Method for recovering white oil in ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber production process
A polyethylene fiber and ultra-high molecular weight technology, which is applied in the fields of rayon recycling, fiber chemical characteristics, refined hydrocarbon oil, etc., can solve the problem of low decolorization efficiency, achieve the effect of improving decolorization effect, increasing interlayer distance, and improving adsorption effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
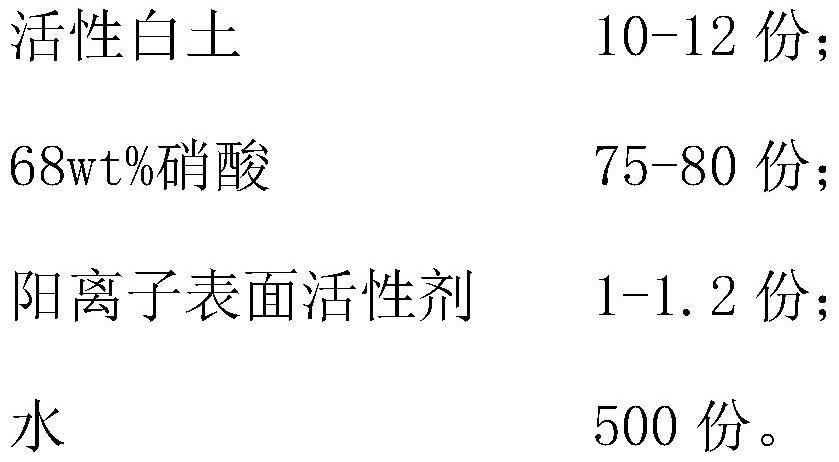
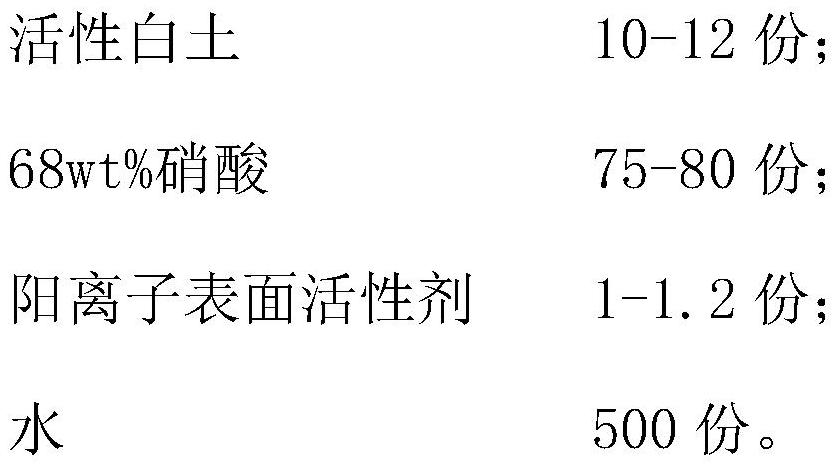
[0068] The preparation example of the present application first discloses a microporous material, which is modified activated carbon, and the raw materials required for each modified activated carbon are as follows:
[0069] Activated carbon 8g;
[0070] Oxidant 230g;
[0071] 3-Chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride 3g.
[0072] Since the main function of the oxidizing agent is to oxidize activated carbon, although there are differences in the oxidation effects of various oxidizing agents on activated carbon, those skilled in the art can select the oxidizing agent according to the requirements and actual processes. In this preparation example, nitric acid is selected as the oxidizing agent, and the concentration of nitric acid is 10wt%.
[0073] The above-mentioned modified activated carbon is prepared by the following process:
[0074] Weigh each raw material according to the above ratio, first put 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride into nitric a...
preparation example 2
[0077] The difference between this preparation example and preparation example 1 is that the raw materials needed for each preparation of a modified activated carbon are as follows:
[0078] Activated carbon 9g;
[0079] Oxidant 250g;
[0080] 3-Chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride 4.5g.
[0081] The preparation process of the above-mentioned modified activated carbon is the same as that of Preparation Example 1, and the oxidized activated carbon after suction filtration is washed to neutral, using about 2.2 L of deionized water.
preparation example 3
[0083] The difference between this preparation example and preparation example 1 is that the raw materials needed for each preparation of a modified activated carbon are as follows:
[0084] Activated carbon 10g;
[0085] Oxidant 270g;
[0086] 3-Chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride 6g.
[0087] The preparation process of the above-mentioned modified activated carbon is the same as that of Preparation Example 1, and the oxidized activated carbon after suction filtration is washed to neutral, using about 2.3 L of deionized water.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com