Zirconium corundum mullite brick for hazardous waste rotary kiln and preparation method
A technology for hazardous waste and mullite bricks, which is used in rotary drum furnaces, lighting and heating equipment, furnaces, etc., can solve the problems of casting with a porosity layer, unfavorable filling, and increased air pressure, so as to reduce the porosity layer or casting. Insufficient, improve firmness, improve the effect of compactness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
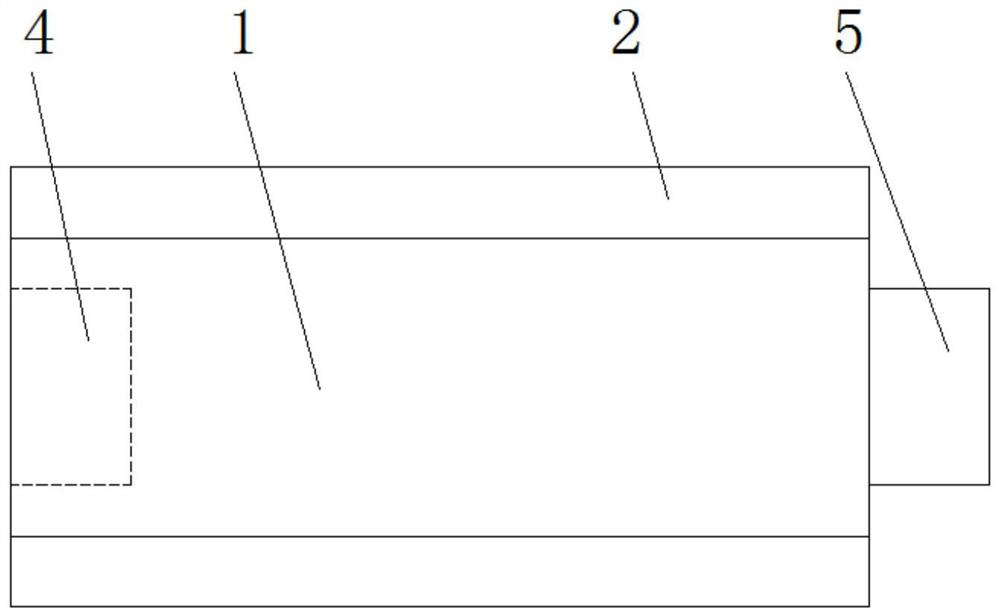
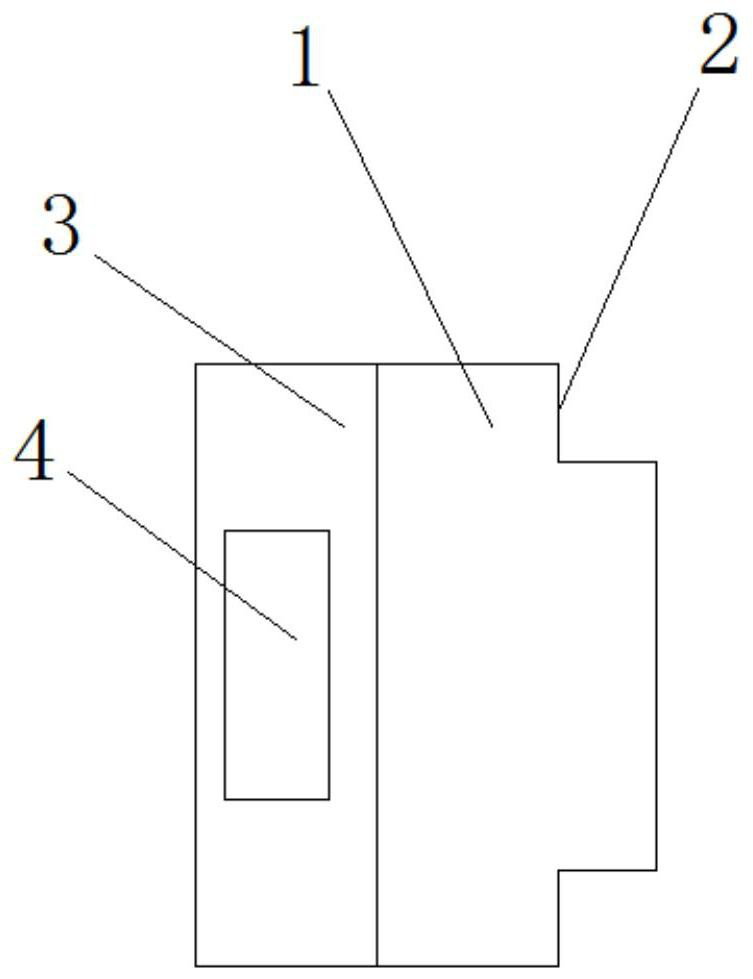
[0049] A zirconium corundum mullite brick for a hazardous waste rotary kiln, comprising a base brick 1, the outer edge of the base brick 1 is arranged in a stepped shape, grooves 2 are left on both sides of the surface of the base brick 1, and the bottom of the base brick 1 The bottom brick 3 is fixed, and the bottom brick 3 and the base brick 1 are integrally connected by die-casting. One side of the bottom brick 3 is provided with a slot 4, and the other side of the bottom brick 3 is fixed with a The protruding block 5 is integrally arranged between the protruding block 5 and the bottom brick 3, and the protruding block 5 is plugged into the slot 4.
