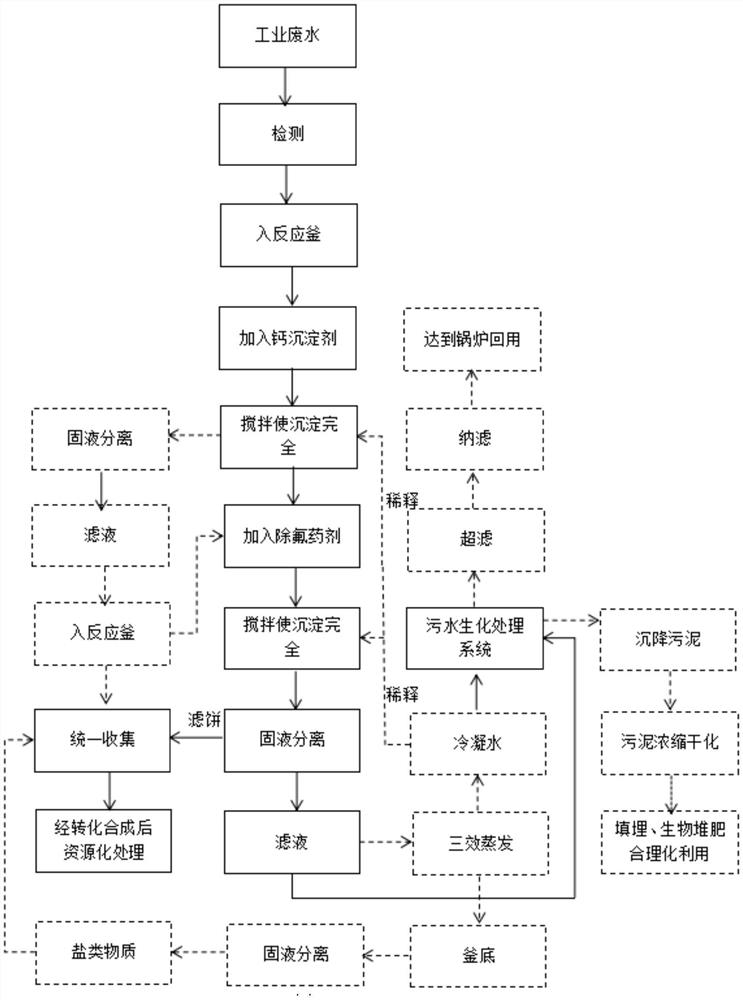
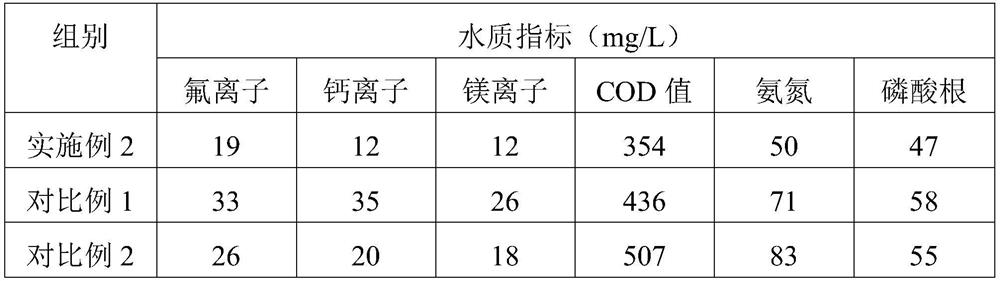
Method for removing fluorine and hardness of industrial wastewater
A technology for industrial wastewater and hardness, applied in water softening, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as ineffective chemical reactions, unfavorable standardized disposal, and failure to consider resource utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] This embodiment provides a method for removing fluoride and hardness from industrial wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0028] (1) After fully mixing the fluorine-containing and calcium-containing industrial wastewater, pump it into the reactor for 7 tons. The water quality test results show that the fluoride ion is 2203mg / L, the calcium ion is 1965mg / L, the magnesium ion is 432mg / L, and the COD is 964mg. / L, ammonia nitrogen is 2654mg / L. Add phosphoric acid to the waste water under stirring for acidification, adjust the pH to 3.5, and after stirring for 60 minutes, a large amount of precipitation occurs;
[0029] (2) After adding 800kg of water to the reaction kettle for dilution, slowly add magnesium carbonate under stirring, adjust the pH to 7.6, and continue stirring for 2 hours. During the period, it is found that the sedimentation is large, continue to add 400kg of water, and check the pH value after the stirring is completed. correct;
[0030] (3) Th...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment provides a method for removing fluoride and hardness from industrial wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0034] (1) After fully mixing the fluorine-containing and calcium-containing industrial wastewater, pump it into the reactor for 7 tons. The water quality test results show that the fluoride ion is 426mg / L, the calcium ion is 402mg / L, the magnesium ion is 175mg / L, and the COD is 506mg. / L, ammonia nitrogen is 782mg / L. Add phosphoric acid to the wastewater under stirring for acidification, adjust the pH to 3.5, and after stirring for 60 minutes, a small amount of precipitation occurs;
[0035] (2) Slowly add magnesium hydroxide to the reaction kettle under stirring, adjust the pH to 7.9, continue to stir for 2h, during which it is found that the sedimentation is relatively large, add 300kg of water, and the pH value is correct after the stirring is finished;
[0036] (3) The waste water obtained in step (2) enters a filter press for press fi...
Embodiment 3
[0039] This embodiment provides a method for removing fluoride and hardness from industrial wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0040] (1) After fully mixing the fluorine-containing and calcium-containing industrial wastewater, pump it into the reactor for 7 tons. The water quality test results show that the fluoride ion is 219mg / L, the calcium ion is 321mg / L, the magnesium ion is 83mg / L, and the COD is 502mg. / L, ammonia nitrogen is 553mg / L. Add phosphoric acid to the wastewater under stirring for acidification, adjust the pH to 3.5, and after stirring for 60 minutes, a small amount of precipitation occurs;
[0041] (2) Slowly add magnesium oxide to the reaction kettle under stirring, adjust the pH to 7.2, continue to stir for 2 hours, during which it is found that the sedimentation is relatively large, add 200kg of water, and check that the pH value is correct after the stirring is completed;
[0042] (3) The waste water obtained in step (2) enters a filter press ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com