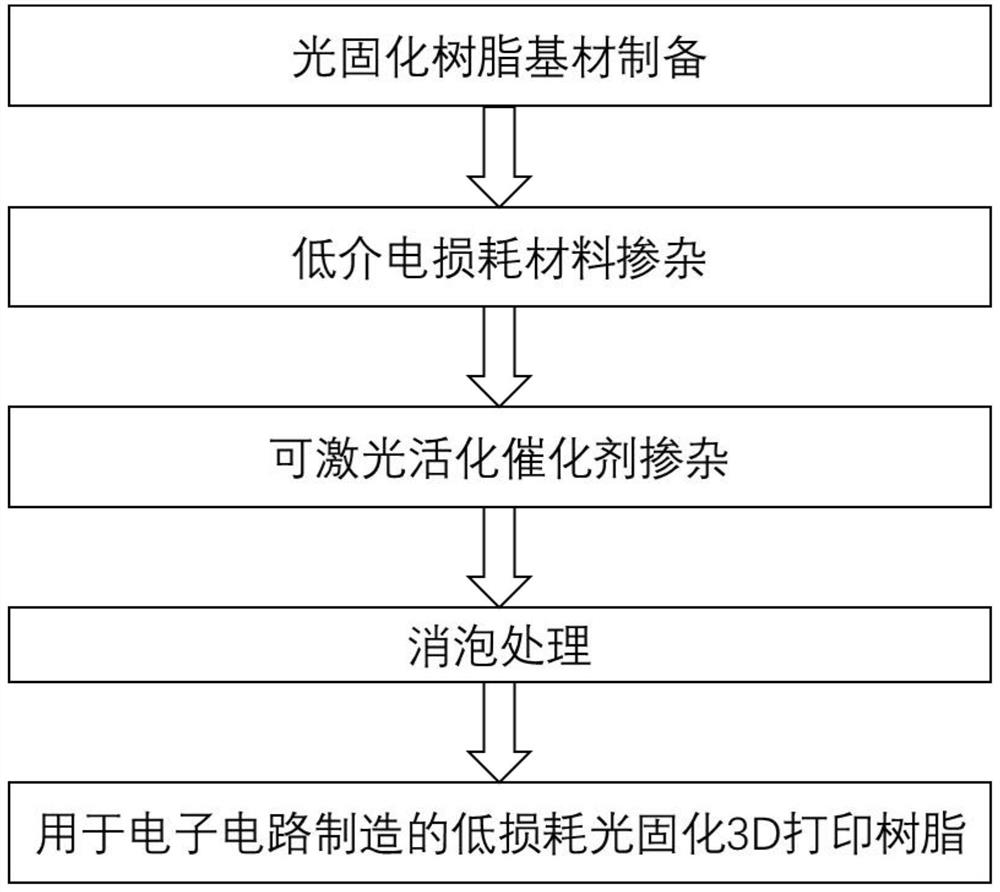
3D printing resin for manufacturing low-loss antenna and application of 3D printing resin
A 3D printing, low-loss technology, applied in the field of new 3D printing resins, to simplify the production process, reduce the loss angle, and achieve good leveling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] The low-loss antenna material used for photocuring 3D printing in this embodiment includes the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0060]
[0061] In this embodiment, the preparation method of the light-cured 3D printing low-loss antenna is as follows:
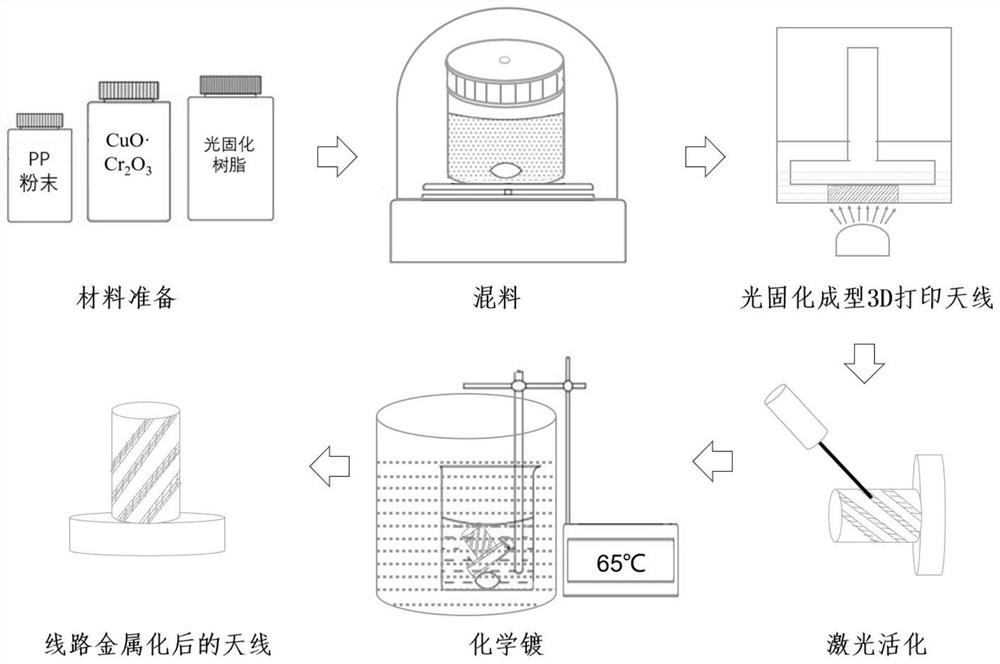
[0062] (1) Mix 70g polyethylene glycol (PEG) and 70g ethylene glycol diacrylate (HDDA) at room temperature and stir evenly to obtain a photocurable resin substrate;
[0063] (2) Add 50 g of polypropylene (PP) powder to the product in (1) several times in a small amount, stir at high speed in a vacuum environment until mixed, and obtain a low-loss photocurable resin;
[0064] (3) Add 10 g of laser-activatable (LDS) metal compound powder to the product in (2), and stir at high speed in a vacuum environment until the mixture is evenly mixed to obtain a laser-activatable low-loss photocurable resin.
