Phycomycete crust cultivation method suitable for calcareous sand soil of South China Sea coral island reef
A sandy soil, calcareous technology, applied in the direction of soil preparation methods, applications, fungi, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing adaptability, increasing biomass, and good adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Optimization of artificial cultivation conditions and technical construction of algal crusts in typical tropical coral reef environments in the South China Sea
[0028] The present invention can ensure that the reef algae crust seed soil derived from typical tropical coral islands in the South China Sea can be used in different concentrations of carbon sources, nitrogen sources, phosphorus sources, and potassium, magnesium and iron elements under the simulated natural environment of South China Sea islands and reefs. Compared and combined with the optimal inoculum amount to cultivate the method of artificially cultivating algae crusts to obtain high biomass in the room. The specific operation is carried out according to the following steps:
[0029] 1. Consider the 7 factors of inoculum size, glucose, sodium nitrate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride and ferrous chloride, set 4 levels for each factor, and then use the seven-f...
Embodiment 2
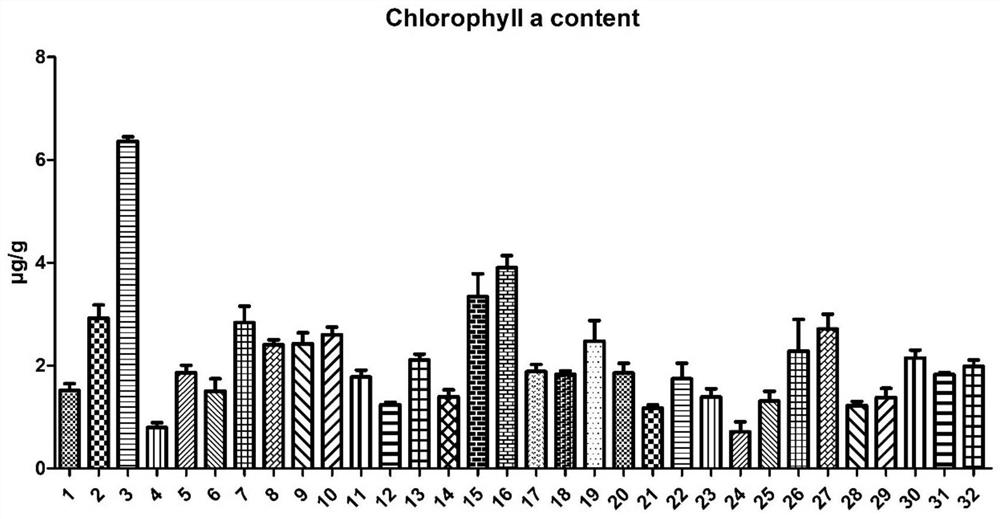
[0040] Example 2: Indoor inspection of the effect of the artificial cultivation technology of algae crusts on tropical coral islands and reefs in the South China Sea
[0041] During the experiment, the biomass of the algal crust samples was measured at the beginning and end of the experiment, respectively. The specific measurement method is:
[0042] 1) Put it into a freeze dryer to remove moisture (48h) before measuring;
[0043] 2) Take out the crust, remove loose sand grains, and record the thickness of the crust with a vernier caliper (unified thickness standard, about 0.1cm), then grind with a mortar in the dark to separate the algae from the sand grains, and disperse algae;
[0044] 3) Weigh 2g (±0.02g) samples respectively and put them in a stoppered scale test tube, and use acetone extraction to measure the content of chlorophyll a (expressed by the content of chlorophyll a per gram of dry crust soil sample), set 3 repetitions ;
[0045] 4) Add 10 mL of 80% acetone...
