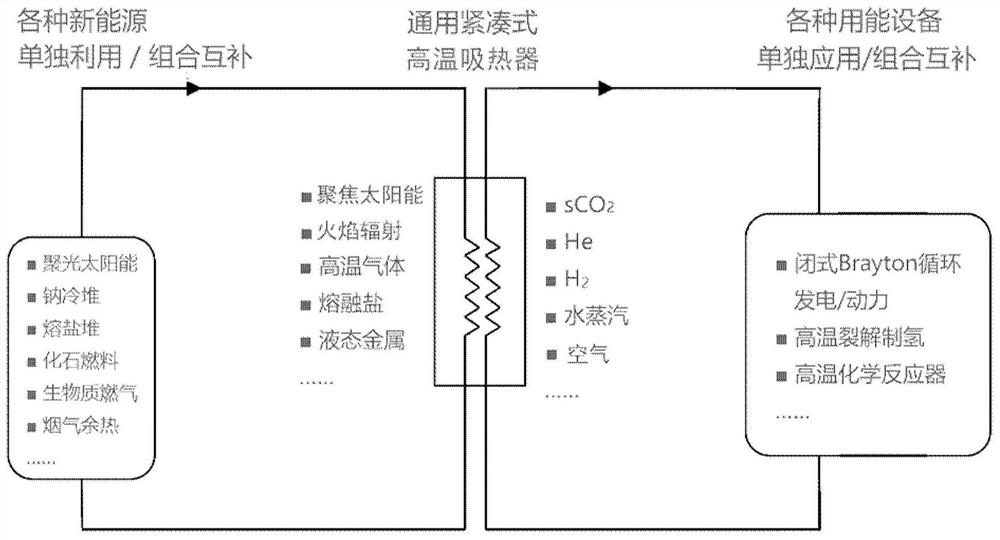
Universal high-temperature heat pipe type heat absorber
A heat absorber and heat pipe type technology, applied in the field of general-purpose high-temperature heat pipe heat absorbers, can solve the problems of inconvenient complementary and comprehensive utilization of multiple heat sources, uneven temperature distribution, limited space layout, etc., and achieve universality , large heat transfer and low flow rate of working fluid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
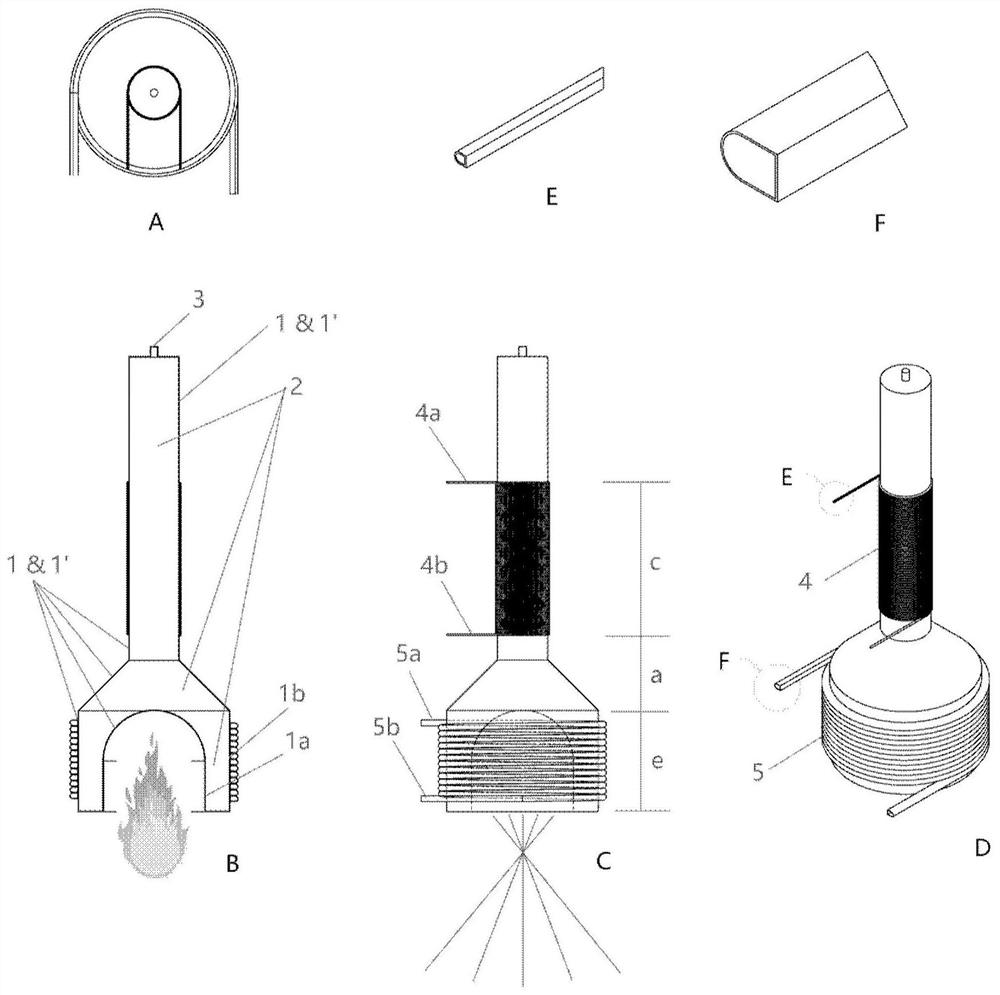
[0044] figure 2 Schematically shows the structural diagram of the heat pipe type heat absorber in Embodiment 1 of the present disclosure.
