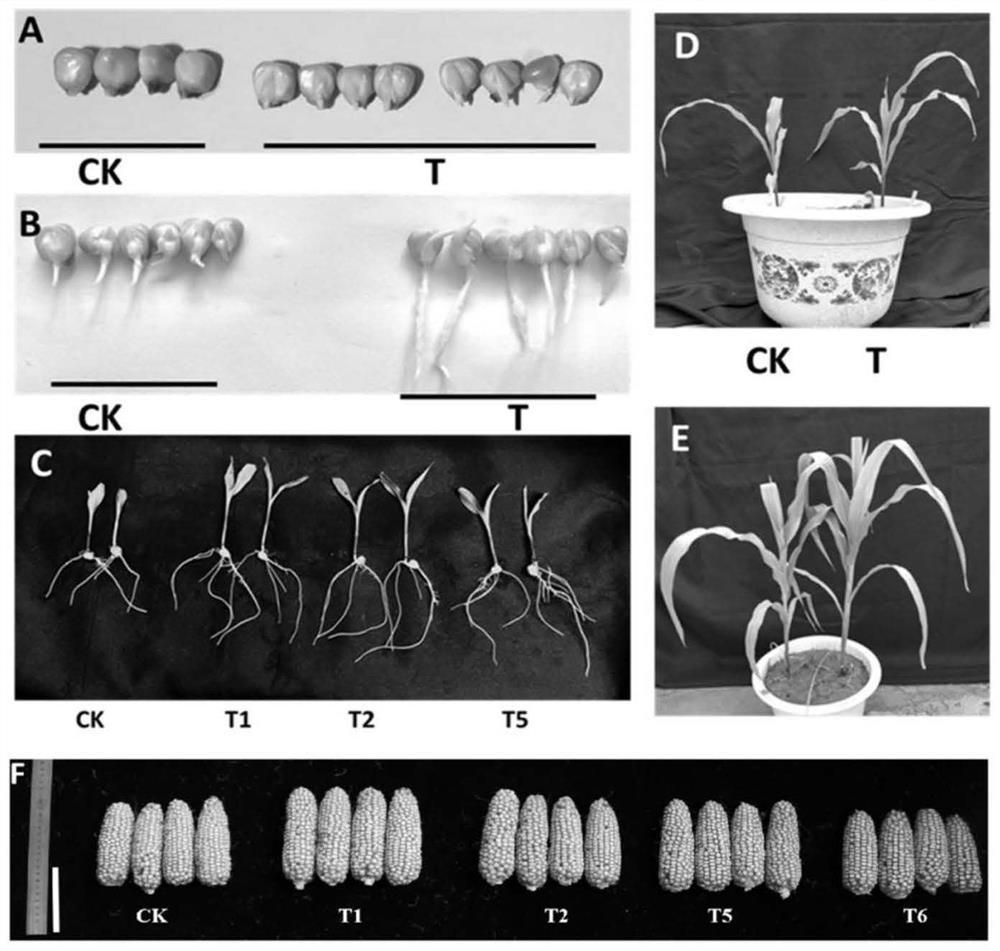
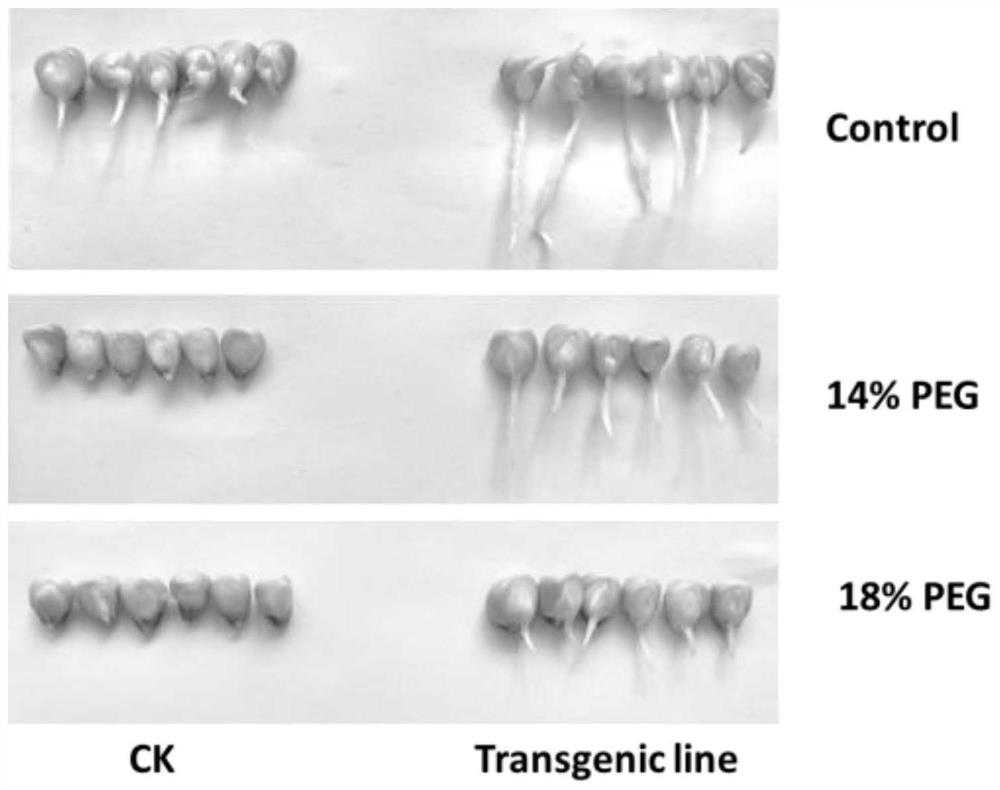
Method for Heterologous Synthesis of γ-polyglutamic Acid in Plants to Improve Plant Stress Resistance and Yield
A technology of polyglutamic acid and heterologous synthesis, applied in the fields of synthetic biology, genetic breeding, and genetic engineering, to achieve the effects of improving salt resistance, increasing biomass, and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1: Obtaining the amino acid sequences of pgsA, pgsB, and pgsC
[0083] The three key enzyme genes PgsA, PgsB, and PgsC for the synthesis of γ-PGA were cloned by known methods from the γ-polyglutamic acid-producing strain Bacillus licheniformis; wherein, the GenBank ID of the gene PgsA: AIA08848.1 , its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the Genebank ID of gene PgsB: AIA08846.1, its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2; the Genebank ID of gene PgsC: AIA08847.1, its amino acid sequence is as SEQ ID NO.1 Shown in ID NO.3.
