Recycling method for releasing sludge carbon source by using sewage plant sludge biological method
A sewage plant and biological method technology, applied in the direction of sludge treatment, biological sludge treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of increased operating costs of sewage plants, low efficiency of biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal, and consumption of carbon sources. Achieve the effects of optimizing operating costs, broadening market prospects, and reducing drug consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
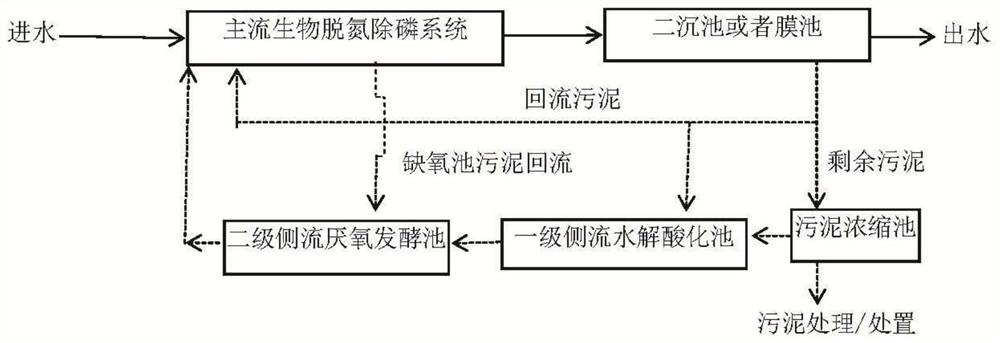
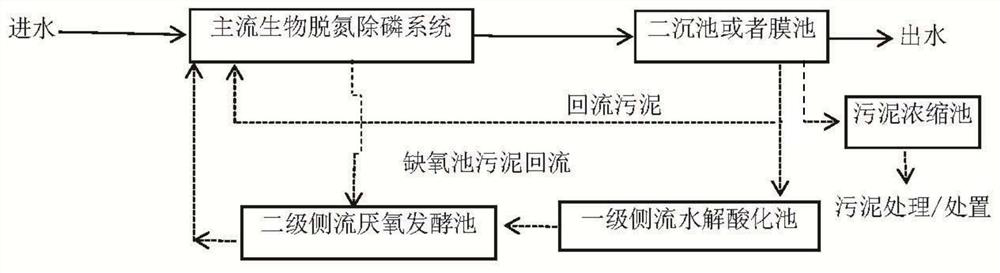
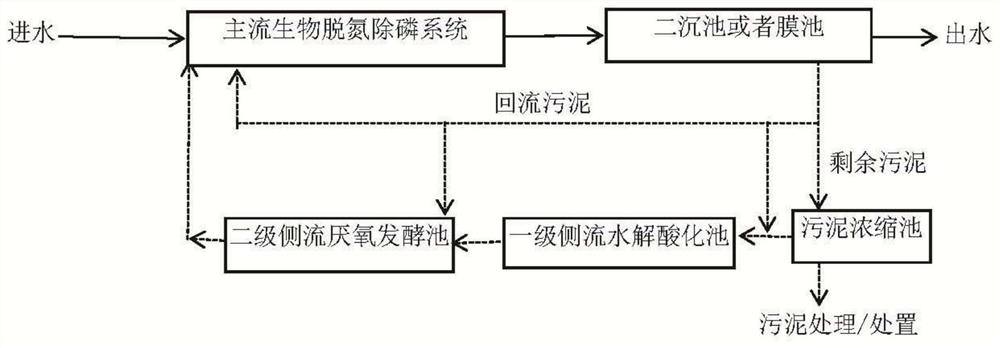
[0046] The concentration of the membrane pool sludge in the biochemical system of the municipal sewage plant is 1.5%, and the membrane pool sludge is added to the hydrolysis acidification reactor equivalent to the first-level side flow hydrolysis acidification tank for continuous operation for hydrolysis acidification, and the first-level side flow hydrolysis acidification The reactor operates in CSTR mode, and the CSTR operates continuously at 35°C for a hydraulic retention time of 3 days. Then, in 1 liter of reactor equivalent to the secondary side flow anaerobic fermentation tank, add 100 milliliters of sludge treated by hydrolysis and acidification of the primary side flow hydrolysis acidification reactor, which is equivalent to 10% Q of membrane tank return sludge Add 300 milliliters of sludge from an anoxic tank with a concentration of 0.9% that has been washed several times with clean water to the sludge after the first-stage side flow hydrolysis and acidification treatm...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The concentration of sludge in the secondary settling tank of the biochemical system of an industrial sewage plant is 1.2%, and the remaining sludge collected from the sludge in the secondary settling tank mixed with the sludge thickening tank is added to the hydrolytic acidification equivalent to the primary side flow hydrolytic acidification tank The reactor runs continuously for hydrolysis and acidification, and the first-stage side-stream hydrolysis and acidification reactor operates in CSTR mode, and the CSTR operates continuously at 35°C for 3 days of hydraulic retention time. Then, in the reactor equivalent to the secondary side flow anaerobic fermentation tank of 1 liter, add 100 milliliters of sludge through the hydrolysis and acidification treatment of the primary side flow hydrolysis acidification reactor, which is equivalent to the return sewage of the secondary settling tank of 10% Q Add 200 ml of sludge from the anoxic tank with a concentration of 0.6% afte...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The concentration of the membrane pool sludge in the biochemical system of the municipal sewage plant is 1.3%, and the membrane pool sludge is added to the hydrolysis acidification reactor equivalent to the first-level side flow hydrolysis acidification tank for continuous operation for hydrolysis acidification, and the first-level side flow hydrolysis acidification tank The reactor operates in CSTR mode, and the CSTR maintains a 4-day hydraulic retention time at room temperature for continuous operation. Then, in 1 liter of reactor equivalent to the secondary side flow anaerobic fermentation tank, add 100 milliliters of sludge treated by hydrolysis and acidification of the primary side flow hydrolysis acidification reactor, which is equivalent to 10% Q of membrane tank return sludge Add 250 milliliters of sludge from an anoxic tank with a concentration of 0.9% after being hydrolyzed and acidified by the primary side stream, which is equivalent to the deficiencies of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com