[0065] (4) Add 2g of photosensitizer (TPO) to the product in (3) under the condition of avoiding light, and st...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The low-loss antenna material in this embodiment includes the following raw material components in parts by weight:
[0081]
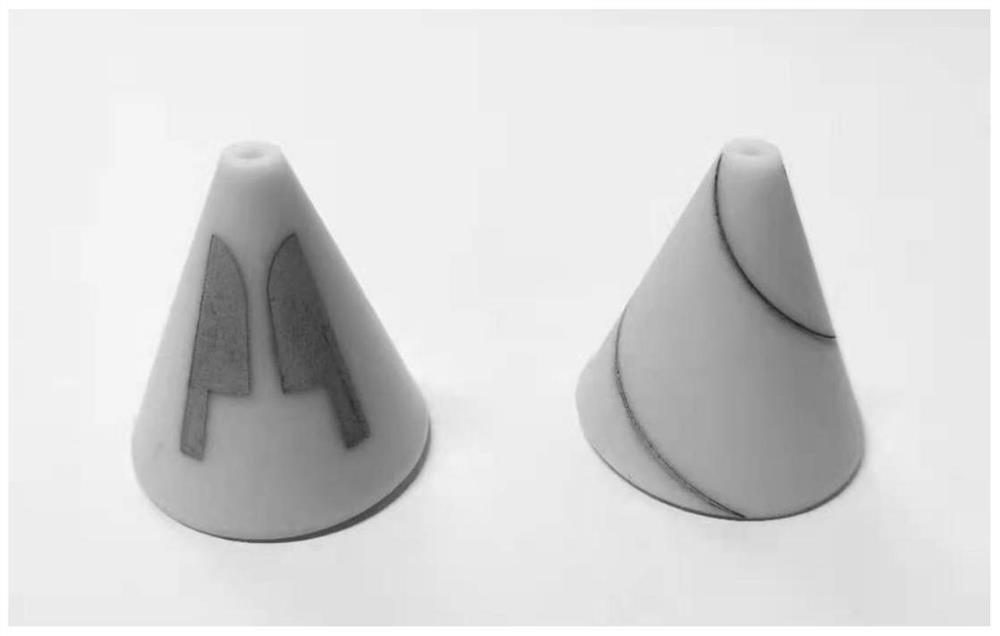
[0082] The material preparation method of the low-loss antenna material of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the only difference is that due to the high content of PP powder, it needs to be diluted with ethanol to help the material to mix and stir better, and because ethanol is volatile , whose mass is not included in the total mass of the material. The PP content of the material can reach 65%, and the loss angle of the obtained low-loss photocurable resin is about 0.0018. .
[0083] The 3D printing method used in this example is extrusion molding: put the prepared material into an opaque metal dispensing syringe in the dark, with a needle diameter of 1.25 mm, use the FDM slicing software to slice the model, and select in the software Corresponding to the diameter of the needle, the thickness of the printing layer is 0.4 / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com