Embodiment 2
[0084] Example 2: Codon optimization
[0085] According to the obtained amino acid sequences of PgsA, PgsB, and PgsC genes, through codon bias analysis in maize or other plants to be transgenic and combined with CpG dinucleotides content, GC content, mRNAsecondary structure, Cryptic splicing sites, Premature PolyA sites, Internal Chisites and ribosomal binding sites, Negative CpG islands, RNA instability motif (ARE), Repeat sequences (direct repeat, reverse repeat, and Dyad repeat), Restriction sites that may interfere with cloning, etc. are analyzed to finally determine the optimized sequence, and according to the sequence De novo synthesis of optimized PgsA, PgsB, and PgsC genes; wherein, the codon-optimized PgsA gene nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.4; the codon-optimized PgsB gene nucleotide sequence is shown in Shown in SEQ ID NO.5; the nucleotide sequence of the codon-optimized PgsC gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.6.
Embodiment 3
[0086] Embodiment 3: plant expression vector construction
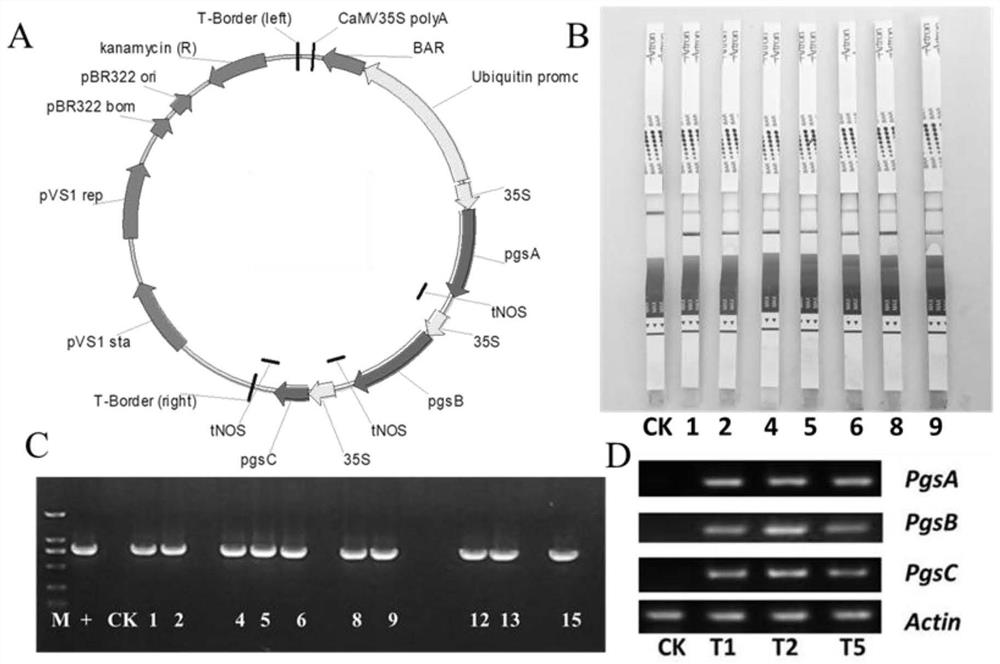
[0087] The PgsA, PgsB, and PgsC genes after the codon optimization were connected into the plant expression vector pU130-bar containing the bar gene screening marker in a known method (the vector map is as follows: Figure 10 shown), obtain the plant expression vector containing the gene of interest, named as the plant expression vector PGA001, the vector map is as follows figure 1 shown; wherein the nucleotide sequence of the plant expression vector PGA001 is shown in SEQ ID NO.7; each functional element of the expression vector is described as:
[0088]
[0089]
[0090] The above-mentioned plant expression vector PGA001 is constructed using a multi-segment recombinase method, and the specific construction steps are:
[0091] 1 μg of vector pU130-bar was digested with restriction endonucleases Hindlll and Spel, reacted at 37°C for 1±0.2 hours, and the digested vector product was recovered using DC301 kit (com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com