Preparation of biochar-based catalyst and method for repairing antibiotics by using biochar-based catalyst
A repair method, biochar technology, applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems that have not been reported, and achieve simple preparation methods, mild process conditions, and applicable target substances wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The preparation method using the highly active biochar-based Fenton catalyst is described in detail by this example. In this embodiment, the preparation process is as follows:
[0033] First, put the agricultural waste grapefruit peel in deionized water, repeat 2-3 times to clean the surface impurities, dry it at 75-100 °C to constant weight, grind it through an 80-mesh sieve, and then, under the protection of nitrogen, dry it in a tube furnace. The temperature was raised to 600 °C at 5 °C / min, and the pyrolysis was maintained for 120 min. After natural cooling, the obtained solid was ground and passed through an 80-mesh sieve to obtain pomelo peel biochar. Subsequently, in a three-necked flask, 200 mL of acidic mine wastewater with an iron mass concentration of 0.89-1.02 g / L after filtration and pretreatment was mixed with 10-20 g of pomelo peel biochar for 300-360 min, and then, under nitrogen protection, the The newly prepared pomelo peel extract of a certain concen...
Embodiment 2
[0035] In this example, the single removal and degradation effects of different biochar-based Fenton catalyst materials on tetracycline and norfloxacin are compared. The steps are as follows: add the following five combined materials or reagents to the contaminated water containing tetracycline or norfloxacin Combinations: Persulfate, Biochar, Biochar-Based Fenton Catalyst, Biochar / Persulfate, and Biochar-Based Fenton Catalyst / Persulfate. A 200 mL beaker is used as a reactor, and the treatment object is a water body whose concentration is 100 mL tetracycline concentration of 15 mg / L or norfloxacin concentration of 30 mg / L, the pH of the water body is 4.0, and the dosage of the catalyst material is 1.5 g / L, and The beaker was placed on a stirrer with a rotation speed of 150 rpm and a reaction time of 60 min. Example 2 results are shown in table 1. It can be seen from the table that both persulfate and biochar have low removal rates for tetracycline and norfloxacin, and the com...
Embodiment 3
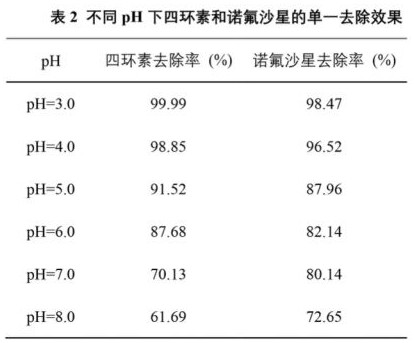
[0038]The difference from Example 2 is that the pH range is adjusted to 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, and 8.0, and the tetracycline or norfloxacin is degraded and removed by using a biochar-based Fenton catalyst / persulfate system. Other conditions were the same as in Example 2, and the changes of tetracycline or norfloxacin in the water before and after the reaction were measured. Example 3 results are shown in table 2. It can be seen from the table that the removal rates of tetracycline and norfloxacin all decrease with the increase of pH, and the removal rates under acidic conditions are greater than those under neutral and alkaline conditions, but the removal rates of both are at pH=3.0 and 4.0 , have reached a higher level, therefore, choose pH=4.0 as the optimal pH condition.
[0039]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com