Gene markers, evaluation methods and applications for stratified evaluation of tumor prognosis
A gene marker and prognosis technology, applied in the field of medical diagnosis, can solve the problems of neglected research and unsatisfactory patient stratification effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Constructing a risk scoring model based on METTL5 in the TCGA lung adenocarcinoma cohort based on gene expression profile data
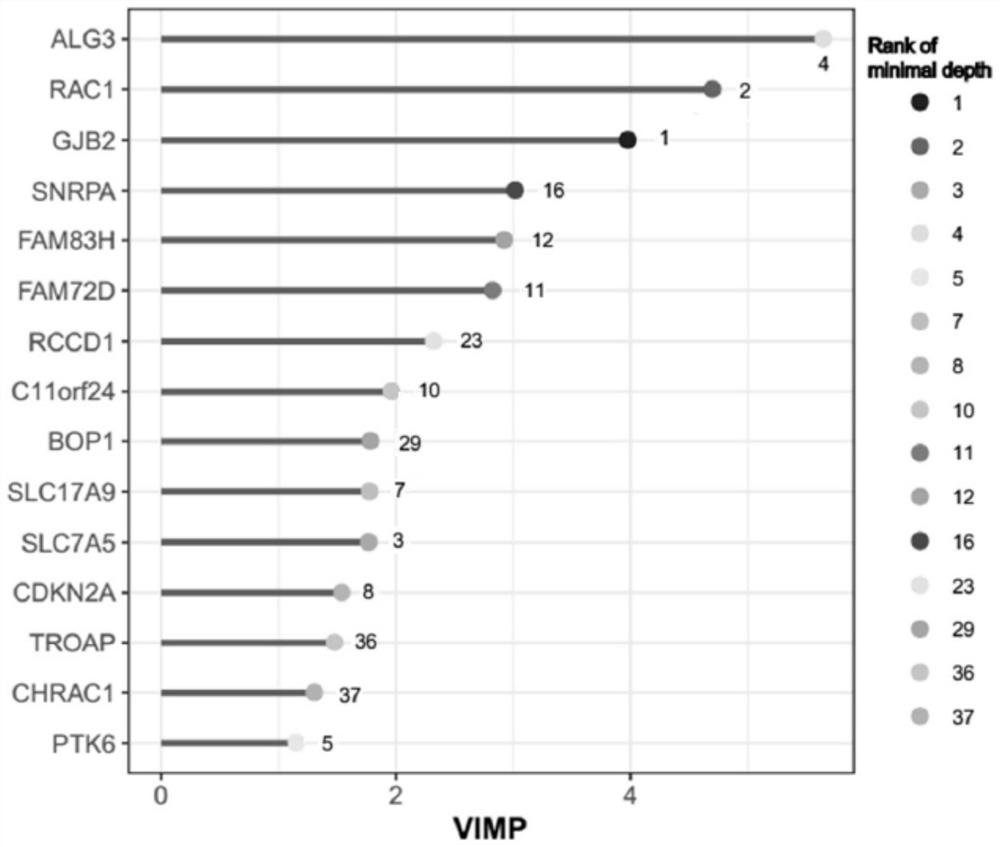
[0027] To develop a METTL5-based prognostic risk model, the Spathial algorithm was first applied to implement evolutionary analysis to find genes associated with different expression levels of METTL5. Spathial uses the main path algorithm to find the most important genes in the change process. The samples were divided into two groups according to the upper and lower quantiles of METTL5 expression, and the starting point and end point of the path were set as the centroids of the two groups. During path analysis, the number of waypoints was set to 50. The significance of each gene was sorted by the corrected P value, and the top 100 genes were screened out, as shown in Gene List 1.
[0028] Table 1
[0029]
[0030]
[0031] Use random survival forests via randomForestSRC to further reduce the number of features in the table a...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Validate the prognostic risk model based on an independent external data set
[0033] The microarray data set comes from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), and the details of the data set are shown in Table 2.
[0034] Table 2
[0035]
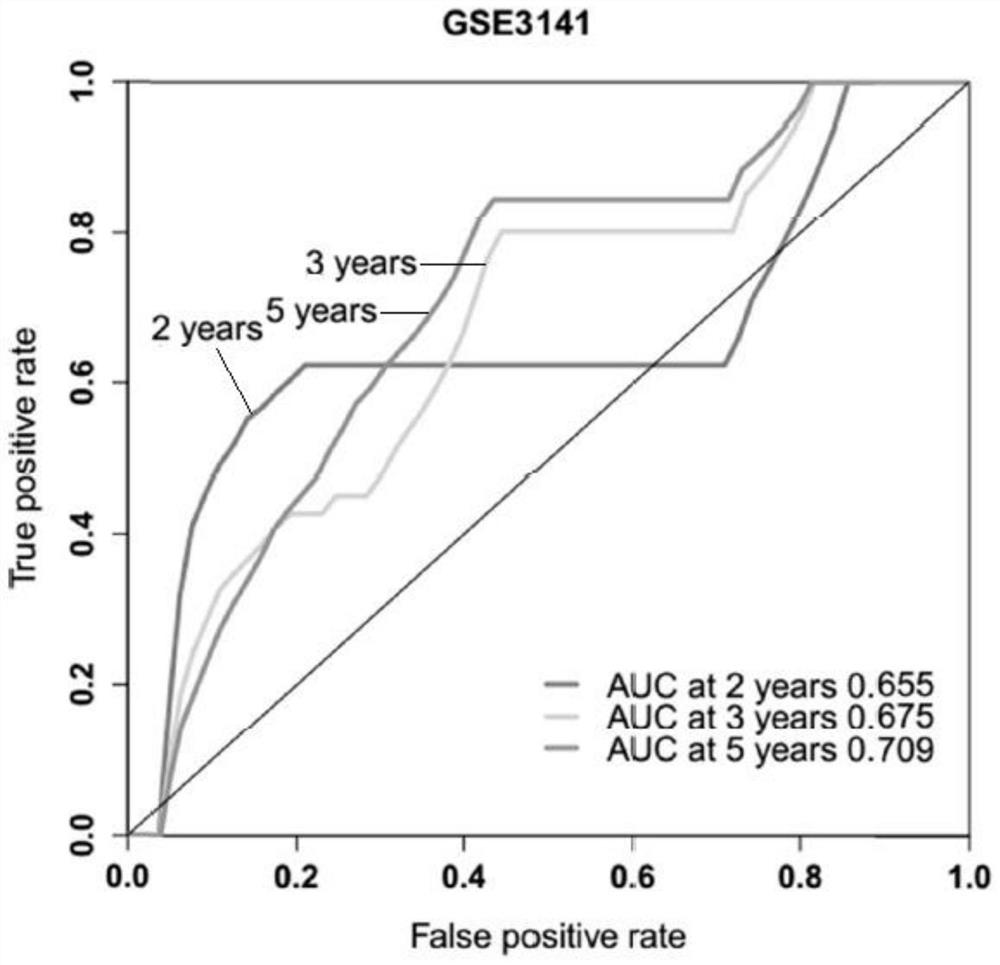
