Solid-liquid conversion device and method for material in micropores
A converter device and micropore technology, which is applied in the field of solid-liquid converter devices for materials in micropores, can solve the problems of slow dissolution rate, low dissolution efficiency of soluble photosensitive resin, and difficulty in material dissolution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
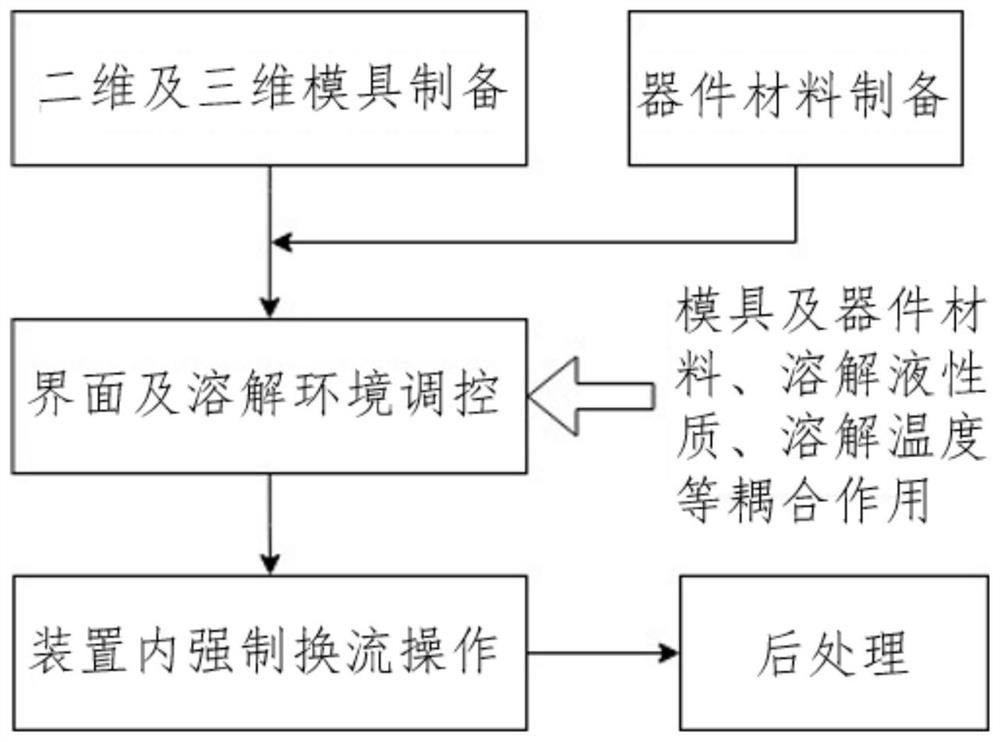
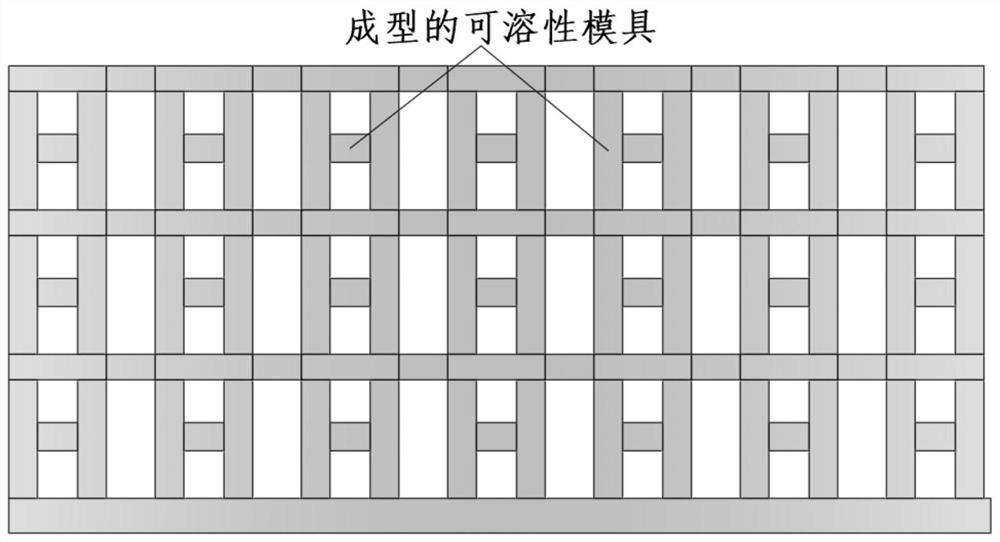
[0039] This implementation case is to realize the 3D printing of soluble resin molds and the solid-liquid commutation and dissolution in paraffin micropores. Refer to figure 1 , the specific process includes the following steps:
[0040] (1) Use 3D printing technology and stereolithography technology to prepare the required two-dimensional photolithographic microchannel mold and three-dimensional structure soluble resin mold, and do corresponding post-processing;
[0041] Preparation of resin mold:
[0042] Weigh 60g comonomer N, N-dimethylacrylamide by electronic scale, pour it into the beaker for later use, then weigh 60g comonomer methyl methacrylate and pour it into the beaker and N, N - Dimethacrylamide is mixed, and then 45g of cross-linking cracking agent methacrylic anhydride is weighed and poured into a beaker so that the three are fully mixed. Put the beaker containing the mixed solution into a magnetic stirring water bath, and stir in an oil bath at 50°C for 30 mi...
