Preparation method of phospholipase C sensor based on atom transfer radical polymerization
A technology of atom transfer and phospholipase, applied in instruments, scientific instruments, analytical materials, etc., can solve the problems of complex post-catalyst removal process, catalyst toxicity, catalyst residue, etc., and achieve low cost, high selectivity, and avoid interference Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
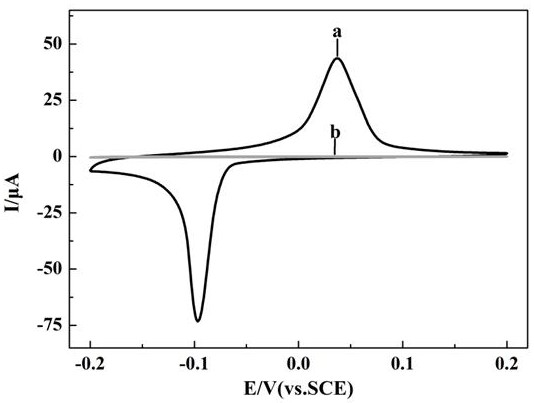
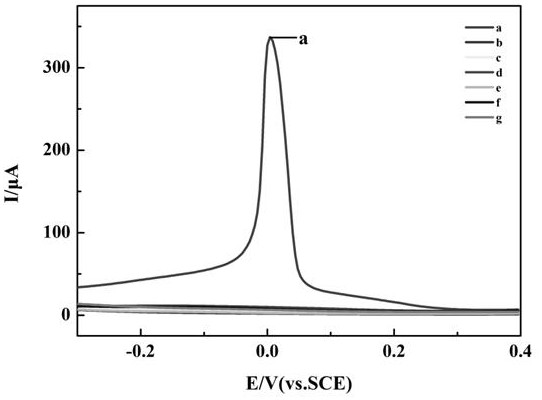
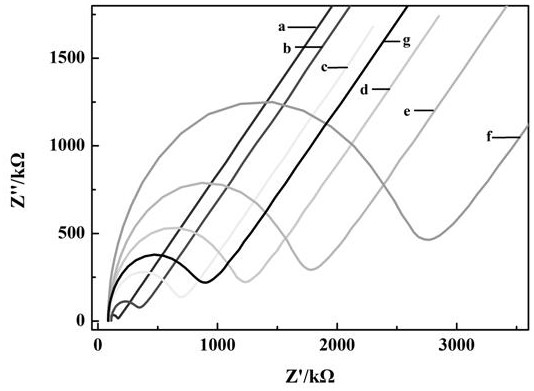
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] A method of preparing a phospholipase C sensor based on an atomic transfer radical polymerization, and the working electrode is performed in accordance with the following steps:
[0022] Step 1: Place the clean gold electrode in a L-cysteine solution having a concentration of 1 mmol / L, resulting in a modified electrode, the L-cysteine solution is 0.1 mmol / L, pH. = 7.0 PBS formulation;
[0023] Step 2: Place the primary modified electrode in the EDC-NHS solution 5 min, activate the L-cysteine carboxylate end, to obtain a secondary modified electrode, the EDC-NHS solution is 0.1 mmol / L, pH = 7.0 The PBS is formulated, the EDC content is 20 mg / ml, the NHS content is 4 mg / ml;
[0024] Step 3: Place the secondary modified electrode for 6 hours in the phosphatidyllet alkanlamine solution, then soaked the electrode for a 2 mmol / l bovine serum albumin (BSA), and the non-specific binding site on the gold electrode is closed. Three modified electrodes, the phospholi...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method of preparing a phospholipase C sensor based on an atomic transfer radical polymerization, and the working electrode is performed in accordance with the following steps:
[0035] Step 1: Place the clean gold electrode in a L-cysteine solution having a concentration of 0.1 mmol / L, resulting in a modified electrode, and the L-cysteine solution is 0.1 mmol / L, pH. = 7.0 PBS formulation;
[0036] Step 2: Place the primary modified electrode in an EDC-NHS solution for 30 min, activate the L-cysteine carboxylate end, to obtain a secondary modified electrode, the EDC-NHS solution is 0.1 mmol / L, pH = 7.0 The PBS is formulated, the EDC content is 5 mg / ml, the NHS content is 1 mg / ml;
[0037] Step 3: Further, the secondary modified electrode is placed in a phosphatidyllet amine solution for 3 hours, and then the electrode is soaked in a 2 mmol / L bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 10 min, and the non-specific binding site on the gold electrode is obtained. Three m...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A method of preparing a phospholipase C sensor based on an atomic transfer radical polymerization, and the working electrode is performed in accordance with the following steps:
[0044] Step 1: Place the clean gold electrode for 12 hours in the L-cysteine solution having a concentration of 0.2 mmol / L, resulting in a modified electrode, the L-cysteine solution is 0.1 mmol / L, pH. = 7.0 PBS formulation;
[0045] Step 2: Place the primary modified electrode for 10 min, activate the L-cysteine carboxylate end, to obtain a secondary modified electrode, the EDC-NHS solution is 0.1 mmol / L, pH = 7.0 PBS is formulated, the EDC content is 10 mg / ml, NHS content is 2 mg / ml;
[0046] Step 3: The secondary modified electrode is placed in a phosphatidyllet alkanlamine solution for 1 hour, and then the electrode is soaked with a 2 mmol / l bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 10 min, and the non-specific binding site on the gold electrode is obtained. Three-time modified electrod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com