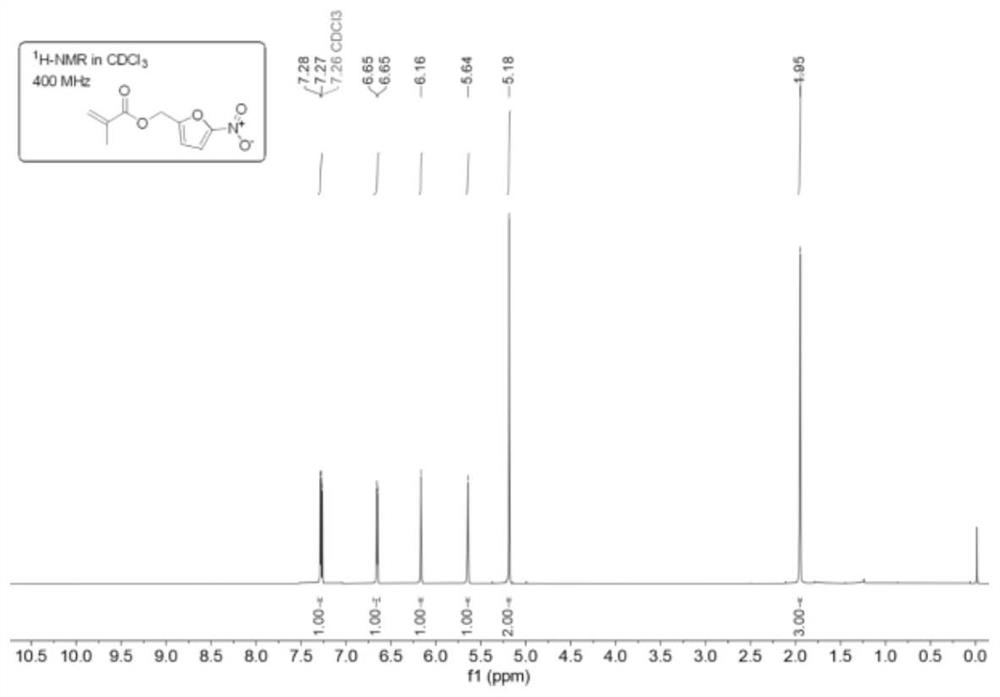
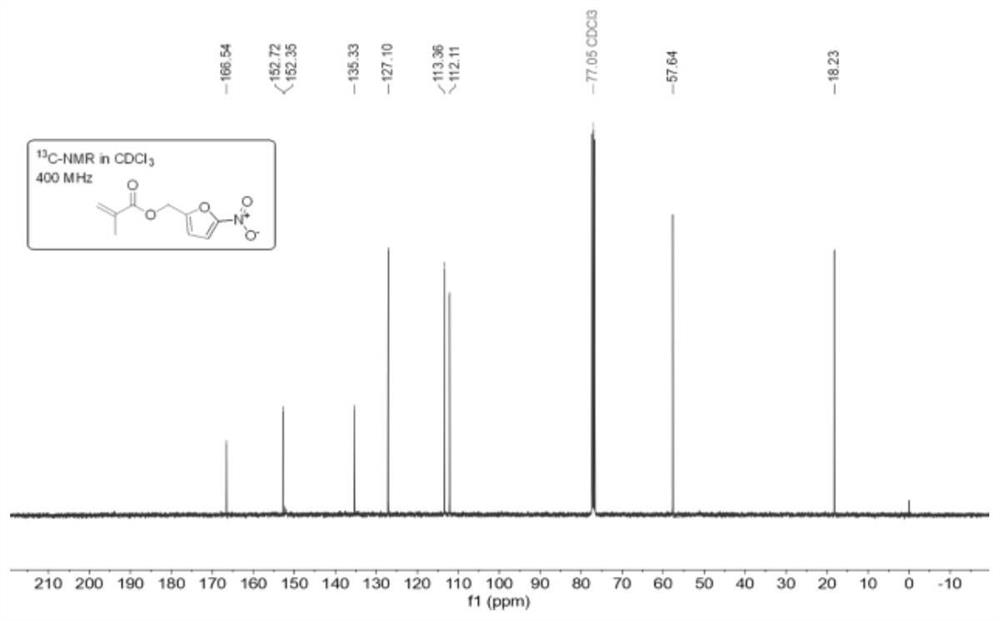
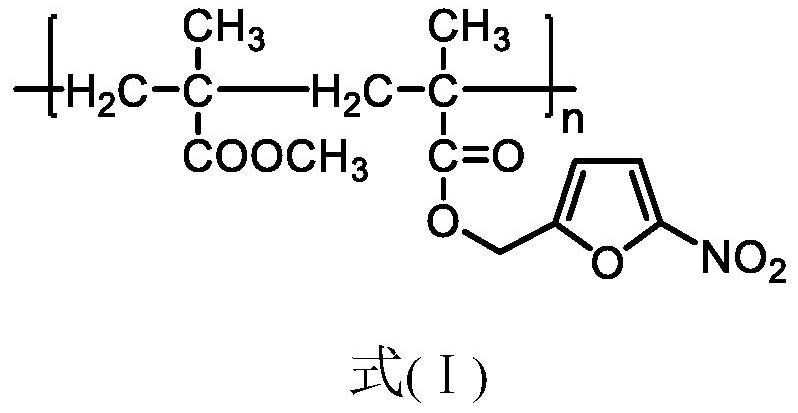
Bio-based antibacterial composite bonding material and preparation method thereof
A kind of adhesive material, bio-based technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of loosening and sinking, inability to connect bone tissue, poor antibacterial performance, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing tissue thermal damage, increasing safety, and good combination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0038] Prepare the bio-based antibacterial composite adhesive material with a mass ratio of 1:1 of the solid phase part and the liquid phase part, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0039] S1: Mix 14.6g polymethyl methacrylate (73wt%), 1g contrast agent zirconium dioxide and 0.4g initiator benzoyl peroxide to obtain mixture A;
[0040] S2: Mix 4g polynitrofurfuryl methacrylate (20wt%) and mixture A to obtain the solid phase part;
[0041] S3: Mix 19.6 g of methyl methacrylate and 0.4 g of N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine, filter and sterilize the resulting solution to obtain the liquid phase;
[0042] S4: Mix the solid phase part obtained in S2 and the liquid phase part obtained in S3 according to the mass ratio of the solid phase part and the liquid phase part at a ratio of 1:1. Curing for 10 minutes under the same conditions;
[0043] S5: The performance test of the bio-based antibacterial composite adhesive material obtained in S4 is performed, and the test results are list...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Prepare the bio-based antibacterial composite adhesive material with a mass ratio of solid phase and liquid phase of 1.5:1, the specific steps are as follows:
