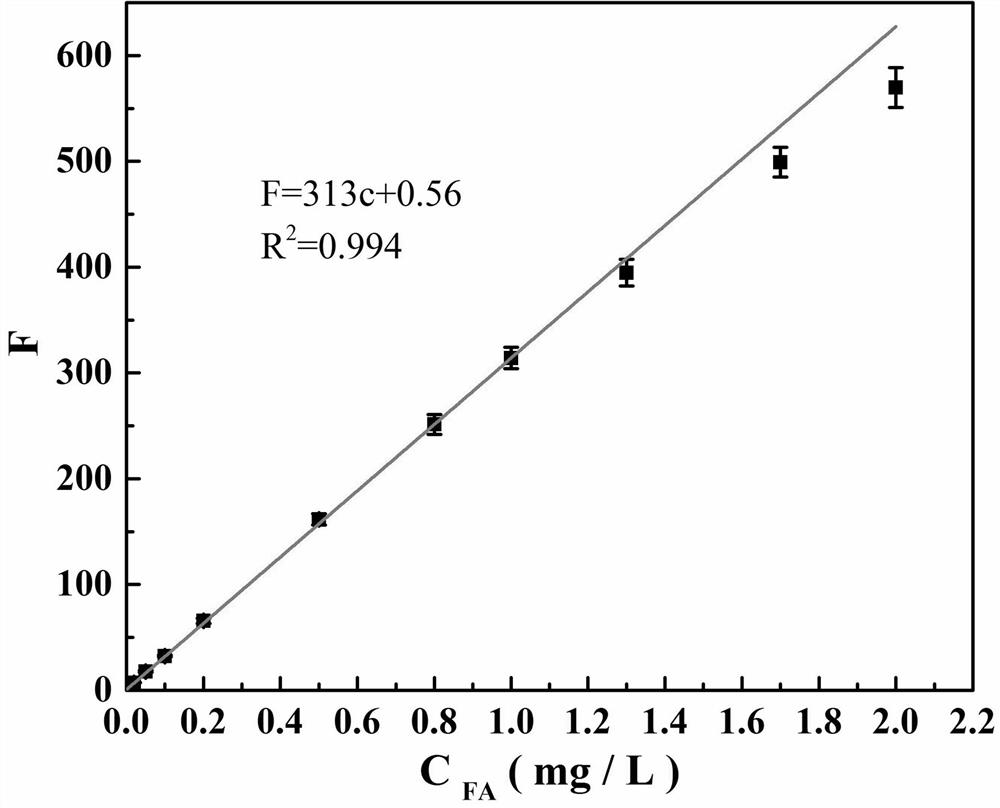
[0041] Establishment of the standard curve: after photocatalytic oxidation of terephthalic acid standard solutions with different concentrations, they...
PUM
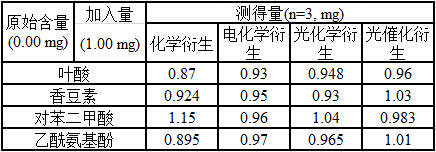
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com