Rice male fertility regulation gene mutant as well as molecular marker and application thereof
A technology of male fertility and mutants, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of fertility affected by light and temperature environment, high risk of seed production, and geographical restrictions of seed production, achieving great application value, Effective method, high utilization rate of germplasm resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Example 1 Screening of rice male sterile mutant gms2
[0092] In June 2013, 10 kg of 93-11 seeds were irradiated with cobalt 60 to obtain M 0 generation. The irradiated seeds were planted in the experimental field of Lingao County, Hainan Province, and harvested by individual plants after maturity. A total of M 1 There are about 6,500 substitute materials. In the spring of 2014, 3617 M with more seeds were selected 1 The generation materials were planted into strains, and 50 individual plants were planted in each strain. Various types of mutants such as plant type, panicle type, fertility, yield, etc. were screened at the tillering stage, booting stage, heading stage, flowering stage, and grain filling stage, and harvested and stored. Among them, a sterile mutant was found in the line numbered 3148, named gms2.
Embodiment 2
[0093] Example 2 Phenotype analysis of rice male sterile mutant gms2
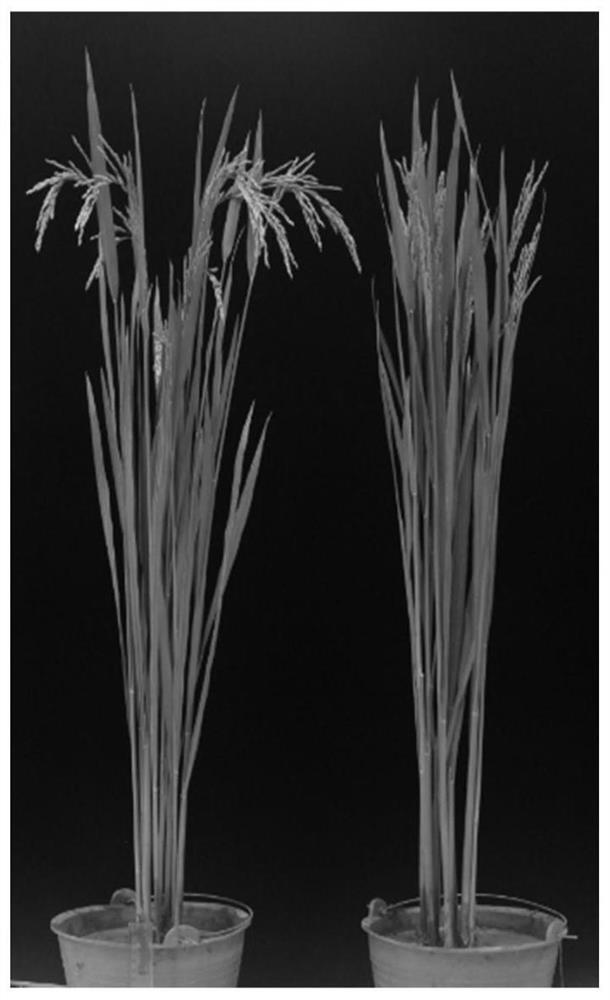
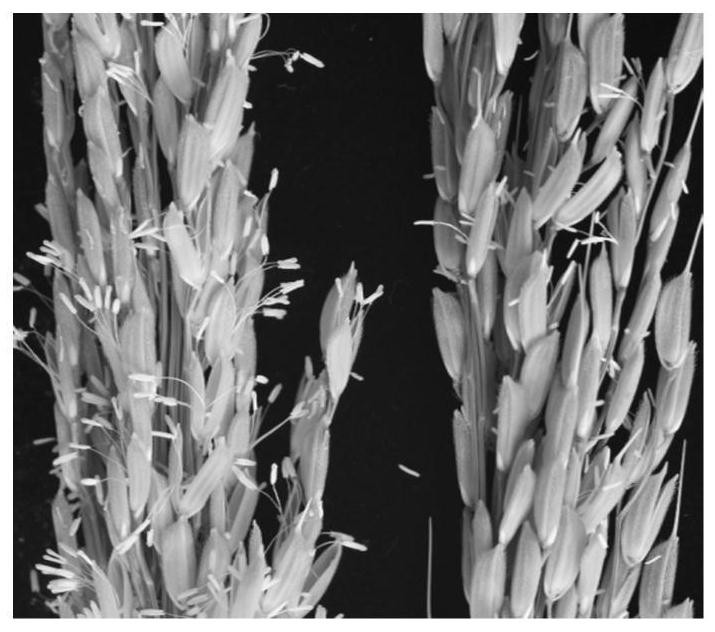
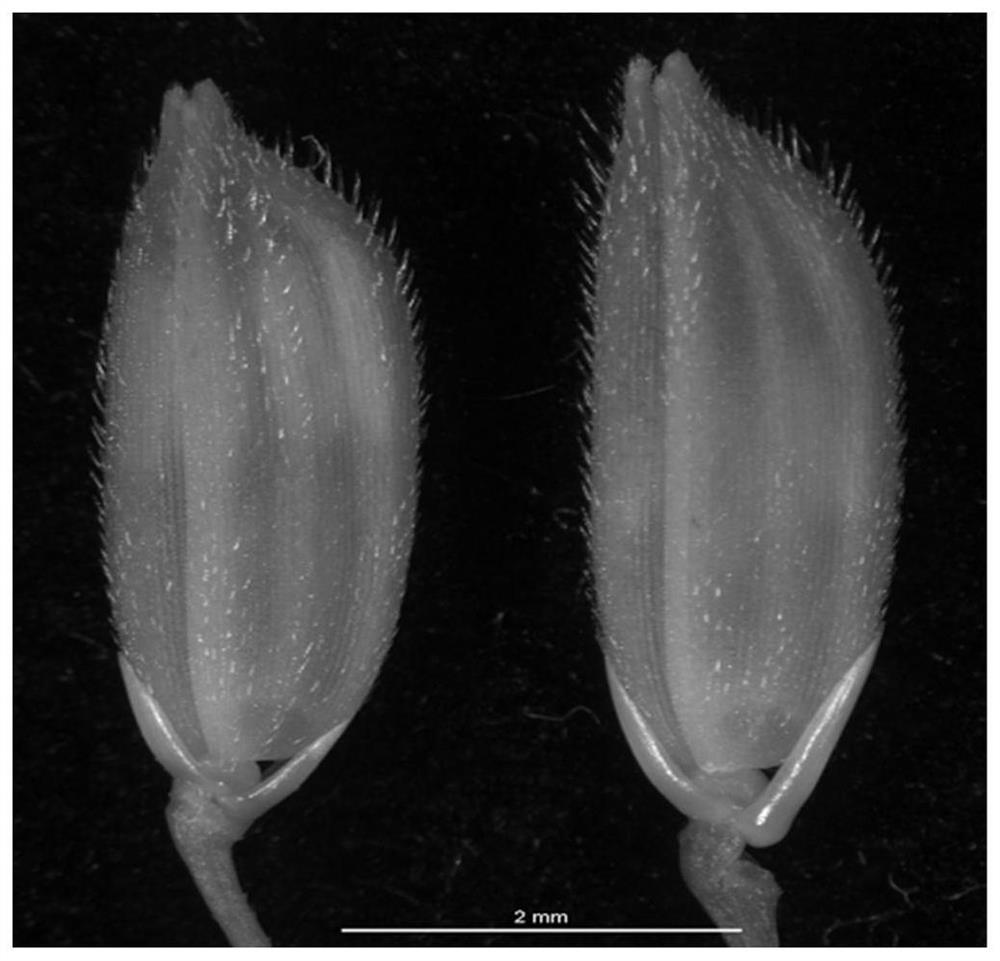