[0046] S1: Mix 17.1g polymethyl methacrylate (85.5wt%), 1.8g contrast agent barium sulfate and 0.1g initiator benzoyl peroxide to obtain mixture A;
[0047] S2: Mix 1.0g polynitrofurfuryl methacrylate (5wt%) and mixture A to obtain the solid phase part;
[0048] S3: Mix 14.88g of methyl methacrylate MMA and 0.12g of N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine dmpt, filter and sterilize the resulting solution to obtain the liquid phase;
[0049] S4: Mix the solid phase part obtained in S2 and the liquid phase part obtained in S3 according to the mass ratio of the solid phase part and the liquid phase part at 1.5:1. After fully stirring, in an environment with a temperature of 21 ° C and a relative humidity of 60% Curing for 15 minutes under the same conditions;
[0050] S5: The performance test of the bio-based antibacterial comp...
Embodiment 4
[0052] The mass ratio of preparing solid phase part and liquid phase part is the bio-based antibacterial composite adhesive material of 2:1, and concrete steps are as follows:
[0053] S1: Mix 15.6g polymethyl methacrylate (78wt%), 0.7g contrast agent barium sulfate and 0.1g initiator benzoyl peroxide to obtain mixture A;
[0054] S2: Mix 3.6g polynitrofurfuryl methacrylate (18wt%) and mixture A to obtain the solid phase part;
[0055] S3: Mix 9.9 g of methyl methacrylate and 0.1 g of N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine dmpt, filter and sterilize the resulting solution to obtain the liquid phase;
[0056] S4: Mix the solid phase part obtained in S2 and the liquid phase part obtained in S3 according to the mass ratio of the solid phase part and the liquid phase part at 2:1, and after fully stirring, in an environment with a temperature of 25 °C and a relative humidity of 50% Curing for 8 minutes under the same conditions;
[0057] S5: The performance test of the bio-based antibacterial ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com