Organic compound and application thereof
An organic compound, unsubstituted technology, applied in the field of organic electroluminescent materials, can solve problems such as difficulty in meeting the performance requirements of high-performance OLED devices, achieve high glass transition temperature and thermal stability, improve overall performance, and reduce operating voltage and energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
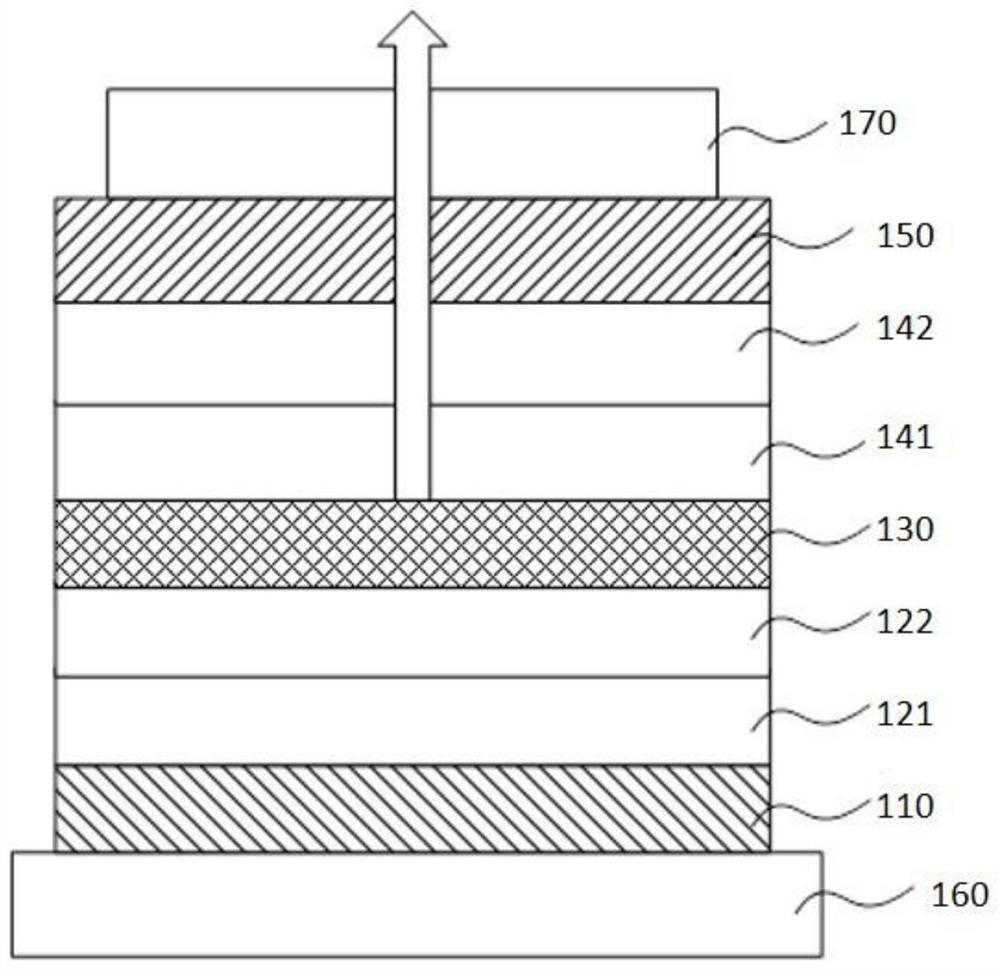
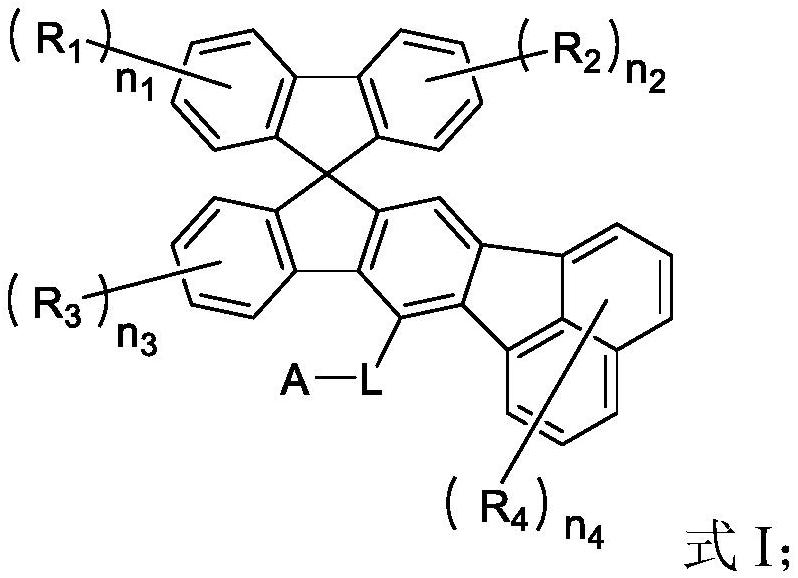
Image
Examples
Synthetic example 1
[0114] Synthesis is used to prepare the intermediate of described organic compound, concrete steps are as follows:
[0115] (1) Synthesis of Intermediate 1
[0116]
[0117] In a 1L three-necked flask, add 0.1mol reactant M1, 0.1mol reactant M2, 0.30mol potassium carbonate, 165.6g water, 1.0mmol tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium Pd (PPh 3 ) 4 , 400mL toluene, 100mL absolute ethanol, N 2 Under protection, raise the temperature to reflux, keep the reaction for 8 hours, stop the reaction, lower the temperature to 25°C, separate the liquid, collect the organic phase, wash with water until neutral, remove the solvent from the organic phase under reduced pressure, and use pure toluene column chromatography to purify, toluene, no Recrystallized from water and ethanol to obtain intermediate 1 with a yield of 85%.
[0118] (2) Synthesis of Intermediate 2
[0119]
[0120] In a 1L three-necked flask, add 0.1mol intermediate 1, 0.375mol sodium hydroxide, 400mL absolute ethan...
Synthetic example 2
[0128] Synthesis is used to prepare the intermediate of described organic compound, concrete steps are as follows:
[0129]
[0130] The only difference from Synthesis Example 1 is that the reactant M3 in step (4) is replaced with an equimolar amount of M3-A, and other raw materials, dosages and process parameters are the same as Synthesis Example 1 to obtain intermediate 4-A.
Synthetic example 3
[0132] Synthesis is used to prepare the intermediate of described organic compound, concrete steps are as follows:
[0133]
[0134] The only difference from Synthesis Example 1 is that the reactant M2 in step (1) is replaced with an equimolar amount of reactant M2-B, and other raw materials, dosages, steps, and process parameters are the same as those in Synthesis Example 1 to obtain the intermediate 4-B.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| internal quantum efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| external quantum efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com