Method for smelting and trapping platinum and rhenium from spent aluminum-based catalyst
A catalyst and catalyst particle technology, applied in the field of smelting and trapping platinum and rhenium, can solve the problems of serious environmental pollution of waste water and slag, short process flow, low yield, etc., and achieve mature main equipment, broad application prospects and high yield. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
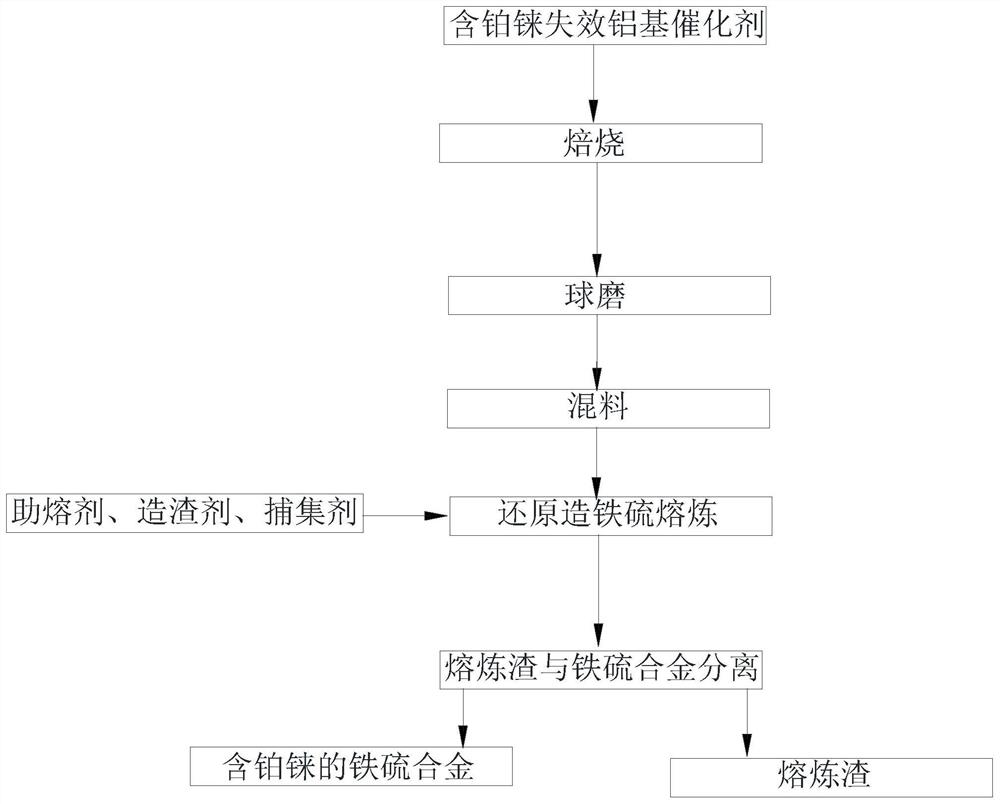
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for smelting and trapping platinum and rhenium from spent aluminum-based catalysts, the method comprising the following steps:
[0032] 5kg of the spent aluminum-based catalyst containing platinum was roasted and ball milled to obtain pulverized spent aluminum-based catalyst particles; the roasting temperature was 450°C and the roasting time was 2h.