Embodiment 2
[0053] This implementation case is to realize the three-dimensional sponge structure solid-liquid commutation method using PDMS as material, refer to Figure 8 , including the following steps:
[0054] (1) Prepare the required PDMS mold and do corresponding post-processing;
[0055] PDMS material preparation:
[0056] Weigh 60g polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS, 184silicone elastomerbase) with an electronic scale, pour it into a beaker for later use, then take 10g of curing agent according to the mass fraction of 10:1, mix PDMS and curing agent to obtain a matrix, and put magnetic stirring in the mixture Use a magnetic stirrer to stir at a speed of 60 rad / s for 10 minutes. After fully stirring, put it into a vacuum pump to draw an absolute vacuum to ensure that there are no air bubbles in the PDMS.
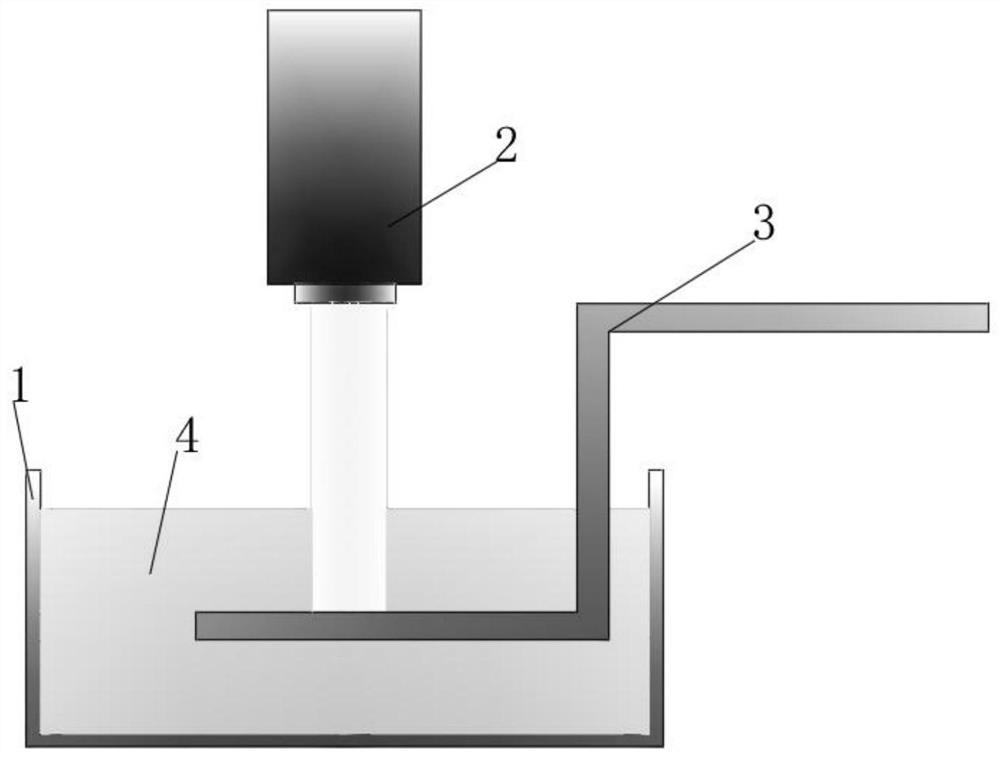
[0057] (2) Cover the formed mold with the liquid insoluble material to be formed, and wait for the insoluble material to solidify to complete the forming of the microporous structure; ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] This implementation case is to realize high-efficiency solid-liquid commutation on a two-dimensional channel-shaped surface. Refer to Figure 9 , the specific preparation process includes the following steps:
[0067] (1) Use 3D printing technology and stereolithography technology to prepare the required two-dimensional photolithographic microchannel mold, three-dimensional structure soluble resin mold or PDMS mold, and perform corresponding post-processing.
[0068] Preparation of photolithographic microchannel molds:
[0069] Select a piece of PC board (or silicon wafer) as the photoresist substrate, ultrasonically put the PC board in alcohol for 10s, then put it in an oven and set the temperature not higher than 60°C to dry, and then spin coat it on the PC board through a coater The photoresist is AZ4620, the spin coating speed is 600 at low speed and 900 at high speed, and the thickness of the photoresist is 15-17 μm. Place the spin-coated photoresist on a drying ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com