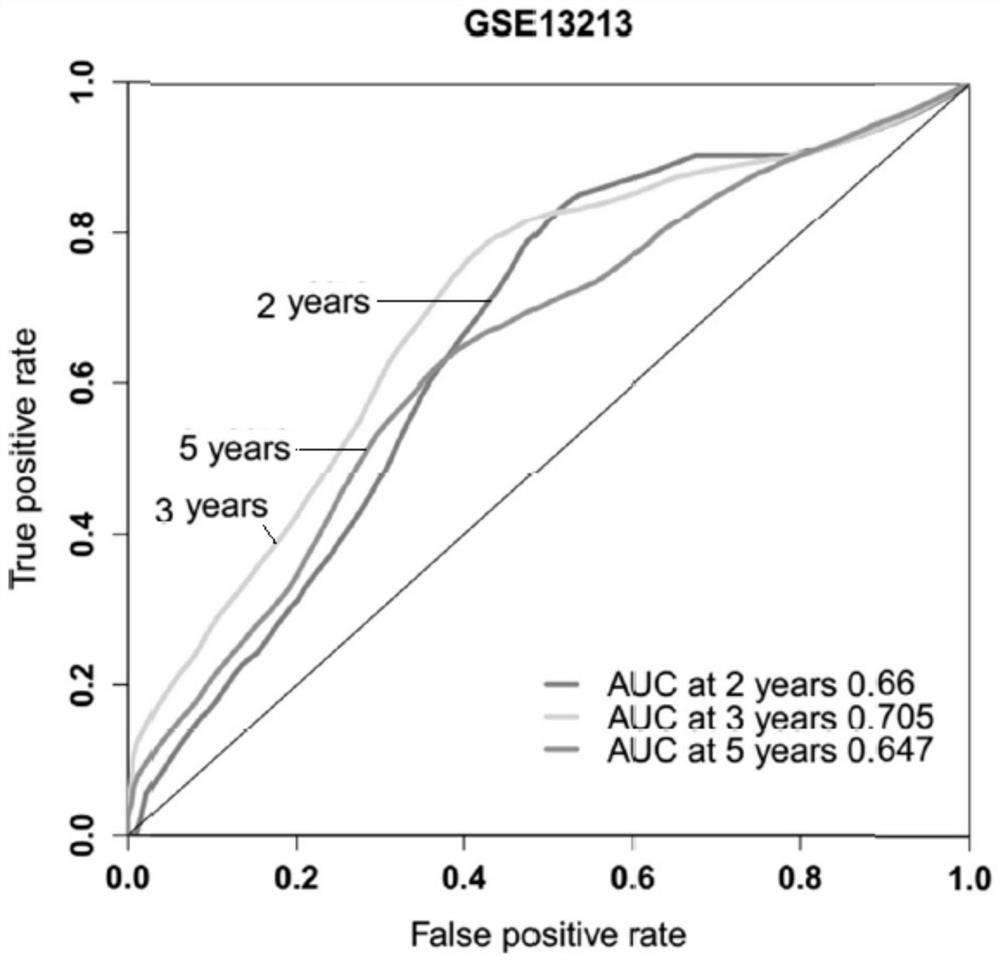
[0036] Firstly, the probe tags are gene-annotated according to the platform file provided by GEO, different probes corresponding to the same gene are merged according to the mean value, and then the samples are normalized. Substituting the genes included in the model into the formula to calculate the risk score for each sample, grouping according to the median risk score of each cohort, and performing survival analysis and 2-year, 3-year and 5-year AUC value calculations for the subgroups to evaluate the prognosis of the model efficacy.
[0037] Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that the overall survival of the high-risk group in the three cohorts was significantly lower than that of the low-risk group (P<0.05). In additio...
Embodiment 3
[0038]Example 3 Verification that the constructed risk score is an independent risk factor for the prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma
[0039] To further demonstrate that the constructed risk score is an independent risk factor, relevant information was extracted from a cohort with clinical information, specifically including age at diagnosis, gender, tumor pathological stage, and smoking history. Multivariate Cox regression analyzes were performed on these datasets to further illustrate the prognostic significance of the maps. The results showed that in the three datasets, the constructed risk score was an independent prognostic factor (P<0.05), and its overall survival hazard ratios in TCGA lung adenocarcinoma, GSE13213 and GSE31210 datasets were 2.106, 2.514 and 2.514 respectively. 3.666.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com