Assembled total intervertebral disc prosthesis based on 3D printing technology and making method thereof
A 3D printing, full intervertebral disc technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of destroying the stability of the cervical spine, paralysis and death of patients, and high cost, eliminating the gap between the plate-bone interface, expanding the scope of surgery, and promoting osteogenesis and bone growth. the effect of entering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
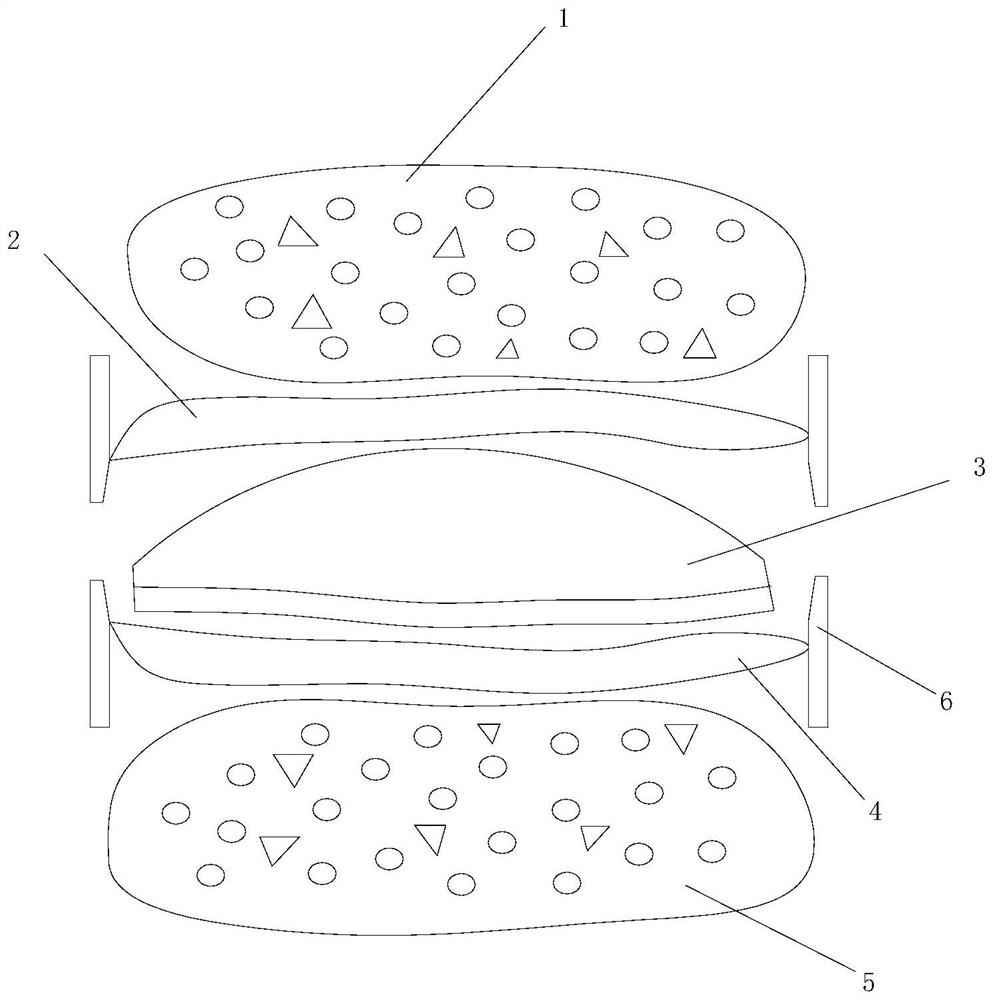
[0047] like figure 1 As shown, it includes an upper backing plate 1, an upper plate 2, a lower plate 4 and a lower backing plate 5 which are detachably connected in turn from top to bottom, and a buffer spacer 3 is arranged between the upper plate 2 and the lower plate 4, and the buffer spacer 3. It has a certain elastic deformation ability and can play a buffering role. It can be made of polyethylene and other materials; the upper backing plate 1 and the lower backing plate 5 are both porous structures, and can be made of porous titanium alloy, porous tantalum metal or porous inorganic composite materials .