Embodiment 3
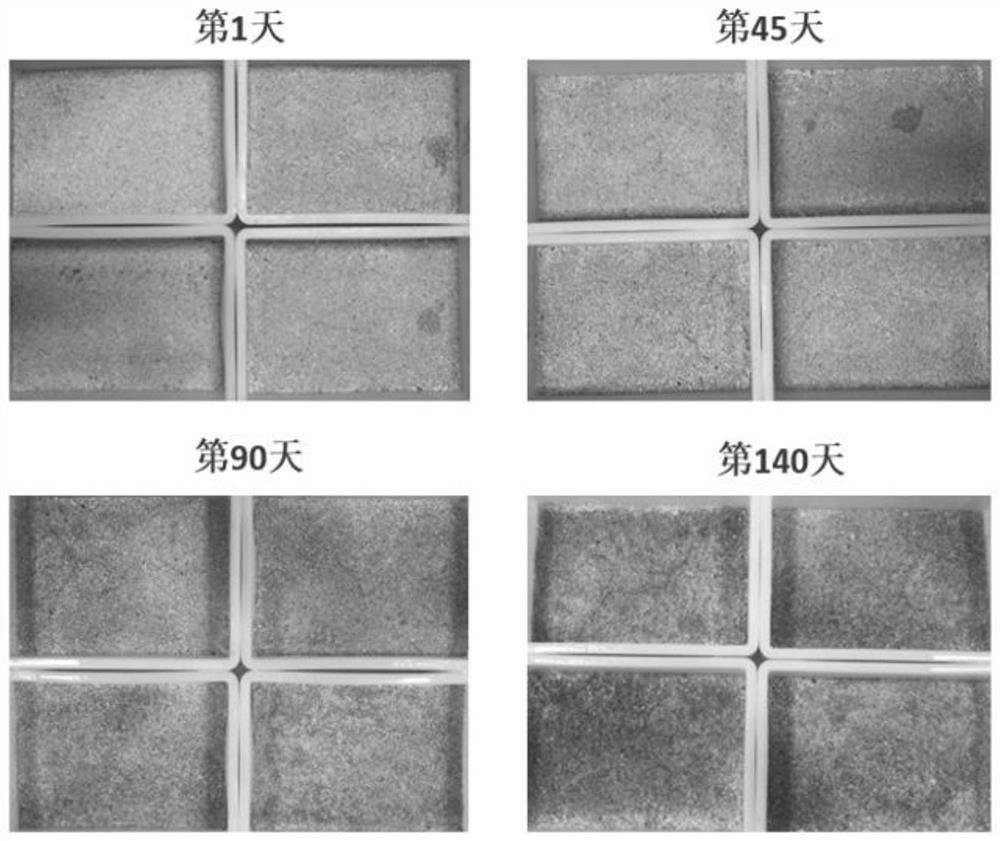
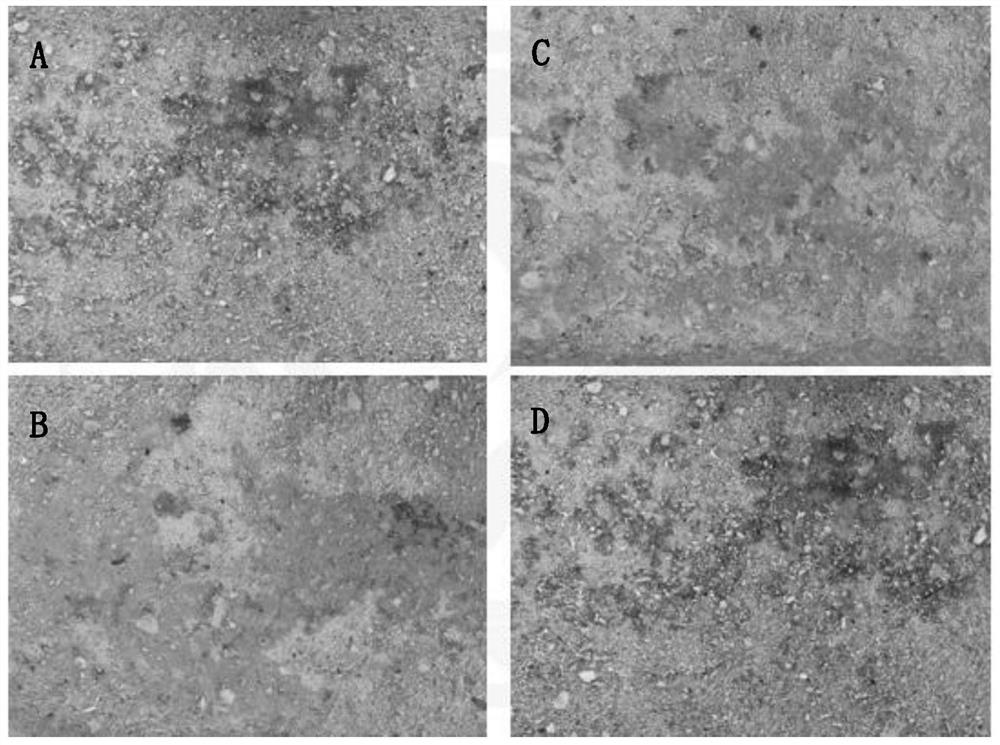
[0050] Example 3: Field inspection of the effect of the artificial cultivation technology of algae crusts on tropical coral islands and reefs in the South China Sea
[0051] The algae crusts artificially cultivated by the method of combination 3 in Example 1, and the fresh samples of algae crusts collected in tropical coral islands and reefs in the South China Sea were made into seed soil respectively, and the two were inoculated into the environment of tropical coral islands and reefs to carry out artificial Test of the adaptability of cultivated algal crusts in the field. The specific operation method is as follows:
[0052] 1) Using a soil grinder, the algal crusts cultivated in the laboratory and the collected fresh algal crusts were evenly crushed to make three types of crust seed soils, namely: artificial algal crust seed soil, in-situ Fresh algae crust seed soil and mixed seed soil evenly mixed in a ratio of 1:1;
[0053] 2) Inoculate the three types of seed soil even...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com