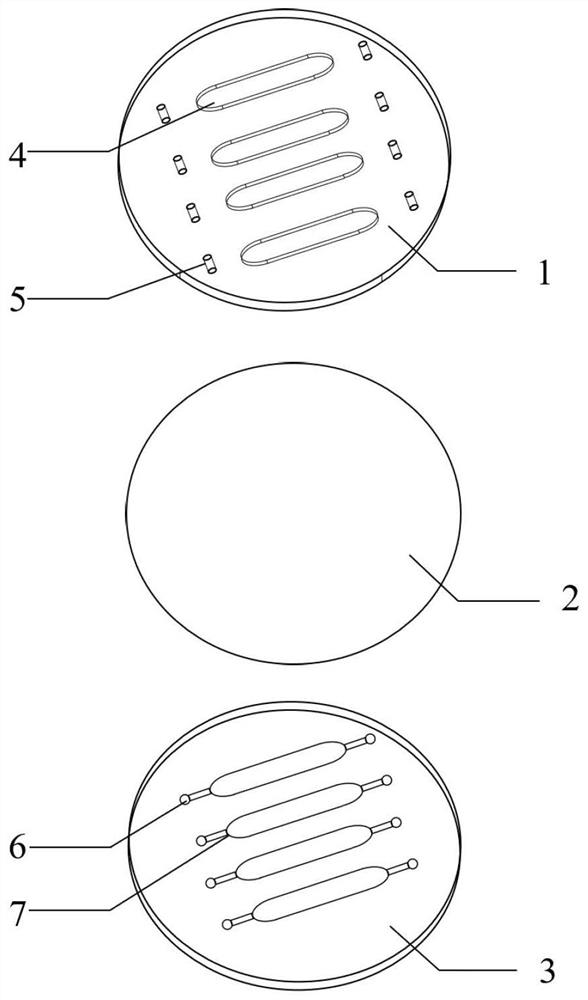
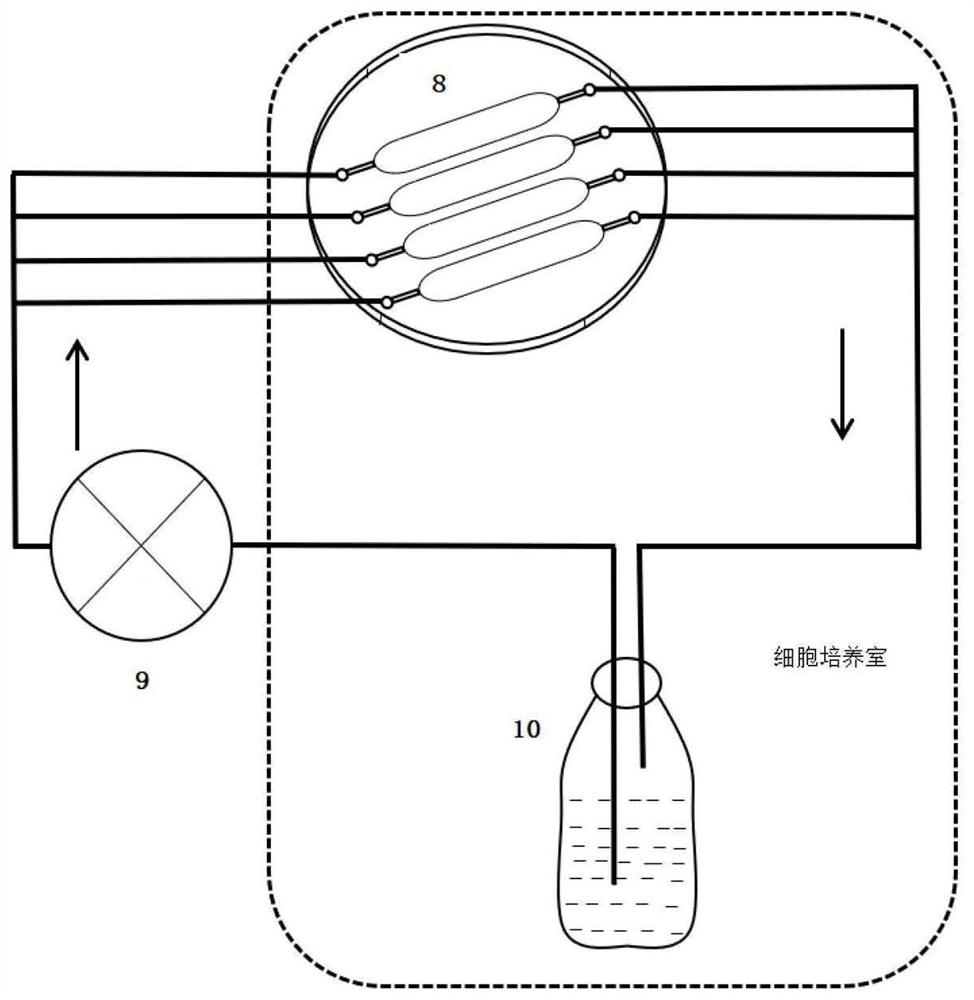
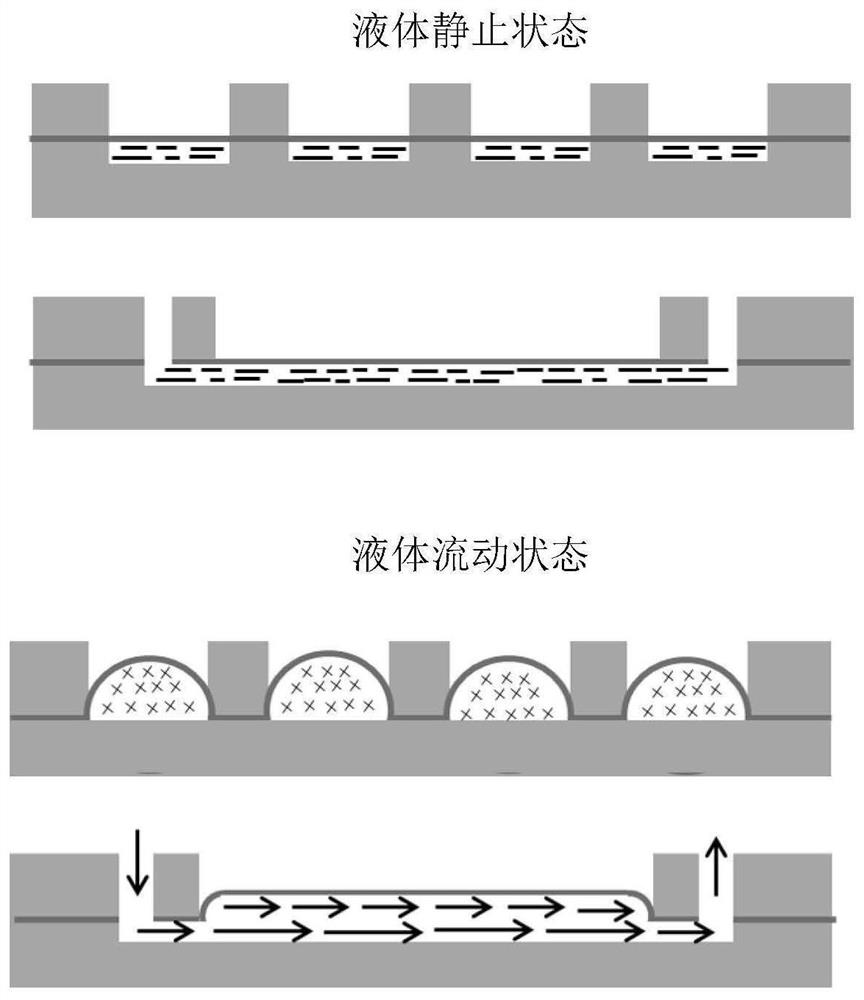
In-vitro vascular tissue-like model with fluid environment and application of in-vitro vascular tissue-like model
A fluid and liquid technology, applied in the field of in vitro vascular tissue model, can solve the problems of high cost, long time and complicated operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1. Fabrication of microfluidic chip and fluid parameter setting of circulation system
[0047] 1. Fabrication of microfluidic chip
[0048] A. Design chip structure and print mask.
[0049] B. Preparation of silicon wafer template
[0050] Soak a 100mm monocrystalline silicon wafer in Piranha solution (98% concentrated sulfuric acid / 30% hydrogen peroxide = 2 / 1) for 30 minutes; take out the silicon wafer, wash it with a large amount of ultrapure water, and dry it at 200°C for 30 minutes; place the silicon wafer in a spin gel Coat photoresist SU-82035 on the instrument to form a film layer with a thickness of about 100 μm; place the silicon wafer coated with photoresist at 65 ° C / 5 min and 90 ° C / 30 min for baking treatment; the prepared mask (fluid The channel part is the light-transmitting part) is attached to the silicon wafer coated with photoresist, and is irradiated with high-intensity ultraviolet light for 60s; the exposed silicon wafer is baked at...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2. Construction of In Vitro Vascular Tissue Model in Circulating Fluid Environment
[0077] The cells are injected into the microchannel 7 of the microfluidic chip to make them attach and grow on the middle PDMS deformable layer 2, and after reaching fusion, they are connected to the fluid circulation system. By changing the flow velocity or the thickness of the middle PDMS deformable layer 2, the corresponding fluid shear force, fluid pressure and tensile force acting on the cells are obtained. Factors that induce and interfere with the occurrence of vascular lesions are introduced by changing the composition of the medium.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com