[0048] The upper backing plate 1 and the lower backing plate 5 are made by 3D printing, and the upper surface of the upper backing plate 1 and the lower surface of the lower backing plate 5 are respectively adapted to the end faces of the adjacent intervertebral spaces where the prosthesis is scheduled to be installed; the upper backing plate of the upper backing plate ...
Embodiment 2
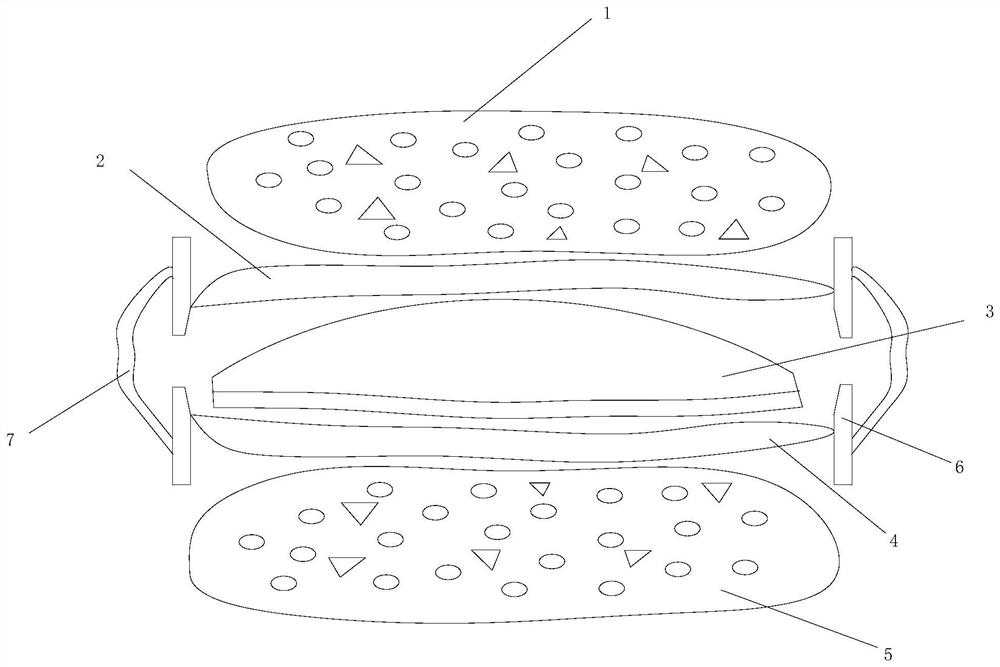
[0051] like figure 2 As shown, embodiment 2 adds a hook vertebra joint reconstruction component 7 on the basis of implementation 1. The hook vertebra joint reconstruction component 7 is connected to the outer side 6 of the upper plate and the lower plate, and the hook vertebra joint reconstruction component is detachable.
Embodiment 3
[0053] This embodiment discloses a manufacturing method of an assembled total intervertebral disc prosthesis based on 3D printing technology, wherein the manufacturing methods of the upper backing plate 1 and the lower backing plate 5 include a personalized customization method and a classified manufacturing method.
[0054] The personalization method includes the following steps:
[0055] a1. Correct the original DICOM format data of the patient's preoperative cervical spine CT three-dimensional scan;
[0056] a2. Extract the parameters of the upper and lower bony endplates in the intervertebral space of the segment to be operated;
[0057] a3. Send the data for 3D printing to the 3D printer for printing.
[0058] The 3D printed material can be porous titanium alloy, porous tantalum metal or porous inorganic composite material, and the printed porous material can also be recoated and compounded with other materials to promote osseointegration, such as composite hydroxyapatit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com