Method for strengthening copper blue bioleaching by comprehensively utilizing ferric ions and ferrous ions
A ferrous ion and ferric iron technology, applied in the field of new bioleaching, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of chalcocite bioleaching, not conducive to the growth of iron-oxidizing bacteria, and affecting the leaching efficiency, so as to improve the leaching efficiency and increase the reaction rate. Effect of surface area and reaction cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
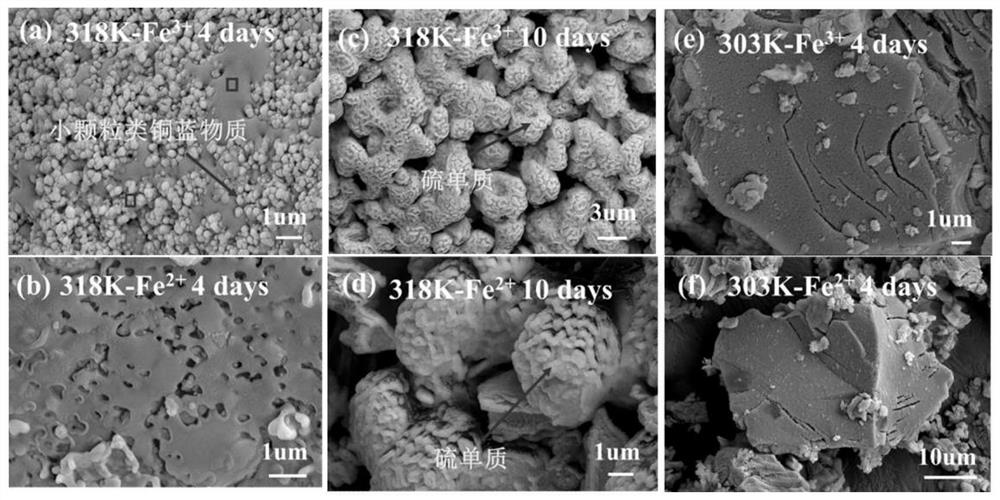
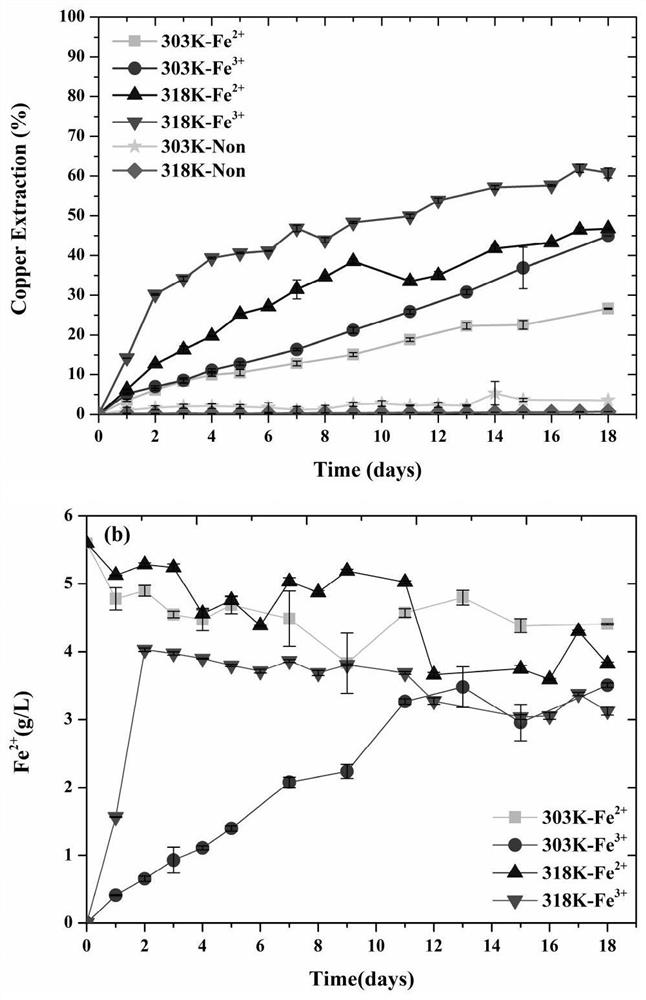
[0079] (1) Design a leaching experiment with bacterial copper blue to explore the enhanced leaching of copper blue by adding ferric iron (ion concentration 0.1M) and reacting with sulfur-oxidizing bacteria at medium temperature (45°C-318K) process.