[0045] like figure 2As shown, the high-temperature heat pipe heat absorber can be composed of a rigid shell 1, an internal high-temperature phase-change working medium 2, a filling port 3, a heat-absorbing fluid pipeline 4 coiled on the outer surface of the shell at the cold end of the heat pipe 1, and a coiled The exothermic fluid pipeline 5 is formed on the outer surface of the tube shell at the hot end of the heat pipe 1 . The inner surface of the shell 1 can be laid or not laid with capillary core 1' according to whether anti-gravity heat transfer is required.
[0046] In this embodiment, the side of the hot end of the heat pipe 1 can be, for example, a cylindrical surface (close to a cylindrical surface) or a cylindrical surface, which is convenient for matching with the heat release fluid pipeline 5 . The end surface of the hot ...
Embodiment 2
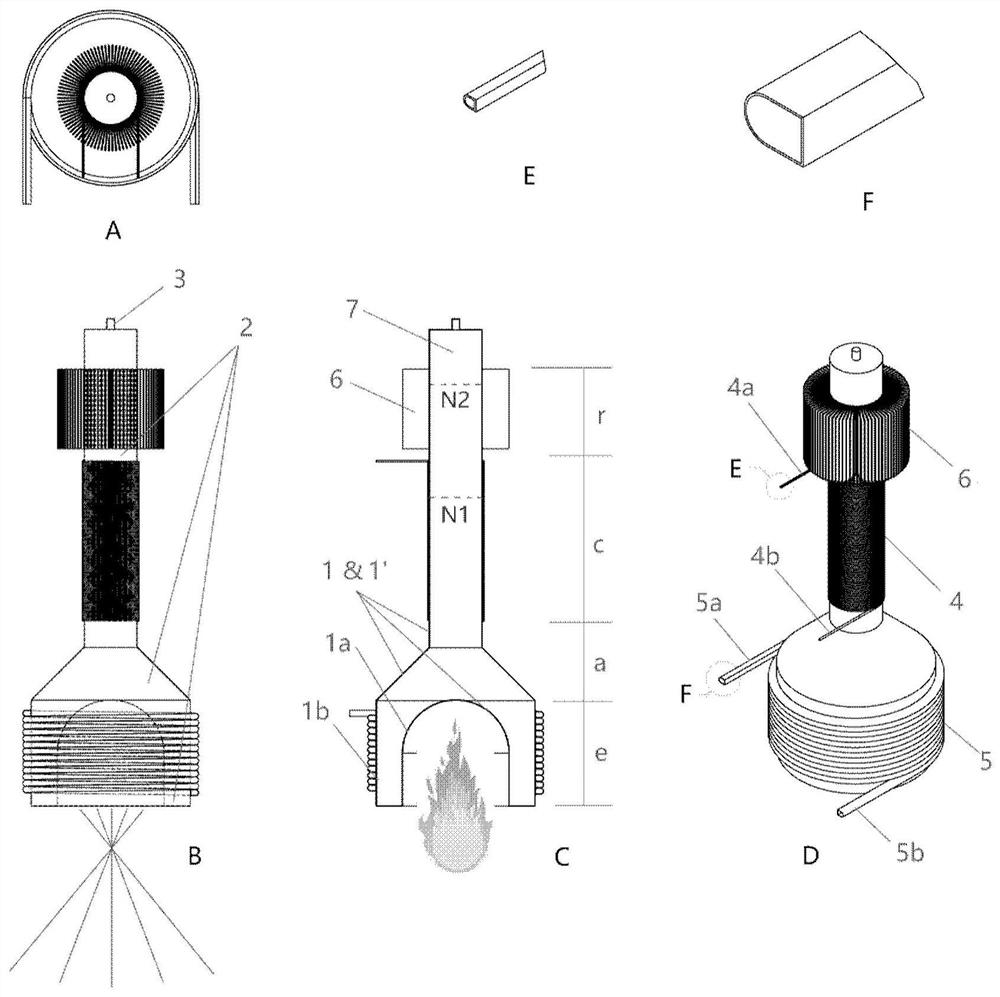
[0050] The structure of the heat pipe heat absorber in Embodiment 2 of the present disclosure is shown as schematically image 3 shown.
[0051] The difference between the heat pipe heat absorber provided in this embodiment and the first embodiment is that: on the side of the heat absorbing fluid pipeline 4 close to the cold end, the heat pipe 1 may also be provided with cooling fins 6 .
[0052] The heat dissipation fins 6 can be closely matched with the outer surface of the heat pipe 1 by means of welding, interference fit, adhesive or high thermal conductivity transition material, for example. When the heat pipe 1 works under normal working conditions, the heat-absorbing fluid has taken out the heat released by the condensation section, so the cooling fins 6 are in a state close to normal temperature and will not dissipate a large amount of heat to the surrounding environment. When the heat-absorbing fluid pipeline 4 or its connected heat-consuming equipment fails or is sh...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The structure of the heat pipe heat absorber in Embodiment 3 of the present disclosure is still as shown image 3 shown.
[0056] The difference between the heat pipe heat absorber provided in this embodiment and the second embodiment is that the cold end of the heat pipe 1 is sealed with a non-condensable gas 7 . The non-condensable gas 7 can also be connected to an external gas storage chamber (not shown in the figure), such as Ar, He, N2, etc. can be used. During the start-up process of the heat pipe 1, the vapor of the phase-change working medium 2 condenses in the condensation section c and returns to the evaporation section e, and the non-condensable gas 7 will be gradually displaced by the phase-change working medium 2 to the cold end of the heat pipe 1 to form a gas plug , and completely cover the radiation + natural convection heat dissipation section r, so that the temperature of the radiation + natural convection heat dissipation section r is low, and the he...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com