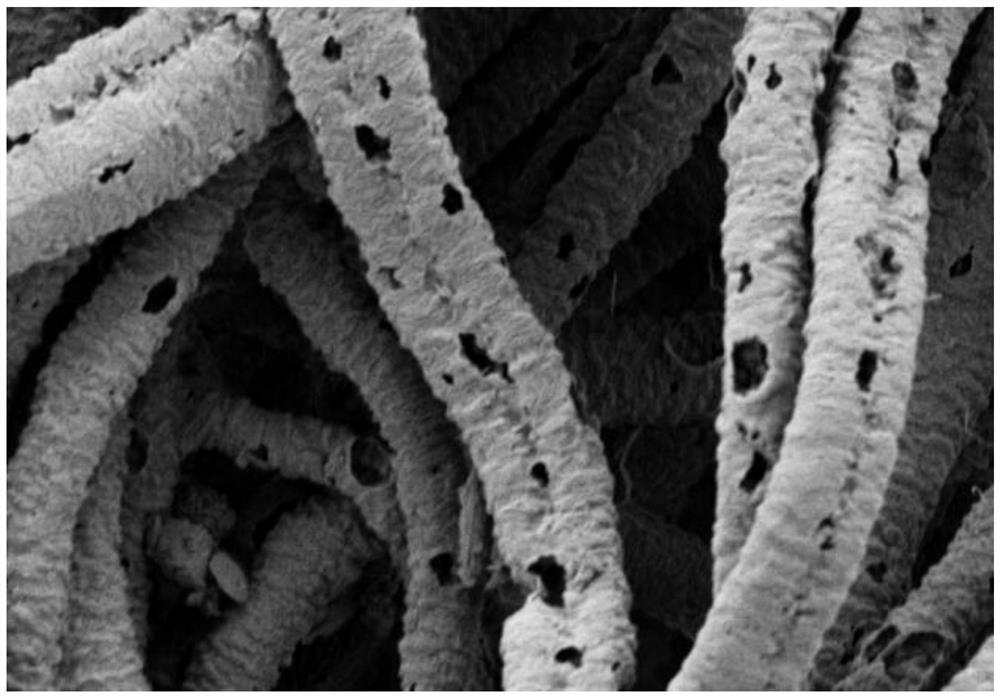
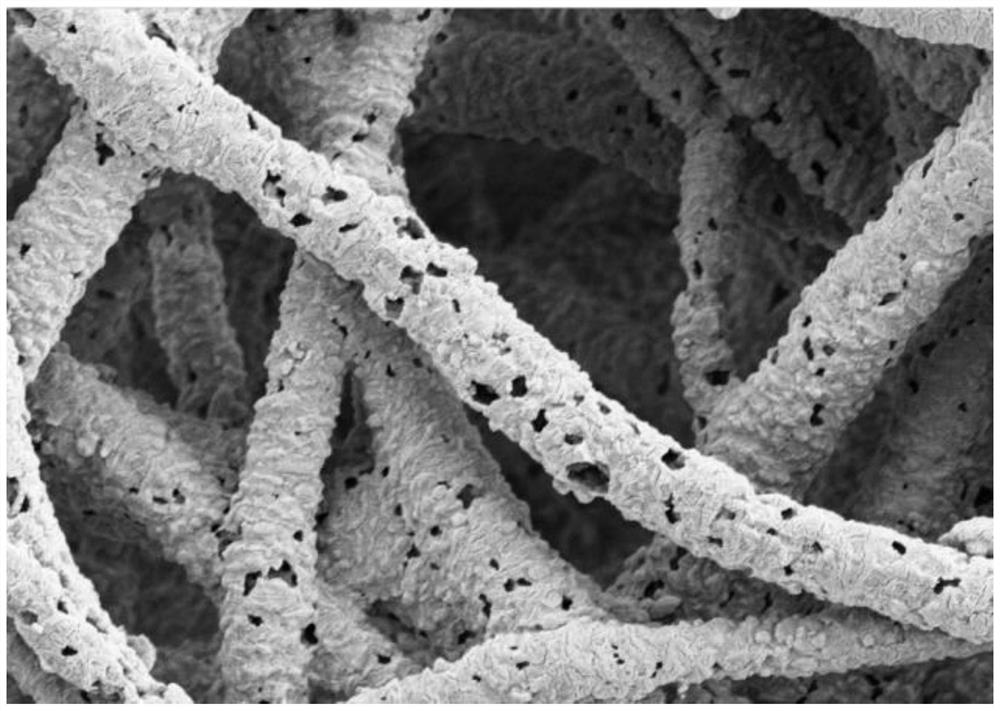
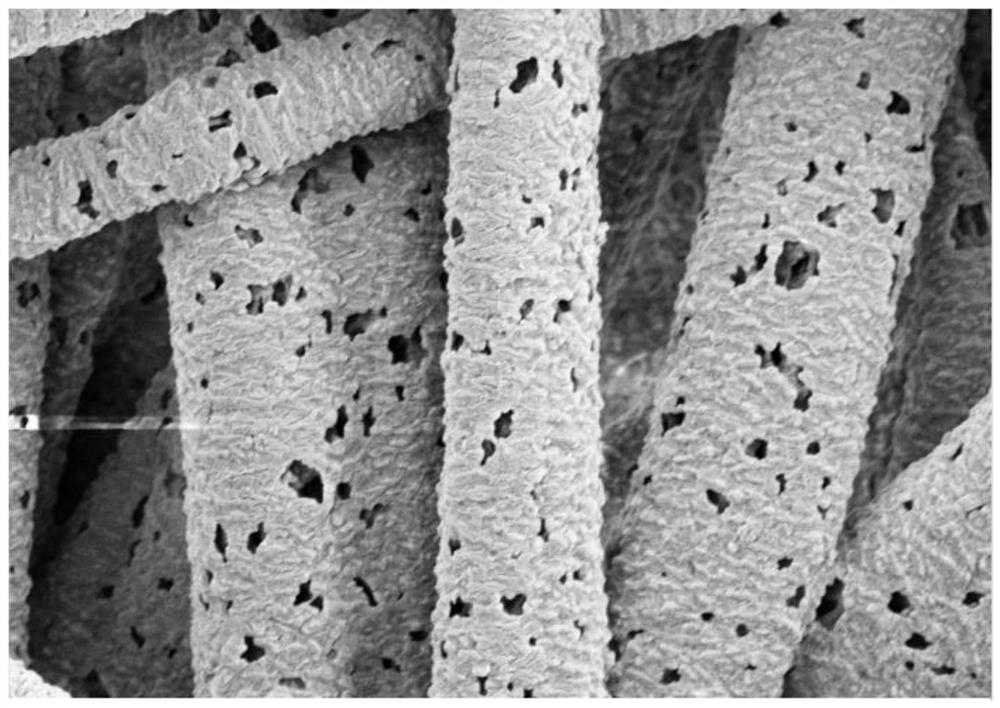
Preparation method of polytetrafluoroethylene fiber with porous structure
A polytetrafluoroethylene, porous structure technology, applied in the direction of fiber chemical characteristics, final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve the problem of single fiber shape, chemical fiber materials that are difficult to meet human needs, and the performance of porous structures that cannot be formed etc. to achieve the effect of increasing the specific surface area and porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031](1) Weigh a certain amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) emulsion in a mass ratio of 1:1, dissolve the two together in deionized water, and stir thoroughly for 2h at room temperature. Phase solution: After standing and defoaming, a solution with a solute concentration of 23 wt% is obtained, which is used as the spinning solution.
[0032](2) Add the spinning solution to the spinning device, and prepare micro-nano fibers through the electrostatic-centrifugal spinning process.
[0033]Electrostatic-centrifugal spinning parameters: Choose a dispensing needle with a diameter of 27G and a needle length of 12mm as the nozzle, and connect the nozzle to the spinneret through a matching connector. The collection method is conveyor belt collection, and the distance between the nozzle and the collector is set to 150mm. A syringe was used to inject 6 mL of spinning solution into the spinner to perform an electrostatic-centrifugal spinning test, where the rotat...
Embodiment 2
[0037](1) Weigh a certain amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) emulsion in a mass ratio of 1:2, dissolve the two together in deionized water, and stir well at room temperature for 2h to become homogeneous Phase solution: After standing for defoaming, a solution with a solute concentration of 33 wt% is obtained, which is used as the spinning solution.