[0080] (2) In the shake flask leaching experiment, the leaching liquid adopts the formula of OK medium: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 3.0g / L, KC1 0.1g / L, K 2 HPO 4 0.5g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g / L, Ca(NO 3 ) 2 0.01g / L; use dilute sulfuric acid solution to control the pH value within the range of 1.7-2.0. Fully dissolve 2g Fe per 100ml leach solution 2 (SO 4 ) 3 On the first day of the reaction, inoculate medium thermophilic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (Acidithiobacillus caldus) at first, and inoculate 5ml per 100ml of leach solution with a concentration of 10 9 cell / ml bacterial solution, after 3-5 days of reaction, all the ferric iron is converted into ferrous iron, then add iron-oxidizing bacteria, the leaching of copper ions in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0084] (1) Design a leaching experiment with bacterial copper blue to explore the enhanced leaching of copper blue by adding ferric iron (ion concentration 0.07M) and reacting with sulfur-oxidizing bacteria at medium temperature (45°C-318K) process.
[0085] (2) In the shake flask leaching experiment, the leaching liquid adopts the formula of OK medium: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 3.0g / L, KC1 0.1g / L, K 2 HPO 4 0.5g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g / L, Ca(NO 3 ) 2 0.01g / L; use dilute sulfuric acid solution to control the pH value within the range of 1.7-2.0. Fully dissolve 1.4g Fe per 100ml leach solution 2 (SO 4 ) 3 On the first day of the reaction, inoculate medium thermophilic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (Acidithiobacillus caldus) at first, and inoculate 5ml per 100ml of leach solution with a concentration of 10 9 cell / ml bacterial solution, after 3-5 days of reaction, all the ferric iron is converted into ferrous iron, then add iron-oxidizing bacteria, the leaching of copper ions in t...
Embodiment 3
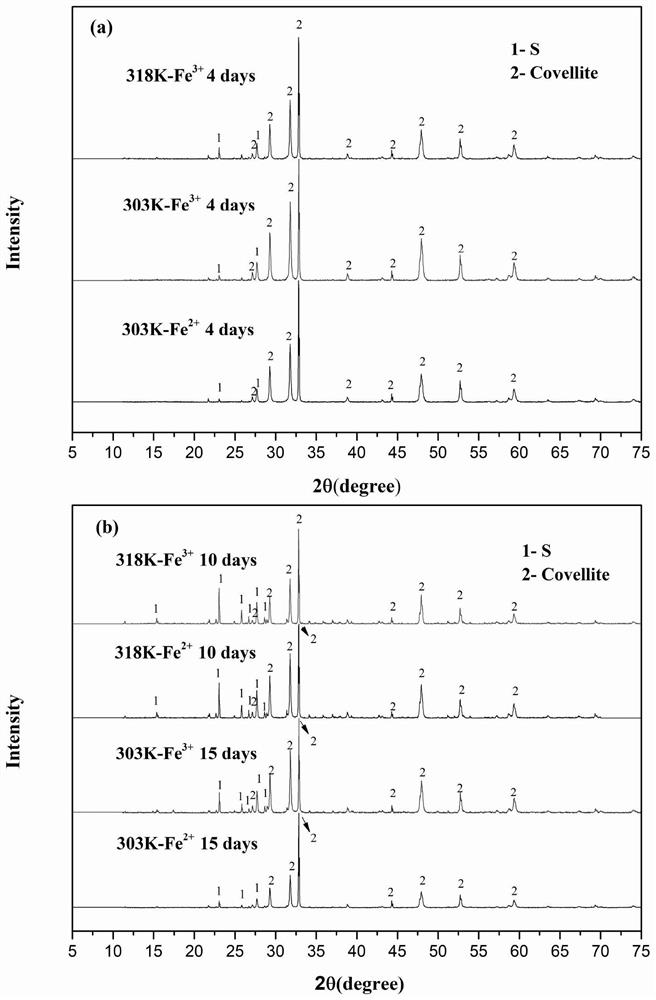
[0089] For the bacterial leaching experiment of copper blue under low temperature (30°C-303K), compared with Example 1, only the temperature is different. After adding ferric iron (ion concentration 0.1M) to react with sulfur oxidizing bacteria, then adding iron oxidizing bacteria to strengthen The process of leaching copper blue, in comparative example 1, under low temperature (30 ℃-303K) reaction conditions, 303K-Fe 3+ Solution Fe in the experimental group 3+ The ion concentration decreased linearly within 12 days of reaction, while Fe 2+ The concentration increases linearly (figure 1 (b)), the copper blue dissolution reaction is slower than that at medium temperature (45°C-318K). Therefore, compared with the medium temperature (45°C-318K) reaction in Example 1, it takes a longer time to reach the final stage of leaching under low temperature (30°C-303K) conditions. Therefore, the conditions in Example 1 are preferred to implement the copper blue bioleaching process.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com