Application of ellagic acid to preparation of medicine for preventing and/or treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver injury
A technology for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which is applied in the field of ellagic acid in the preparation of drugs for preventing and/or treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver damage, and achieves the effects of protecting liver cells and reducing oxidative stress damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1. Preliminary research on the therapeutic effect and mechanism of EA and MoA on NAFLD mouse model
[0070] 1. Establishment and verification of NAFLD mouse model
[0071] 1.1 Experimental animal grouping, feeding and sample collection
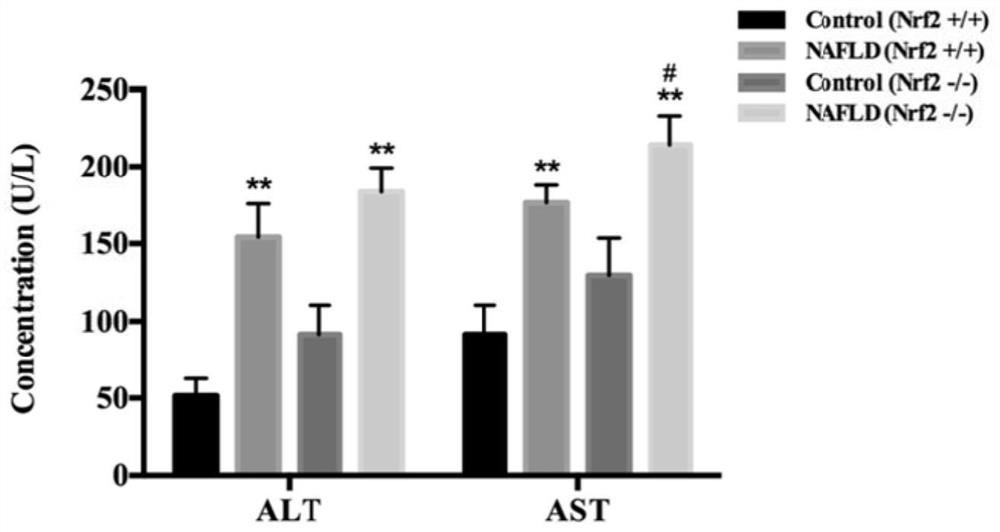
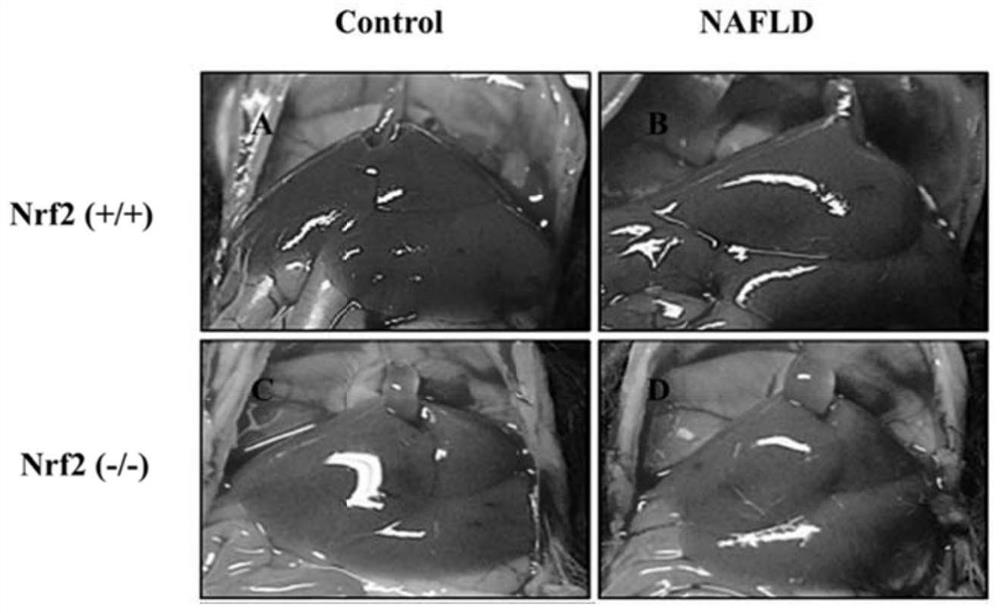
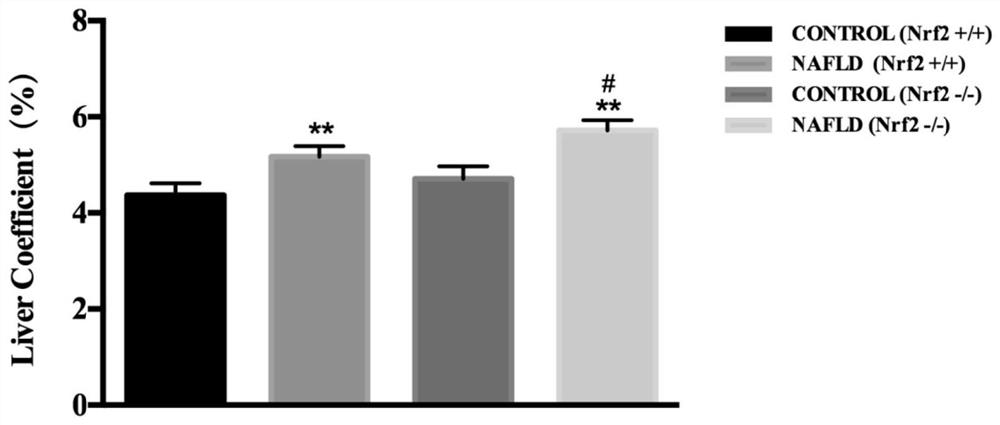
[0072] 12 wild-type and Nrf2 knockout homozygous (Nrf2- / -) C57BL / 6 mice (bred by our laboratory) were selected, and the mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (same genotype), 6 in each group, male and female Half and half. After 1 week of adaptive feeding with 12h light and 12h darkness alternately, they were fed with high-fat feed for 2 months. See Table 2-1 for grouping and feeding scheme.
[0073] Table 2-1 Grouping and feeding scheme of mice (n=6).
[0074]
[0075] After feeding for 2 months, mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate (0.5g / kg). The liver tissue was soaked in 4% paraformaldehyde fixative, and the remaining liver tissue was stored at -70°C until use. Whole blood was...
Embodiment 2
[0237] Example 2. In vitro cell model verification of the therapeutic effect of EA and MoA on NAFLD through the Nrf2 pathway In this example, except for the following drugs, the sources of other drugs are the same as above:
[0238] Reactive oxygen species (ROS) test box (E004, built in Nanjing); fatty acid-free-BSA (B2064, SIGMA, USA); oleic acid (O1383, SIGMA, USA); palmitic acid (P0500, SIGMA, USA).
[0239] 1. Establishment and verification of NAFLD cell model
[0240] 1.1 Solution preparation
[0241] 1) 1640 complete medium: same as Example 1.
[0242] 2) DMEM complete medium: same as Example 1.
[0243] 3) 0.25% trypsin: same as Example 1.
[0244] 4) PBS solution: Take a bag of PBS powder, add 1L UP water according to the instructions, mix well, and set aside.
[0245] 5) 20% fatty acid-free-BSA solution: Weigh 0.6g of fatty acid-free-BSA, put it in a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 3mL of PBS solution preheated to 55°C, and centrifuge directly at room temperature (about...
Embodiment 3
[0463] Example 3. Study on the preventive effect and mechanism of EA and MoA on APAP liver injury in NAFLD mouse model
[0464] In this experimental example, except for the following drugs, the sources of other drugs are the same as above: acetaminophen suspension drops (Tylenol, Shanghai Johnson Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.).
[0465] 1.1 Determination of APAP administration time
[0466] 1.1.1 Experimental animal grouping, drug administration and sample collection
[0467] Eighteen wild-type C57BL / 6 mice bred in our laboratory were selected and randomly divided into three groups, with six mice in each group, half male and half male. After 1 week of adaptive feeding with 12h light and 12h darkness alternately, the treatment group was given the maximum safe dose of APAP (150mg / kg) by intragastric administration at 9:00 in the morning (APAP-AM) and 5:00 in the afternoon (APAP-PM). Administration for 3 days, once a day. See Table 4-1 for grouping and dosing regimen.
[0468] Tab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com