Method for preparing tannic acid iron coordination modified molybdenum disulfide hydrogel dressing
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and tannic acid, which is applied in the fields of molybdenum sulfide, pharmaceutical formulations, medical science, etc., can solve the problems such as rapid wound healing and cell death that cannot function, cannot create a suitable healing environment, and achieves good ductility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This embodiment provides a method for preparing molybdenum disulfide hydrogel dressing modified with iron tannate coordination, comprising the following steps:
[0034] Step 1, mixing sodium molybdate, thiourea and water to obtain a molybdenum source solution; the quality of the thiourea is 1.26 times the quality of sodium molybdate, and the quality of the water is 62.02 times the quality of sodium molybdate;
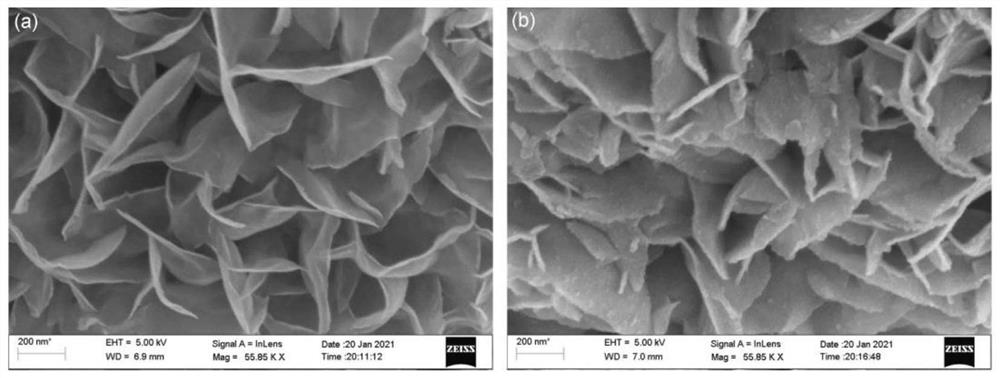
[0035] Step 2: Under the temperature condition of 220°C, react the molybdenum source solution described in step 1 for 24 hours, cool it naturally to room temperature, wash with deionized water and ethanol, centrifuge, remove the supernatant, and dry the precipitate at 60°C Dry to constant weight to obtain molybdenum disulfide nanosheets;
[0036] Step 3. Under ultrasonic conditions, the molybdenum disulfide nanosheets described in step 2 are dispersed in deionized water to obtain a molybdenum disulfide nanosheet dispersion system, and the molybdenum disulfide nan...
Embodiment 2
[0062] This embodiment provides a method for preparing molybdenum disulfide hydrogel dressing modified with iron tannate coordination, comprising the following steps:
[0063] Step 1, mixing sodium molybdate, thiourea and water to obtain a molybdenum source solution; the quality of the thiourea is 1.26 times the quality of sodium molybdate, and the quality of the water is 62.02 times the quality of sodium molybdate;
[0064] Step 2. Under the temperature condition of 220°C, react the molybdenum source solution described in step 1 for 24 hours, cool it naturally to room temperature, wash with deionized water and ethanol, centrifuge, remove the supernatant, and dry the precipitate at 50°C Dry to constant weight to obtain molybdenum disulfide nanosheets;
[0065] Step 3. Under ultrasonic conditions, the molybdenum disulfide nanosheets described in step 2 are dispersed in deionized water to obtain a molybdenum disulfide nanosheet dispersion system, and the molybdenum disulfide nan...
Embodiment 3
[0073] This embodiment provides a method for preparing molybdenum disulfide hydrogel dressing modified with iron tannate coordination, comprising the following steps:
[0074] Step 1, mixing sodium molybdate, thiourea and water to obtain a molybdenum source solution; the quality of the thiourea is 1.26 times the quality of sodium molybdate, and the quality of the water is 92.88 times the quality of sodium molybdate;
[0075] Step 2. Under the temperature condition of 220°C, react the molybdenum source solution described in step 1 for 24 hours, cool it down to room temperature naturally, wash with deionized water and ethanol, centrifuge, remove the supernatant, and dry the precipitate at 70°C Dry to constant weight to obtain molybdenum disulfide nanosheets;
[0076] Step 3. Under ultrasonic conditions, the molybdenum disulfide nanosheets described in step 2 are dispersed in deionized water to obtain a molybdenum disulfide nanosheet dispersion system, and the molybdenum disulfid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com