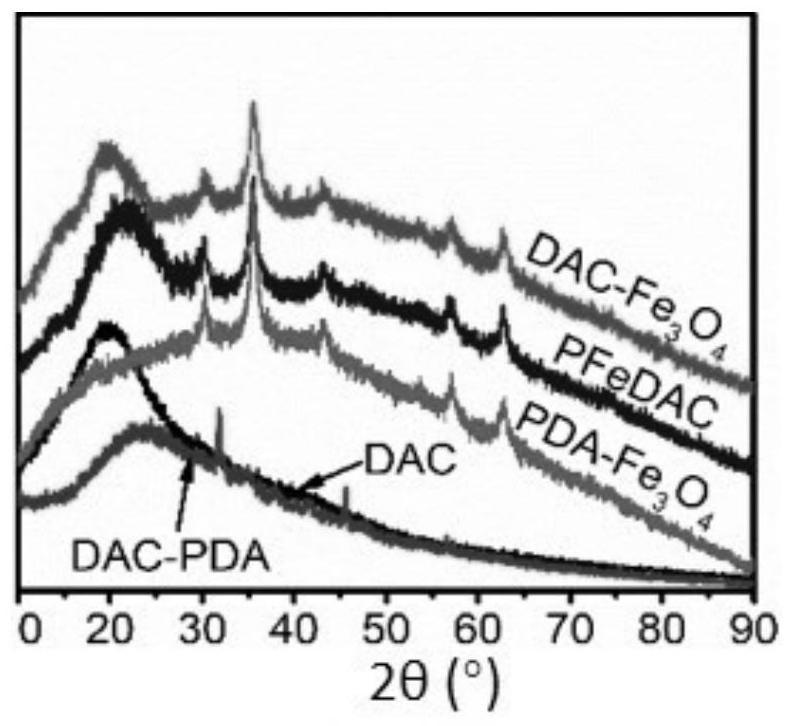
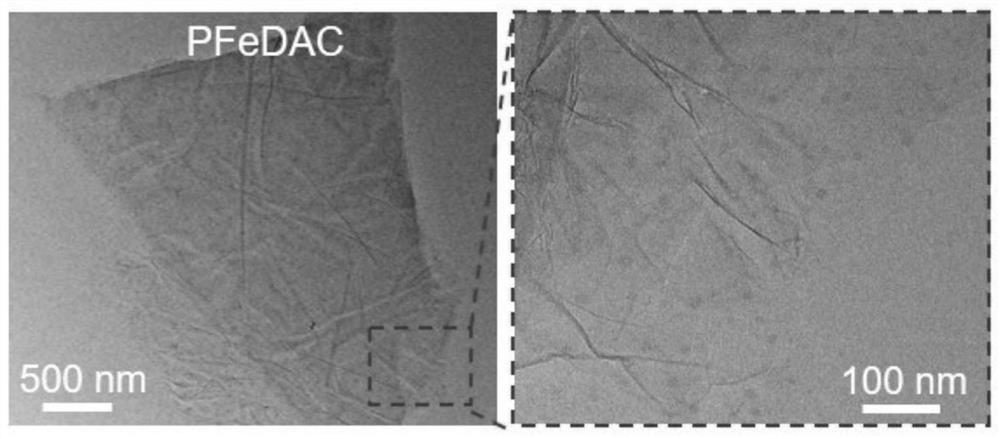
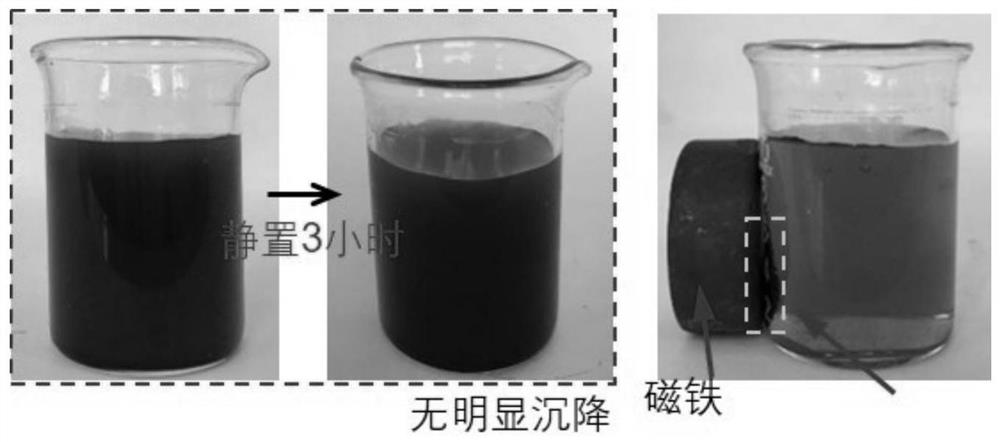
A kind of preparation method of anisotropic cellulose-based hydrogel
A cellulose-based, anisotropic technology, which is applied in the field of anisotropic cellulose-based hydrogel preparation, can solve problems such as difficult hydrogels, and achieve the effects of strong covalent bonds, high development potential, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This example was carried out as follows.
