Antibody targeting influenza A virus N1 subtype NA protein
A type A influenza virus and antibody technology, applied in the field of cellular immunology and genetic engineering, can solve the problems that it is difficult to quickly develop vaccines and antiviral drugs are not completely reliable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Example 1 Screening Anti-NA Protein Antibody
[0062] 1. Construction of phage antibody library
[0063] An antibody library targeting the N1 subtype NA protein of influenza A virus was constructed by means of computer-aided molecular design, and candidate antibodies were screened using phage display technology.
[0064] (1) The displayed phage library adheres to the N1 subtype NA protein of H1N1;
[0065] (2) Repeated washing to remove non-specific binding, eluting and collecting phages with N1 subtype NA protein of H1N1;
[0066] (3) Re-infect Escherichia coli, select a single clone to display on the surface of the phage, and screen positive clones that recognize the N1 subtype NA protein of H1N1 by ELISA.
[0067] 2. Determination and analysis of antibody variable region gene sequence
[0068] Positive clones were sent to Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for antibody variable region gene sequence determination, and the sequencing results were searched and a...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2 Preparation of Monoclonal Antibody FNA1
[0084] 1. Use the PCR method to amplify the heavy chain variable region sequence of the antibody FNA1 (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.4, and the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.17) and the light chain variable region sequence (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.8, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.18), and the fragment is cloned into the expression vector by the method of molecular cloning.
[0085] 2. Transfect the vector containing both the light chain and heavy chain genes of the monoclonal antibody into mammalian cells for expression.
[0086] 3. Collect the expression supernatant, and use GE's Protein A FF protein column for purification.
[0087] 4. Elute with pH 3.0 citric acid buffer, collect the effluent, and immediately neutralize with 1mol / L pH 8.5 TRIS-HCL buffer, dialyze with pH 7.2, 0.01mol / L PBS for 72h, 0.22μm Sterilize by membrane filtration.
[0088] ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3 Specific detection of monoclonal antibody FNA1
[0091] 1. Detection of the specificity of the monoclonal antibody FNA1 by ELISA
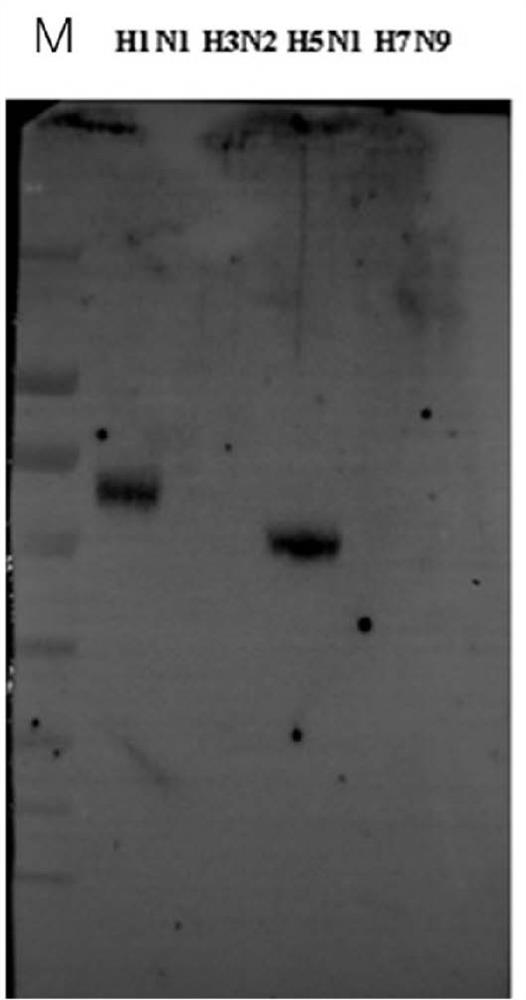
[0092] 1. Coat 2 μg / ml of NA antigens of influenza A virus H1N1, H3N2, H5N1 and H7N9 on an ELISA plate, overnight at 4°C;
[0093] 2. Block unbound sites with skimmed milk powder, and then wash 5 times with PBS buffer containing 0.1% Tween;
[0094]3. Prepare different concentrations of antibody FNA1, add to the ELISA strip in step 2, incubate at 37°C for 1 hour, and wash 5 times with PBS buffer containing 0.1% Tween;
[0095] 4. Add HRP-labeled goat anti-human antibody, incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes, wash 5 times with PBS buffer containing 0.1% Tween; add TMB to develop color, and detect OD after 1mol / L sulfuric acid terminates 450 value.
[0096] 5. Results
[0097] The result is as figure 2 As shown, the antibody FNA1 can effectively bind the NA antigens of influenza A viruses H1N1 and H5N1 in a dose-dependent manner. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com