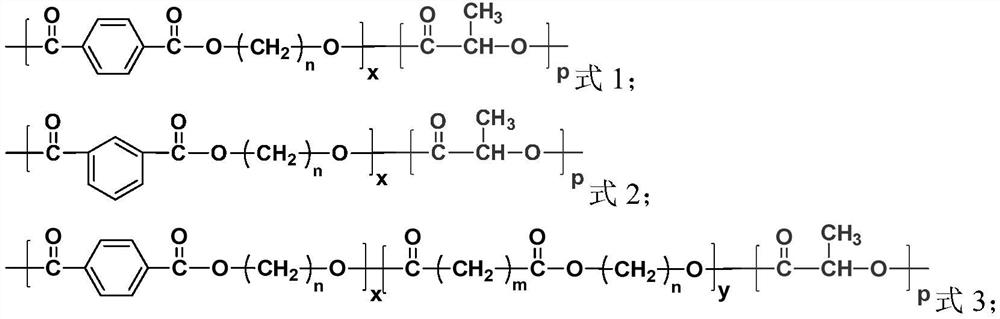
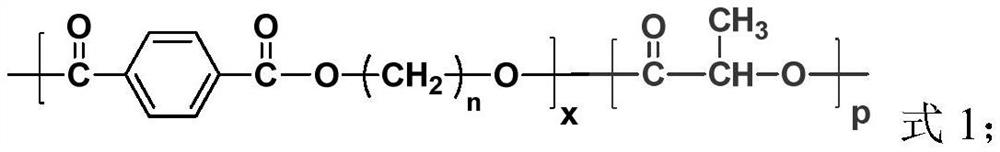
Degradable copolyester as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of copolyester and polyester, which is applied in the field of degradable polymer materials, can solve the problems of high cost, low molecular weight, poor mechanical properties and high-efficiency biodegradation of polyester, and achieve reduction of synthesis steps, simple method, and accelerated degradation rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0079] The invention provides a kind of preparation method of copolyester, comprises the steps:
[0080] Mixing the dibasic acid, dibasic alcohol and lactic acid monomers used to form the segment of the difficult-to-hydrolyze polyester, in the presence of a catalyst, temperature programming, esterification and polycondensation to obtain the copolyester;
[0081] or
[0082] The dibasic acid, dibasic alcohol or the lactic acid monomer used to form the segment of the difficult-to-hydrolyze polyester is programmed to increase the temperature in the presence of a catalyst, and firstly undergo esterification and polycondensation to obtain a low-molecular-weight segment that is difficult to hydrolyze permanent polyester or low molecular weight polylactic acid fragments;
[0083] Adding the above-mentioned low-molecular-weight segments of difficult-to-hydrolyzable polyester or low-molecular-weight polylactic acid during the esterification and polycondensation process of polylactic a...
Embodiment 1
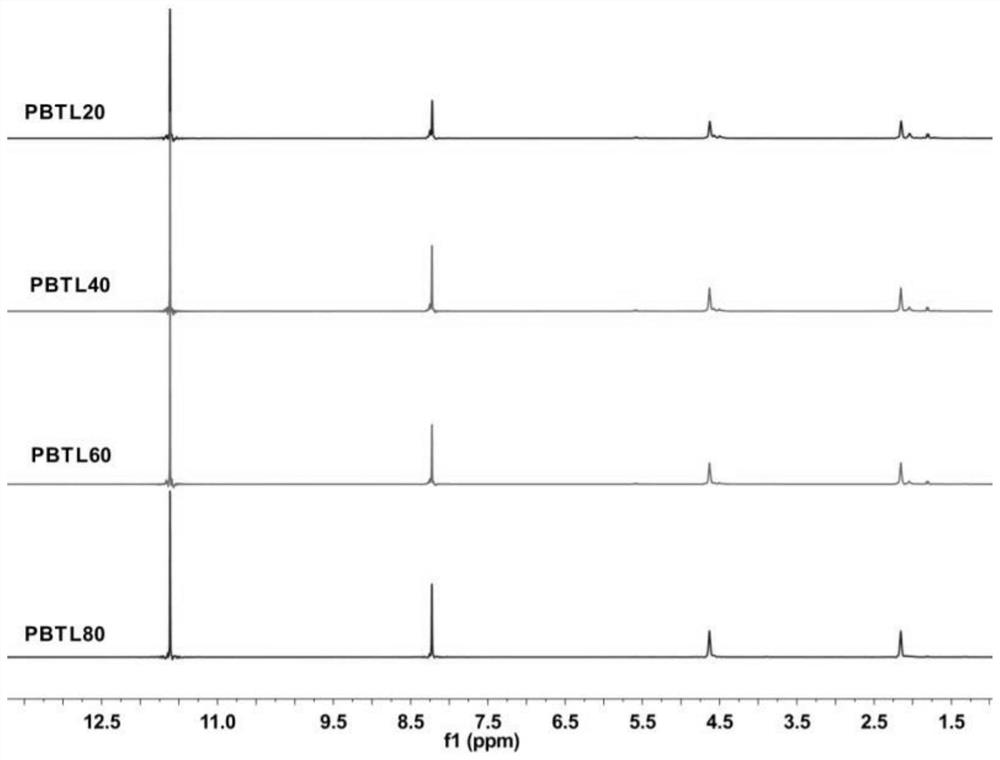
[0117]10mol terephthalic acid, 1,4-butanediol (excess) 15mol, 2-10mol lactic acid, tetrabutyl titanate, stannous chloride, triethyl phosphate composite catalyst 0.85-1.2g, start at 180°C Raise the temperature by 10°C every 10 minutes, until it reaches 230°C, stop the esterification after no more water, add 3.5-5g of composite catalyst, vacuumize, raise the temperature by 10°C every 10 minutes, program the temperature to 250°C, control the reaction temperature at 250°C to continue the reaction After 1 hour, 1.5-3g of catalyst was added, and the reaction was continued for 1.5h to obtain random copolyesters PBTLA20, PBTLA40, PBTLA60, PBTLA80, PBTLA100, and the NMR spectra of the obtained PBTL series polymers were as follows: figure 1 As shown, the relevant data are shown in Table 1:
[0118]
[0119] Table 1
[0120]
Embodiment 2
[0122] 10 mol of terephthalic acid, 13 mol of ethylene glycol (excess), 2-8 mol of lactic acid, tetrabutyl titanate, stannous chloride, and 0.85-1.2 g of composite catalyst composed of triethyl phosphate, starting at 180°C, heating up 10 minutes per 10 minutes ℃, until it rises to 230 ℃, the esterification is finished after no more water is released, add 3.5-5g of composite catalyst, vacuumize, increase the temperature by 10 ℃ every 10min, program the temperature to 260 ℃, control the reaction temperature at 260 ℃ and continue the reaction for 1 hour, supplement Add 1.5-3g of catalyst and continue the reaction for 1.5h to obtain random copolyester PETLA20, PETLA40, PETLA60, PETLA80, PETLA100. The relevant data are shown in Table 2:
[0123]
[0124] Table 2
[0125]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com