[0038](2) Add the spinning solution to the spinning device, and prepare micro-nano fibers through the electrostatic-centrifugal spinning process.
[0039]Electrostatic-centrifugal spinning parameters: Choose a dispensing needle with a diameter of 27G and a needle length of 12mm as the nozzle, choose an independently designed spinneret, and connect the nozzle to the spinneret through a matching connector. The collection method is conveyor belt collection, and the distance between the nozzle and the collector is set to 150mm. A syringe was used to inject 6 mL of spinning solution into the spinner to perform ...
Embodiment 3
[0043](1) Weigh a certain amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) emulsion in a mass ratio of 1:3, dissolve the two together in deionized water, and stir thoroughly for 2h at room temperature to become homogeneous Phase solution: After standing for defoaming, a solution with a solute concentration of 40 wt% is obtained, which is used as the spinning solution.
[0044](2) Add the spinning solution to the spinning device, and prepare micro-nano fibers through the electrostatic-centrifugal spinning process.
[0045]Electrostatic-centrifugal spinning parameters: Choose a dispensing needle with a diameter of 27G and a needle length of 12mm as the nozzle, choose an independently designed spinneret, and connect the nozzle to the spinneret through a matching connector. The collection method is conveyor belt collection, and the distance between the nozzle and the collector is set to 150mm. Using a syringe, 6 mL of spinning solution was injected into the spinneret to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com