Method for detecting oxalic acid by using quantum dots and application
A technology of quantum dots and quantum dot solution, which is applied in the field of chemical detection to achieve the effects of easy operation, mild reaction conditions and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] 1. Oxalic acid analysis
[0044] to the solution containing 5 µl CuSO 4 (e.g., 1-100 μmM) and 50 μl of MOPS buffer (100 mmol / L NaNO 3 , 2.5 mmol per liter Mg(NO 3 ) 2 ,pH 7.4) solution, add 40 μl of detection solution containing different concentrations of oxalic acid (for example, oxalic acid concentration is 0.1 μM-10mM), incubate at room temperature (for example, 1–5 minutes) to complete the reduction reaction. Subsequently, 1-100 microliters of quantum dots (CdTe and / or CdSe) were added to the above solution and incubated at room temperature (eg, 1-5 minutes). Finally, the above solution was diluted to 200 μl with high-purity water. Under the excitation of 365 nm light, the quantification of oxalic acid was realized by measuring the fluorescence spectrum in the range of 570-720 nm.
[0045] 2. Pretreatment of urine
[0046] The research team of the present invention collected 24-hour urine from 36 stone patients and 11 healthy people from West China Hospital o...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Feasibility Analysis of Oxalic Acid Detection
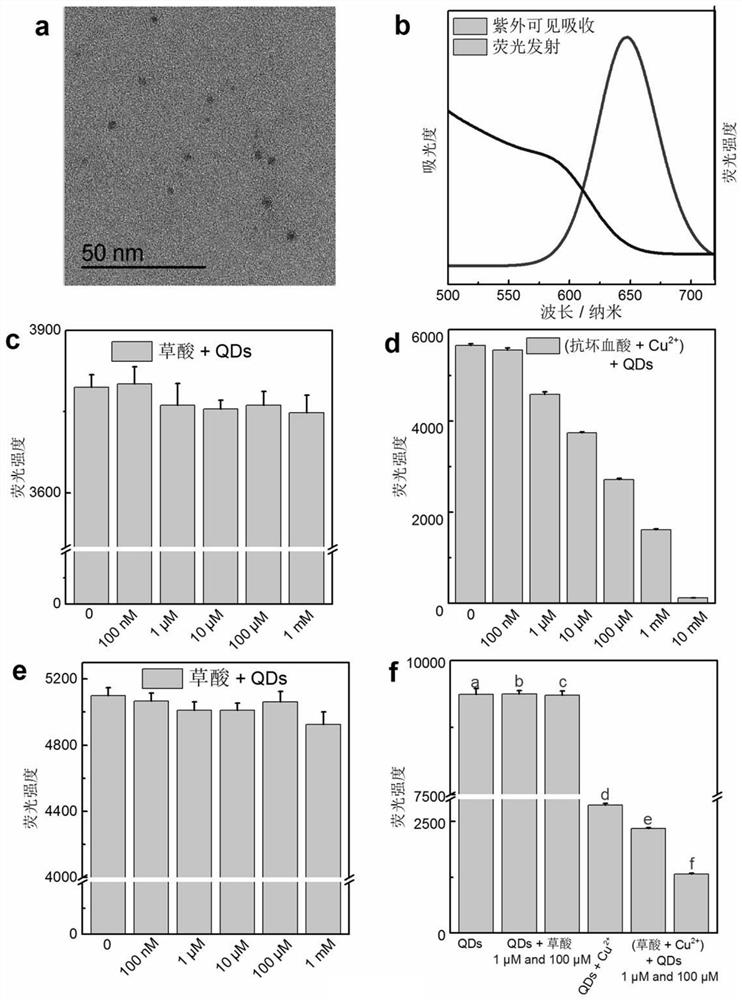
[0054] Quantum dots were characterized in several ways using transmission electron microscopy, UV absorption-visible spectrometer and fluorescence spectrophotometer. The synthesized quantum dots have a spherical shape and an average particle size of 4 nm ( figure 2 a). The ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence emission characteristic peaks ( figure 2 b).
[0055] Subsequently, the effect of oxalic acid on the fluorescence signal of quantum dots was detected. In the range of 0 to 1 mmol / L, oxalic acid had no significant effect on the fluorescence signal of quantum dots ( figure 2 E), exhibits a low interference signal similar to that of ascorbic acid.