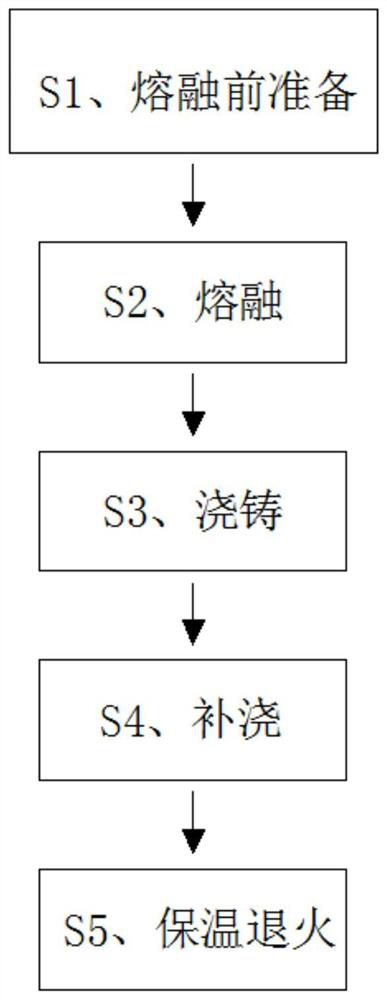
[0050] A method for preparing zirconium corundum mullite bricks for hazardous waste rotary kilns, comprising the following steps;
[0051] S1, preparation before melting;
[0052] S101, adding alumina, alkali powder and zircon sand raw materials into the electric furnace;
[0053] Mix the selected zircon sand and industrial a...
Embodiment 2
[0083] The difference with Embodiment 1 is:
[0084] S101. Combine the selected zircon sand and industrial alumina powder in a weight ratio of 1:1, and add 40% Na by weight to the solid material 2 O (added in the form of sodium carbonate), B 2 o 3 (added in the form of boric acid or borax) mixed flux, mixed evenly with solid materials;
[0085] S2, melting:
[0086] S201, oxidizing and melting the raw material at high temperature;
[0087] The raw material is melted to a molten state at 1800°C in an electric furnace
[0088] S202, blowing oxygen into the melt;
[0089] After the reduction and melting of the raw materials is completed, oxygen is blown into the melt, and the trace carbon in the melt burns and escapes through contact with oxygen.
Embodiment 3
[0091] The difference with embodiment one and two is;
[0092] S101. Combine the selected zircon sand and industrial alumina powder in a weight ratio of 1:1, and add Na with a weight of 50% of the solid material 2 O (added in the form of sodium carbonate), B 2 o 3 (added in the form of boric acid or borax) mixed flux, mixed evenly with solid materials;
[0093] S2, melting:
[0094] S201, oxidizing and melting the raw material at high temperature;
[0095] The raw material is melted to a molten state at 1900°C in an electric furnace
[0096] S202, blowing oxygen into the melt;
[0097] After the reduction and melting of the raw materials is completed, oxygen is blown into the melt, and the trace carbon in the melt burns and escapes through contact with oxygen.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com