[0094] Compared with wild type, gms2 mutant plants ( figure 1) and Xiaosui ( figure 2 ) is normal in shape, and the flowering period is a little later. The size of palea and lemma, the opening size of florets, and the opening time were not significantly different from those of the wild type ( image 3 ). Observing the shape of the mutant florets under a stereomicroscope, it was found that the ovary, style, and stigma were slightly larger than those of the wild type ( Figure 4 ), but the anthers are thinner and lighter than the wild type ( Figure 5 ). With iodine-potassium iodide solution (0.6% KI, 0.3% I 2 , w / w) solution dyes pollen, such as Image 6 As shown, the wild-type pollen grains are large and round and are stained blue-black, while the mutant pollen grains are shrunken and cannot be stained. The wild-type plants of the same family set fruit normally after bagging selfing, but the gms2 m...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3 Genetic Analysis of Rice Male Sterility Mutant gms2
[0096] In the M5 generation, 80 strains of the segregation population of gms2 were planted, of which 64 strains had normal fertility and 16 strains were sterile, and the segregation ratio between fertile and sterile strains was 3:1 (χ 2 =0.57, P>0.05). By backcrossing gms2 with 93-11, all F1 plants were fertile. In the F2 generation, 70 strains of gms2 segregation population were planted, of which 57 strains had normal fertility and 13 strains were sterile, and the segregation ratio between fertile and sterile strains was 3:1 (χ 2 =0.85, P>0.05). The above results indicated that the sterility trait of gms2 was controlled by a recessive single gene.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com