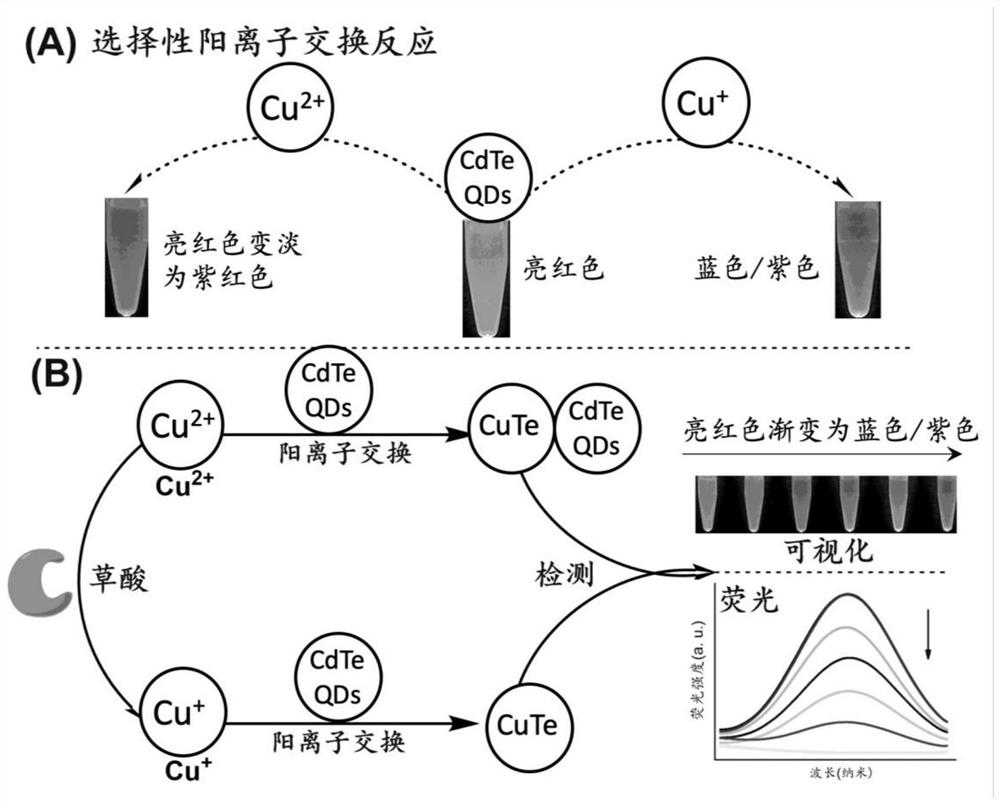
[0056] Compared with the effect of oxalic acid on quantum dots, Cu 2+ It shows obvious quenching effect on the fluorescence signal of quantum dots ( figure 2 f-d compared to 2f-b and c). Add oxalic acid at a concentration of 1 to 100 micromolar per liter to Cu ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] This embodiment is a preferred embodiment. Optimized conditions that affect assay performance, including Cu 2+ Reaction time with oxalic acid, Cu + and quantum dot reaction time, Cu + and the incubation time of quantum dots, and the volume of quantum dots.
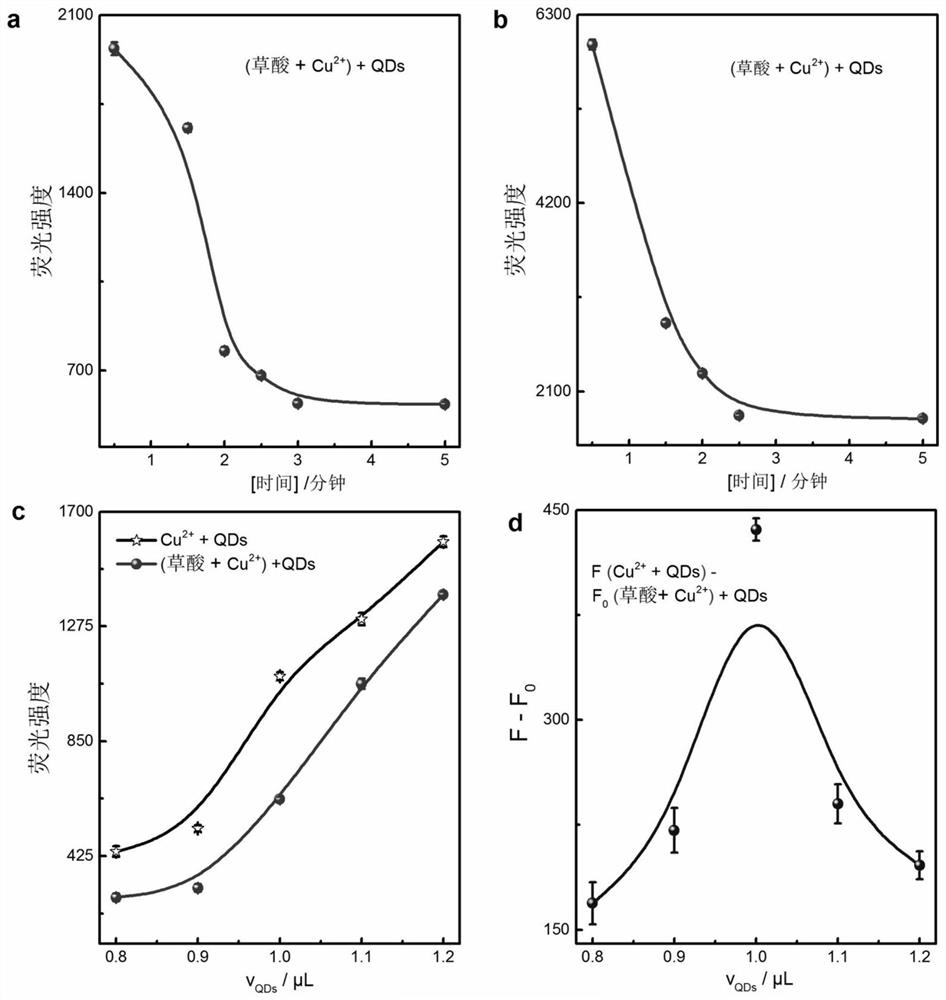
[0059] As the reaction time prolongs, the fluorescence signal of quantum dots decreases rapidly, indicating that oxalic acid reduces Cu 2+ Can be done in 3 minutes ( image 3 a). Cu + The quenching reaction to quantum dots is fast and can be completed within 2.5 minutes ( image 3 b). As the volume of quantum dots increased, the fluorescence signals of solutions with and without oxalic acid increased ( image 3 c). At 1 microliter of quantum dots, the above solution obtained the maximum fluorescence signal difference ( image 3 d). Therefore, in the follow-up experiments, 3 min was used for oxalic acid reduction of Cu 2+ , 2.5 min was adopted for quenching QDs, and 1 µl QDs as signaling molecules.
[00...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com