Vascular intervention stent
A vascular and tubular technology, applied in the field of vascular interventional stents, can solve the problems of high difficulty and risk in intracranial surgery, high difficulty in assembly, and large filter mesh, so as to avoid the risk of intracranial hemorrhage, use it safely and reliably, and improve surgical procedures. effect of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
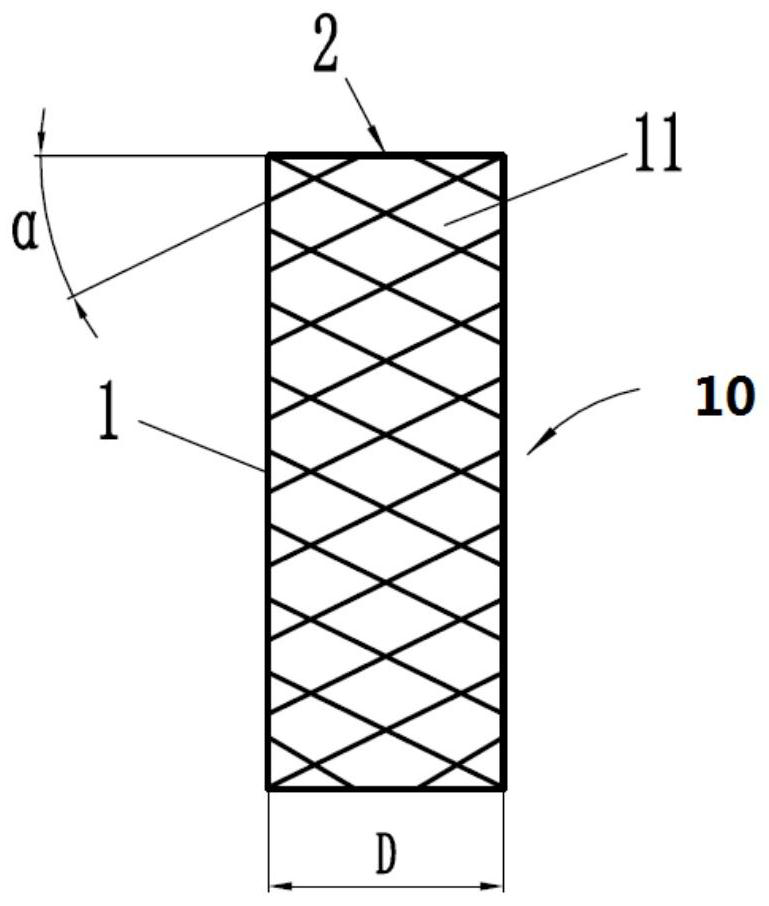
[0072] Figure 1a ~ Figure 1c They are respectively the front view, the axial sectional view and the top view of the vascular interventional stent provided by the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0073] Such as Figure 1a ~ Figure 1c As shown, the vascular intervention stent 10 includes a support structure 1 and a filter structure 2 . The support structure 1 is in the shape of a tube, which can be braided from braided wire, or cut by laser. The supporting structure 1 may be a self-expanding structure, or be passively expanded by an expandable balloon. Furthermore, the expanded diameter D of the support structure 1 is 3.0 mm to 4.5 mm, preferably 3.5 mm, which can be applied to relatively thin blood vessels, especially intracranial blood vessels.
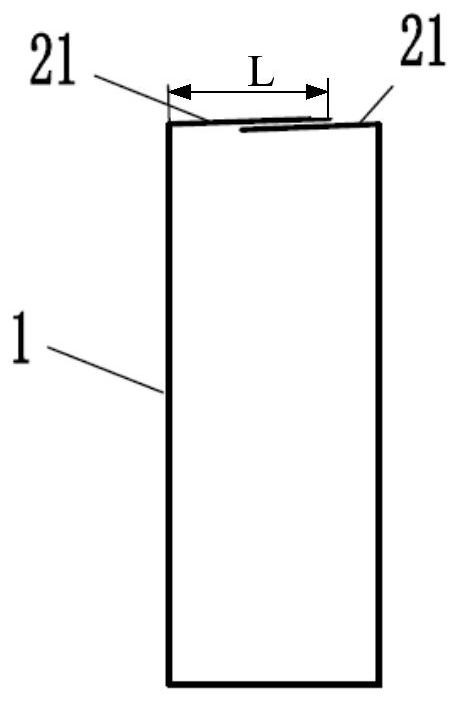
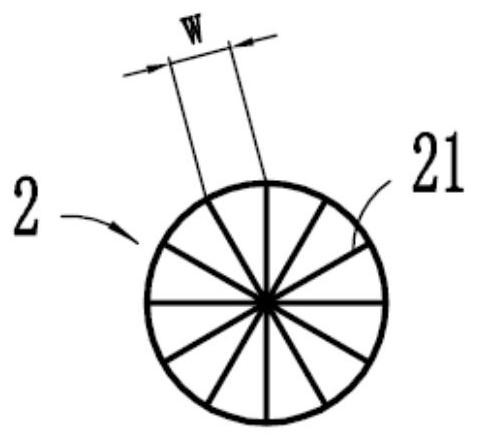
[0074] The support structure 1 specifically includes a plurality of support rods 11, and the plurality of support rods 11 are distributed in a certain way to form a network-like support structure 1. However, the presen...
Embodiment 2
[0086] The structure of the vascular interventional stent provided in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, and the following description will only focus on the different points, and the same parts will not be described in detail.
[0087] Figure 2a ~ Figure 2c They are the front view, axial sectional view and plan view of the vascular interventional stent provided by the second embodiment of the present invention, respectively.
[0088] Such as Figure 2a ~ Figure 2c As shown, the vascular intervention stent 20 includes a support structure 3 and a filter structure 4 . The expanded diameter D of the support structure 3 can be selected to be 5.5 mm to 6.0 mm, which can be applied to blood vessels with larger diameters. The support structure 3 includes several support rods 31, and the included angle α between the support rods 31 and the radial cross section of the support structure 3 is preferably 10°-15°, so as to provide good radial support for sten...
Embodiment 3
[0092] The structure of the vascular interventional stent provided in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, and the following description will only focus on the different points, and the same parts will not be described in detail.
[0093] Figure 3a ~ Figure 3c They are the front view, axial sectional view and top view of the vascular interventional stent provided by the third embodiment of the present invention, respectively.
[0094] Such as Figure 3a ~ Figure 3c As shown, the vascular intervention stent 30 includes a support structure 5 and a filter structure 6 . The expanded diameter D of the support structure 5 can be selected to be 4.5 mm to 5.5 mm, which can be applied to blood vessels with medium diameters. The support structure 5 includes several support rods 51, and the included angle α between the support rods 51 and the radial cross-section of the support structure 5 is preferably 20°-25°, so as to provide good radial support for stents...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com