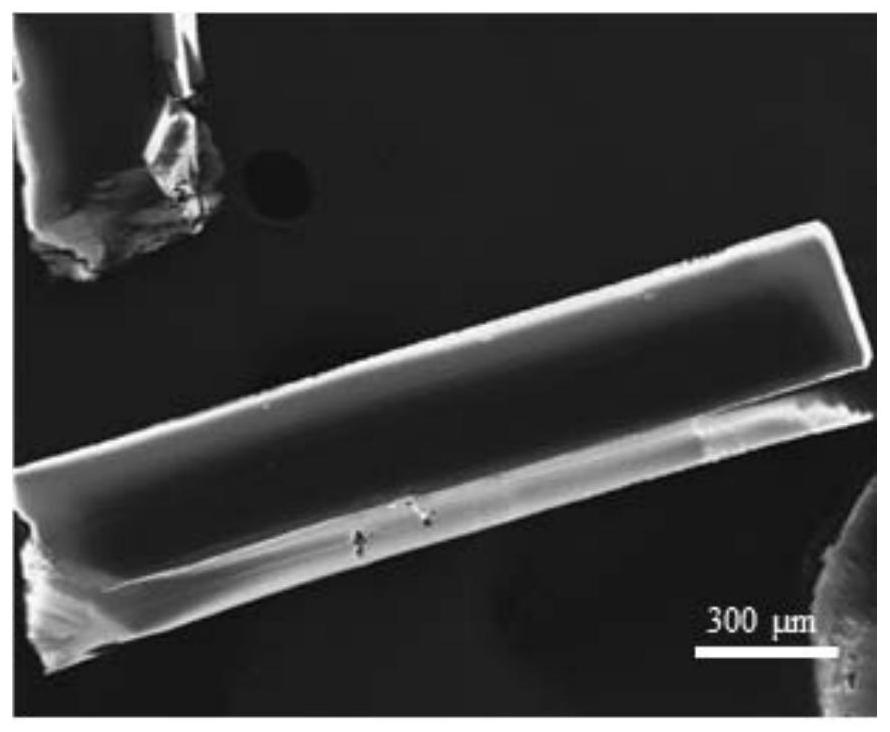
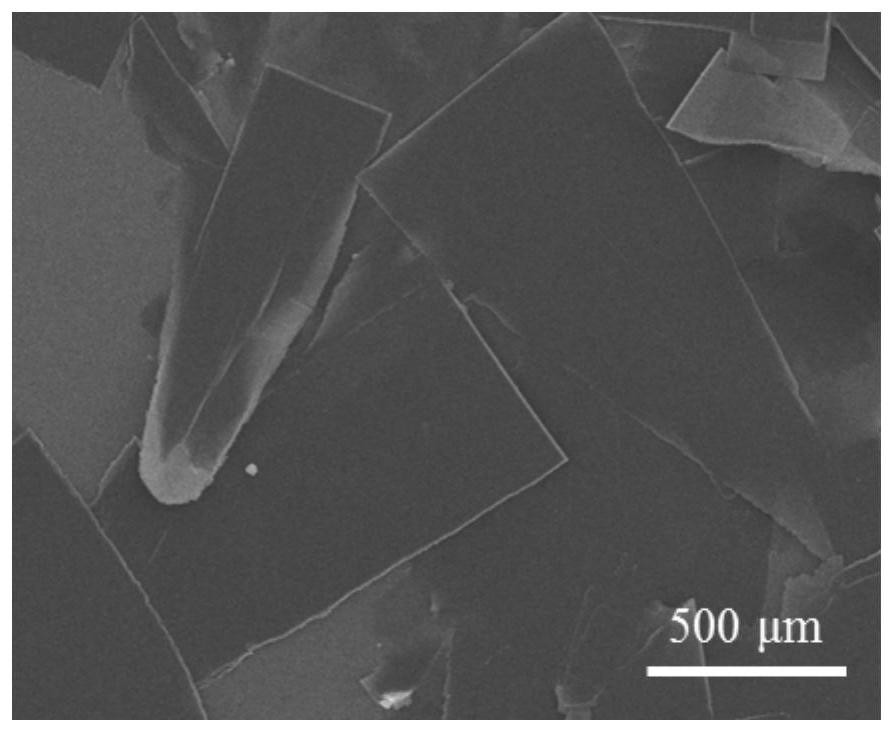
Preparation method of strong-polarity organic solvent tolerance macroscopic blue-phase polydiyne material based on co-assembly way
An organic solvent and polar organic technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of macroscopic blue-phase polydiacetylene materials with strong polar organic solvent tolerance, can solve problems such as difficult sensors, difficult polymerization diacetylene materials, and restricted development, and achieves easy polymerization. , the method is simple, the side chain structure is easy to achieve
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: PCDA and NMA are slowly added dropwise in DMF to assemble
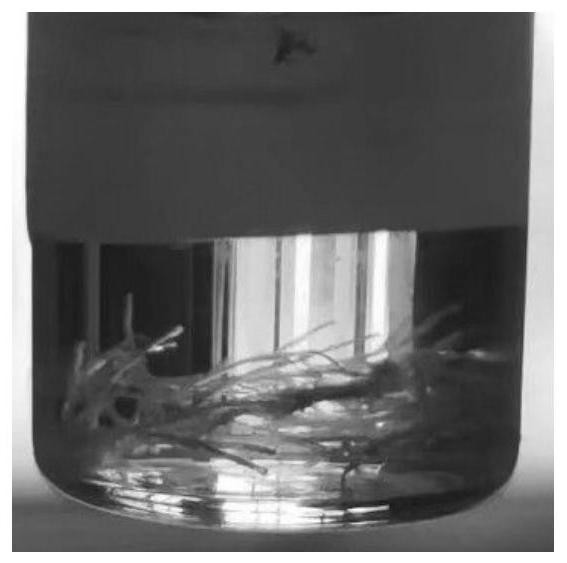
[0029] Prepare 1 mL of PCDA-DMF solution with a concentration of 20 mg / mL; prepare 1 mL of NMA-DMF solution with a concentration of 15 μL / mL. The PCDA-DMF solution was slowly added dropwise to the NMA-DMF solution at room temperature 25°C at a rate of 0.2 mL / h to obtain a macroscopic white co-assembly solution with a single co-assembly size greater than 1 mm. The white precipitate obtained from the assembly was polymerized under 365nm ultraviolet light irradiation for 3 minutes. In the field of view, it is obvious that the macroscopic white assembly completely changes into the macroscopic blue phase polydiyne material, indicating that the co-assembly unit is completely aggregated. The DMF solution of the gained macroscopic blue phase polydiyne was placed at room temperature for 12 months, and its color and ultraviolet absorption spectrum did not change significantly (see Figure 7 ).
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: DPDA and NMA are slowly added dropwise in DMF to assemble
