Method for evaluating immunomodulatory function of substance
An immunomodulatory and material technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, cells modified by introducing foreign genetic material, blood/immune system cells, etc., can solve cumbersome operations, inability to accurately evaluate the immunomodulatory activity of active substances, and inability to be precise Assess issues such as natural product targeting and regulation of immune cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
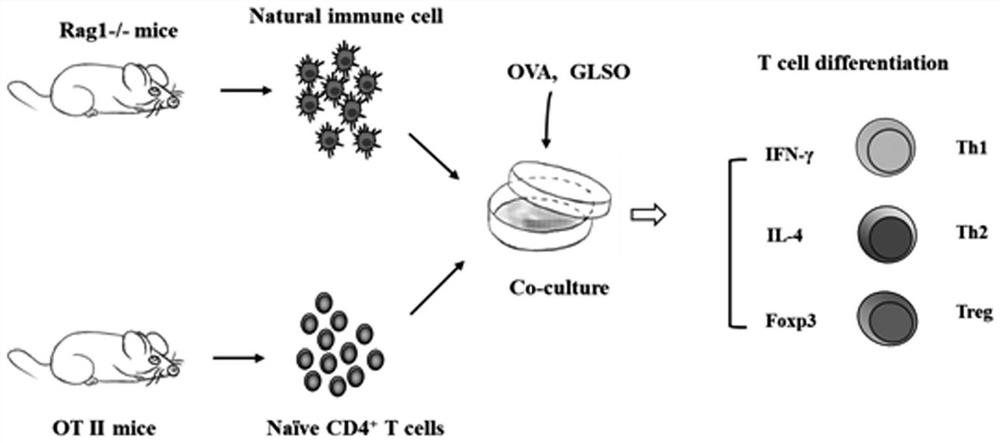
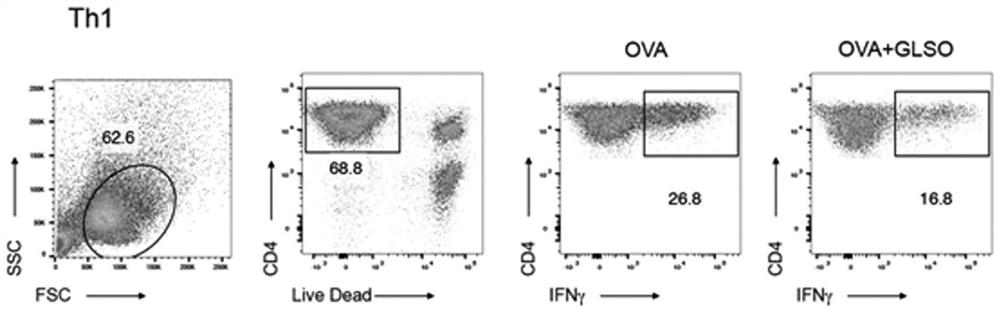
[0028] Example 1 In vitro model of T cells to evaluate the effect of asparagus sulfated oligosaccharides on Th1 cell differentiation
[0029] 1) Take the spleen of Rag1 mice, remove the red blood cells, and make the primary natural immune cell suspension, add 1×10 5 Add 2 μg / mL OVA and 300 μg / mL sulfated oligosaccharide of Gracilaria lemaneiformis (GLSO) to the culture system, 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator for 24 hours, wherein no sulfated oligosaccharides from asparagus was used as the control group.
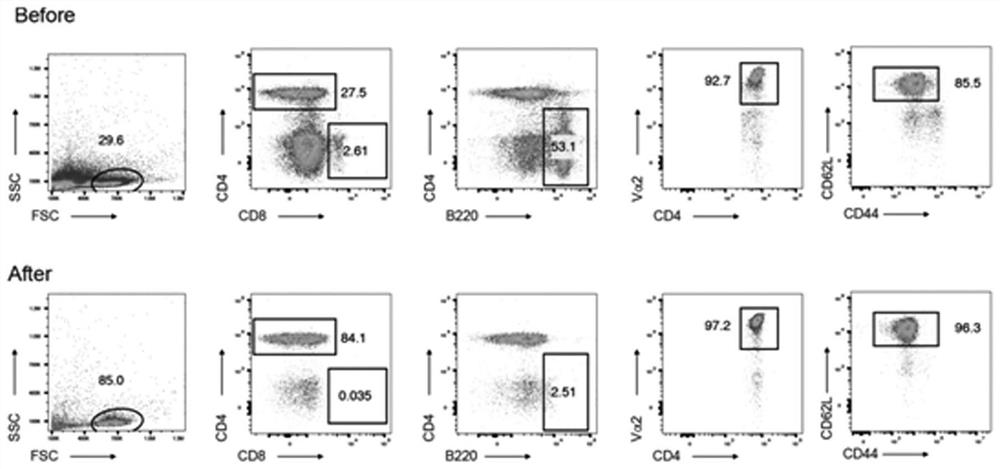
[0030] 2) Collect OT-II mouse spleen single cell suspension, and use magnetic bead sorting method to obtain CD4 + CD62L + Naive T cells, after sorting, 96.3% of the cells expressed CD4 + CD44 + CD62L + Naive T cells (combined with figure 1 ), according to 2×10 5 Add cells / well into the above culture system and continue to culture for 3 days to construct an in vitro model of T cell differentiation, such as figure 2 shown.
[0031] 3) Collect all the cells on t...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 In vitro model of T cells to evaluate the effect of asparagus sulfated oligosaccharides on Th2 cell differentiation
[0034] 1) Take the spleen of Rag1 mice, remove the red blood cells, and make the primary natural immune cell suspension, add 1×10 5 Add 2 μg / mL OVA and 300 μg / mL sulfated oligosaccharide of Gracilaria lemaneiformis (GLSO) to the culture system, 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator for 24 hours, wherein no sulfated oligosaccharides from asparagus was used as the control group.
[0035] 2) Collect OT-II mouse spleen single cell suspension, and use magnetic bead sorting method to obtain CD4 + CD62L + Naive T cells, after sorting, 96.3% of the cells expressed CD4 + CD44 + CD62L + Naive T cells (combined with figure 1 ), according to 2×10 5 Add cells / well into the culture system and continue to culture for 3 days to construct an in vitro model of T cell differentiation, such as figure 2 shown.
[0036] 3) Collect all the cells on the 4th...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3 In vitro model of T cells to evaluate the effect of asparagus sulfated oligosaccharides on the differentiation of Treg cells
[0039] 1) Take the spleen of Rag1 mice, remove the red blood cells, and make the primary natural immune cell suspension, add 1×10 5 Add 2 μg / mL OVA and 300 μg / mL sulfated oligosaccharide of Gracilaria lemaneiformis (GLSO) to the culture system, 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator for 24 hours, wherein no sulfated oligosaccharides from asparagus was used as the control group.
[0040] 2) Collect OT-II mouse spleen single cell suspension, and use magnetic bead sorting method to obtain CD4 + CD62L + Naive T cells, after sorting, 96.3% of the cells expressed CD4 + CD44 + CD62L + Naive T cells (combined with figure 1 ), according to 2×10 5 Add cells / well into the culture system and continue to culture for 3 days to construct an in vitro model of T cell differentiation, such as figure 2 shown.
[0041] 3) Collect all the cells o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com