[0033] (1) 100mL concentration is 0.55wt% wood pulp cellulose suspension, 0.6g NaIO , 2mL isopropanol are mixed in Erlenmeyer flask, under 500rpm stirring velocity, 65 ℃ dark reaction 12h, then through centrifugation, Wash with deionized water and freeze-dry to obtain dialdehyde cellulose; add dialdehyde cellulose to a round-bottomed flask containing 100 mL of deionized water, react at 100°C for 2 hours at a stirring speed of 300 rpm, centrifuge and concentrate to obtain transparent dialdehyde cellulose Plain aqueous solution, its concentration is determined to be 3.3g / 10g.
[0034] (2) Get the dialdehyde cellulose (10g) gained in step (1) to remove moisture by centrifugation, and then mix with NH 3 ·H 2 O (6 mL), methanol (30 mL) were mixed well. Using a 100mL reactor in Ru / C catalyst (0.1g), 2MPa of H 2 Under pressure, react at 100°C for 2 hours to obtain ammoniated cellulose derivatives.
[0035] (3) Add the ammoniated ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This example was carried out as follows.
[0042] (1) Obtain a transparent dialdehyde cellulose aqueous solution according to the embodiment step (1).
[0043] (2) The operation of step (2) was carried out with reference to the corresponding steps in Example 1, except that the reaction time in step (2) was 3h.
[0044] (3) The operation of step (3) was carried out with reference to the corresponding steps in Example 1, except that the amount of dopamine added in step (3) was 0.03 g, and the reaction pH was 8.2.
[0045] (4) The operation of step (4) is carried out with reference to the corresponding steps in Example 1, except that 0.1 mL of 28% NH 3 ·H 2 The reaction after O was 80°C, 5h.
[0046] (5) The operation of step (5) is carried out with reference to the corresponding steps in Example 1, except that the amount of magnetic hybrid compound added in step (5) is 0.026 g. Under these conditions, the longitudinal tensile strength of the oriented hydrogel obtained...
Embodiment 3
[0048] This example was carried out as follows.
[0049] (1) Obtain a transparent dialdehyde cellulose aqueous solution according to the embodiment step (1).
[0050] (2) The operation of step (2) is carried out with reference to the corresponding steps in the embodiment one, and the difference is that H in the reaction in the step (2) 2 The pressure is 3MPa.
[0051] (3) The operation of step (3) was carried out with reference to the corresponding steps in Example 1, except that the amount of dopamine added in step (3) was 0.03 g, and the reaction pH was 8.5.
[0052] (4) The operation of step (4) is carried out with reference to the corresponding steps in Example 1, except that 0.1 mL of 28% NH 3 ·H 2 The reaction after O was 90 °C for 1 h.
[0053] (5) The operation of step (5) is carried out with reference to the corresponding steps in Example 1, except that the amount of magnetic hybrid compound added in step (5) is 0.1 g. Under this condition, the longitudinal tensi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com