Method for preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide
A single nucleotide and nicotinamide technology, applied in the direction of fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of NMN process, achieve the effect of reducing production cost, complete conversion of raw materials, and simple operation of synthesis reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051]Example 1 Genetic engineering construction of enzyme-producing strains
[0052]1. Nucleosidase (NCBI accession number WP_012699601.1), ribose phosphopyrophosphate kinase (amino acid sequence NCBI accession number A3MV85, BAA 05286 mutant N120S, BAA 05286 mutant L135I), nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (amino acid sequence NCBI Accession numbers AAR87771, NP_717588, WP_115638626), inorganic pyrophosphatase (NCBI accession number Q58025) according to its amino acid sequence, commissioned Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Company to optimize the nucleotide sequence to facilitate expression in E. coli. The coding genes of the above four enzymes are SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NOs: 2-4, SEQ ID NOs: 5-7 and SEQ ID NO: 9, respectively cloned into pET24a(+) NdeI and BamI restriction enzymes Cut the site. According to the conventional operation method, the 8 pET24a plasmids were transferred into BL21(DE3) competent cells by the calcium chloride method, and the plates containing kanamycin we...
Embodiment 2
[0058]Example 2 Obtaining enzyme
[0059]Inoculate the strains of each enzyme obtained in Example 1 in a test tube containing 4 mL of LB medium (yeast extract 5g / L, tryptone 10g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L.), cultivate overnight at 37°C, and cultivate Inoculate a triangle containing 1L of TB medium (yeast extract 24g / L, tryptone 12g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate trihydrate 16.4 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 2.3 g / L, and glycerol 5 g / L.) Bottle, shake culture, add final concentration of 0.3mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) for induction, and cool to 25°C to continue culturing overnight. The precipitate is collected by centrifugation to obtain the bacterial cells containing each enzyme for use.
Embodiment 35
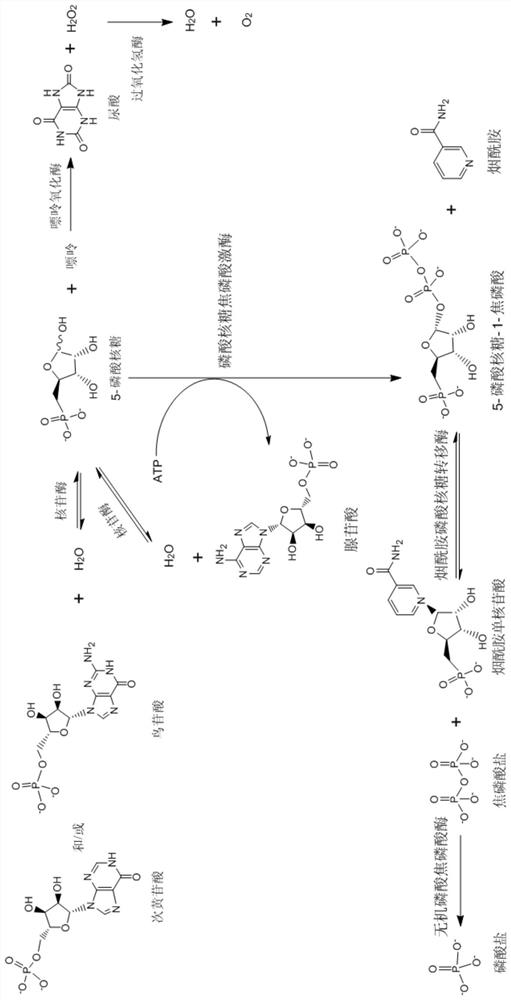
[0060]Example 3 Preparation of nicotinamide mononucleotide using 5-phosphoribose as raw material
[0061]Add 0.187g of 5-phosphate ribose, 0.462g of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) sodium salt, 0.103g of nicotinamide, 0.03g of magnesium chloride hexahydrate and 20mL of 50mM Tris-HCl (pH7.5) into the flask, and shake well. After dissolving, adjust pH=7.5 with sodium hydroxide solution. Then add 0.1g ribose phosphopyrophosphate kinase BL21(DE3) / 2 cells and 0.3g nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase BL21(DE3) / 5 cells, shake in a shaker at 25°C for 8 hours, take samples, and use HPLC The concentration of NMN in the sample is 5.86 g / L.
[0062]The experimental results verified the functions of ribose phosphopyrophosphate kinase and nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase constructed in the above examples. They can be used to prepare NMN according to the method of CN108949865A, but because 5-phosphoribose is expensive, in the following examples This method is no longer used.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com