[0031] Prepare 1 mL of DPDA-DMF solution with a concentration of 20 mg / mL; prepare 1 mL of NMA-DMF solution with a concentration of 20 μL / mL. The DPDA-DMF solution was slowly added dropwise to the NMA-DMF solution at a room temperature of 25 °C at a rate of 0.2 mL / h to obtain a macroscopic white co-assembly solution with a single co-assembly size greater than 1 mm. The white precipitate obtained from the assembly was polymerized under 365nm ultraviolet light irradiation for 3 minutes. In the field of view, it is obvious that the white assembly is completely transformed into a blue phase polydiyne material. The DMF solution of gained blue phase polydiyne is placed 12 months at room temperature, and its color and ultraviolet absorption spectrum do not change significantly (see Figure 8 ).
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Sensing and color-changing performance test of macroscopic blue phase polydiyne
[0033] Prepare 1 mL of PCDA-ethanol solution with a concentration of 20 mg / mL; prepare 1 mL of NMA-ethanol solution with a concentration of 15 μL / mL. The PCDA-ethanol solution was slowly added dropwise to the NMA-ethanol solution at a normal temperature of 25° C. at a rate of 0.2 mL / h to obtain a macroscopic white assembly. The white precipitate obtained from the assembly was polymerized under 365nm ultraviolet light irradiation for 3 minutes. In the field of view, it is obvious that the macroscopic white assembly is aggregated to obtain the macroscopic blue phase polydiyne material. The above operation steps were repeated three times to obtain three sets of macroscopic blue phase polydiyne solutions. Add acid (HCl) and alkali (NaOH) to the three groups of solutions respectively or increase the temperature of the solution (50°C), the blue phase macroscopic polydiyne obviously ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com