A kind of hot-melt phenolic resin, prepreg, composite material and preparation method
A technology of phenolic resin and composite materials, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of reducing the density of composite materials, heat conduction, and low volatile content, and achieve the effect of improving high-temperature mechanical properties, low volatile content, and low volatile content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
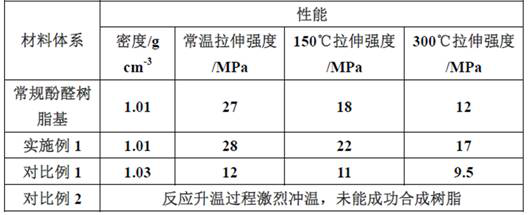
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The preparation method of the composite material of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0039] (1) The preparation of hot-melt phenolic resin comprises the following steps:
[0040] S1. Put the melted phenol into the reaction kettle, add formaldehyde under stirring condition, keep the temperature of the reaction kettle at 32°C, add ammonia water in 2-3 times, and carry out condensation reaction at 80°C, phenol, formaldehyde, ammonia water The molar ratio is 1:1.4:0.01, and the reaction time is 120min;
[0041] S2. Pump the filtrate obtained from the condensation reaction in step S1 into the reaction kettle, start stirring, heat up, and start vacuum dehydration; when the temperature of the filtrate rises to 50-60°C, it enters the low-temperature azeotropic dehydration stage, and the corresponding vacuum degree is 0.08 MPa-0.085 MPa; when a large amount of water is released, the temperature begins to rise, and the dehydration temperature of the final ...
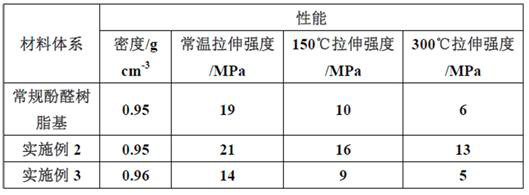
Embodiment 2
[0058] The preparation method of the composite material of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0059] (1) The preparation of hot-melt phenolic resin comprises the following steps:
[0060] S1. Put the melted phenol into the reaction kettle, add formaldehyde under stirring condition, keep the temperature of the reaction kettle at 30°C, add ammonia water in 2-3 times, and carry out condensation reaction at 80°C, phenol, formaldehyde, ammonia water The molar ratio is 1:1.23:0.02, and the reaction time is 120min;
[0061] S2. Pump the filtrate obtained from the condensation reaction in step S1 into the reaction kettle, start stirring, heat up, and start vacuum dehydration; when the temperature of the filtrate rises to 50-60°C, it enters the low-temperature azeotropic dehydration stage, and the corresponding vacuum degree is 0.08 MPa-0.085 MPa; when a large amount of water is released, the temperature begins to rise, and the dehydration temperature of the final...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The rest of the steps and the preparation of raw materials for the composite material in this comparative example are the same as those in Example 2. The difference is that in step S3, the refractive index at the end of the reaction is 1.6250, and the dehydration is completed when the gel time is 58s at (150±1)°C. Obtain the hot-melt phenolic resin.
[0072] The properties of the composite materials obtained in Examples 2 and 3 are shown in Table 2.
[0073] Table 2
[0074]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com