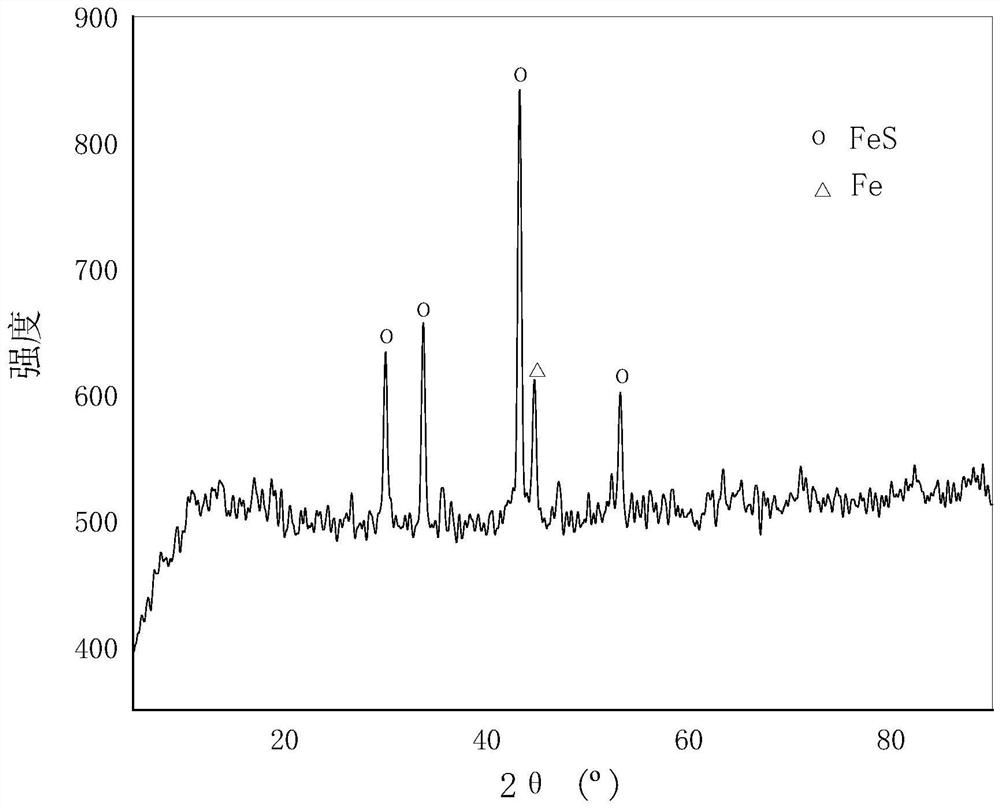
[0033] The exhausted aluminum-based catalyst particles are uniformly mixed with the trapping agent, the slagging agent and the fluxing agent to obtain the mixed material. Among them, the flux calcium fluoride is 0.3 times that of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst, the flux sodium carbonate and borax are respectively 20% of the weight ratio of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst, and the reducing agent charcoal is 20% of the weight ratio of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst. The addition amount of the collector ferrous sulfate is 2.0 t...
Embodiment 2
[0037] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for smelting and trapping platinum and rhenium from a spent aluminum-based catalyst, the method comprising the following steps:
[0038] 10 kg of spent aluminum-based catalysts containing platinum were calcined and ball-milled to obtain pulverized spent aluminum-based catalyst particles; the roasting temperature was 500° C., and the roasting time was 3 hours.
[0039] The exhausted aluminum-based catalyst particles are uniformly mixed with the trapping agent, the slagging agent and the fluxing agent to obtain the mixed material. Wherein, the flux calcium fluoride is 0.3 times of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst, the flux sodium carbonate and borax are respectively 20% of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst weight ratio, and the reducing agent charcoal is 20% of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst weight ratio; The amount of iron powder added is 0.2 times the weight ratio of the spent aluminum-based catalyst. T...
Embodiment 3
[0043] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for smelting and trapping platinum and rhenium from a spent aluminum-based catalyst, the method comprising the following steps:
[0044] 8 kg of spent aluminum-based catalysts containing platinum were roasted and ball milled to obtain pulverized spent aluminum-based catalyst particles; the roasting temperature was 550° C., and the roasting time was 3 hours.
[0045] The exhausted aluminum-based catalyst particles are uniformly mixed with the trapping agent, the slagging agent and the fluxing agent to obtain the mixed material. Wherein, the flux calcium fluoride is 0.3 times of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst, the flux sodium carbonate and borax are respectively 20% of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst weight ratio, and the reducing agent charcoal is 20% of the invalid aluminum-based catalyst weight ratio; The amount of iron powder added is 0.4 times the weight ratio of the spent aluminum-based catalyst. The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com